Linux: 企业级高性能 WEB 服务 Nginx
- TAGS: Linux
Web服务基础介绍:
Web服务介绍:
互联网发展历程回顾:
1993年3月2日,中国科学院高能物理研究所租用AT&T公司(美国电话电报公司)的国际卫星信道建立的接入美国SLAC国家实验室的64K专线正式开通,成为我国连入Internet的第一根专线。
参考链接: http://www.ihep.cas.cn/kxcb/kpcg/jsywl/201407/t20140714_4156699.html
1995年马云开始创业并推出了一个web网站 中国黄页
1999年创建阿里巴巴 https://www.alibabagroup.com
2003年5月10日创立淘宝网
2004年12月,马云创立第三方网上支付平台支付宝(蚂蚁金服旗下,共有蚂蚁金服支付宝、余额宝、招财宝、蚂蚁聚宝、网商银行、蚂蚁花呗、芝麻信用等子业务板块。)
2009年开始举办双十一购物狂欢节,以下是历年交易成交额:
2009年双十一:5000万元; 2010年双十一:9.36亿元; 2011年双十一:33.6亿元; 2012年双十一:191亿元; 2013年双十一:350亿元; 2014年双十一:571亿元; 2015年双十一:912.17亿元; 2016年双十一:1207亿元元; 2017年双十一:1682.69亿元; 2018年双十一:2135亿元; 2019年双十一:2684亿; 。。。。。
2012年1月11日淘宝商城正式更名为“天猫”。
2014年9月19日里巴巴集团于纽约证券交易所正式挂牌上市。
web服务介绍:
Netcraft公司于1994年底在英国成立,多年来一直致力于互联网市场以及在线安 全方面的咨询服务,其中在国际上最具影响力的当属其针对网站服务器,域名解 析/主机提供商,以及SSL市场所做的客观严谨的分析研究。
Apace-早期的web服务端:
Apache 起初由美国的伊利诺伊大学香槟分校的国家超级计算机应用中心开发, 目前经历了两大版本分别是1.X和2.X,其可以通过编译安装实现特定的功能,官 方网站 http://www.apache.org。
Apache prefork模型 :
预派生模式,有一个主控制进程,然后生成多个子进程,使用select模型,最大 并发1024,每个子进程有一个独立的线程响应用户请求,相对比较占用内存,但 是比较稳定,可以设置最大和最小进程数,是最古老的一种模式,也是最稳定的 模式,适用于访问量不是很大的场景。
优点:稳定
缺点:大量用户访问慢,占用资源,1024个进程不适用于高并发场景
Apache woker 模型 :
一种多进程和多线程混合的模型,有一个控制进程,启动多个子进程,每个子进程里面包含固定的线程,使用线程程来处理请求,当线程不够使用的时候会再启动一个新的子进程,然后在进程里面再启动线程处理请求,由于其使用了线程处理请求,因此可以承受更高的并发。
优点:相比prefork 占用的内存较少,可以同时处理更多的请求
缺点:使用keepalive的长连接方式, 某个线程会一直被占据,即使没有传输数据,也需要一直等待到超时才会被释放 。如果过多的线程,被这样占据,也会导致在高并发场景下的无服务线程可用。(该问题在prefork模式下,同样会发生)
Apache event模型
Apache中最新的模式,2012年发布的apache 2.4.X系列正式支持event模型,属 于事件驱动模型(epoll),每个进程响应多个请求,在现在版本里的已经是稳定 可用的模式。它和worker模式很像,最大的区别在于,它解决了keepalive场景 下,长期被占用的线程的资源浪费问题(某些线程因为被keepalive,空挂在哪 里等待,中间几乎没有请求过来,甚至等到超时)。event MPM中,会有一个专 门的线程来管理这些keepalive类型的线程,当有真实请求过来的时候,将请求 传递给服务线程,执行完毕后,又允许它释放。这样增强了高并发场景下的请求 处理能力。
优点:单线程响应多请求,占据更少的内存,高并发下表现更优秀, 会有一个 专门的线程来管理keep-alive类型的线程 ,当有真实请求过来的时候,将请求 传递给服务线程,执行完毕后,又允许它释放
缺点:没有线程安全控制
Nginx-高性能的web服务端
Nginx是由1994年毕业于俄罗斯国立莫斯科鲍曼科技大学的同学为俄罗斯 rambler.ru公司开发的,开发工作最早从2002年开始,第一次公开发布时间是 2004年10月4日,版本号是0.1.0,官网地址 https://nginx.org
Nginx历经十几年的迭代更新(https://nginx.org/en/CHANGES),目前功能已 经非常完善且运行稳定,另外Nginx的版本分为开发版、稳定版和过期版,Nginx 以功能丰富著称,即可以作为http服务器,也可以作为反向代理服务器或者邮件 服务器,能够快速的响应静态网页的请求,支持FastCGI/SSL/Virtual Host/URL Rwrite/Gzip/HTTP Basic Auth/http或者TCP的负载均衡(1.9版本以上且开启 stream模块)等功能,并且支持第三方的功能扩展。
为什么使用Nginx:
天猫 淘宝 小米 163 京东新浪等一线互联网公司都在用Nginx或者进行二次开发
说明:nginx会根据请求的类型进行动静分离,静态的请求交给存储服务器,动态请求交给MySQL
用户访问体验统计
互联网存在用户速度体验的1-3-10原则,即1秒最优,1-3秒较优,3~10秒比较慢, 10秒以上用户无法接受。用户放弃一个产品的代价很低,只是换一个URL而已。
http://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1643187950686234006&wfr=spider&for=pc #用户体验的重要性 http://www.sohu.com/a/218426004_573333
全球最大搜索引擎 Google:慢500ms = 20% 将放弃访问。
全球最大的电商零售网站 亚马逊:慢100ms = 1% 将放弃交易
有很多研究都表明,性能对用户的行为有很大的影响:
79%的用户表示不太可能再次打开一个缓慢的网站
47%的用户期望网页能在2秒钟以内加载
40%的用户表示如果加载时间超过三秒钟,就会放弃这个网站
页面加载时间延迟一秒可能导致转换损失7%,页面浏览量减少11%
8秒定律:用户访问一个网站时,如果等待网页打开的时间超过8秒,会有超过30%的用户放弃等待
影响用户体验的几个因素:
据说马云在刚开始创业在给客户演示时,打开一个网站花了两个多小时。
影响用户体验的因素:
客户端原因:
- 客户端硬件配置
- 客户端网络速率
- 客户端与服务端距离
服务端原因:
- 服务端网络速率
- 服务端硬件配置
- 服务端架构设计
- 服务端应用程序工作模式
- 服务端并发数量
- 服务端响应文件大小及数量
- 服务端I/O压力
应用程序工作模式:
httpd MPM(Multi-Processing Module,多进程处理模块)模式:
- prefork:进程模型,两级结构,主进程master负责生成子进程,每个子进程负责响应一个请求
- worker:线程模型,三级结构,主进程master负责生成子进程,每个子进程负责生成多个线程,每个线程响应一个请求
- event:线程模型,三级结构,主进程master负责生成子进程,每个子进程生成多个线程,每个线程响应一个请求,但是增加了一个监听线程,用于解决在设置了keep-alived场景下线程的空等待问题。
*Nginx(Master+Worker)模式*:
- 主进程
- 工作进程 #直接处理客户的请求
#Centos 7.x目前默认为prefork模式,ubuntu 18.04已经使用event模式 Apache线程验证方式: [root@localhost ~]# httpd -V #Centos系统 AH00558: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name,using localhost.localdomain. Set the 'ServerName' directive globally to suppress thismessage Server version: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Server built: Aug 8 2019 11:41:18 Server's Module Magic Number: 20120211:24 Server loaded: APR 1.4.8, APR-UTIL 1.5.2 Compiled using: APR 1.4.8, APR-UTIL 1.5.2 Architecture: 64-bit Server MPM: prefork #MPM模式为prefork threaded: no # ps -ef | grep httpd root 2757 1 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND apache 2758 2757 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND apache 2759 2757 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND apache 2760 2757 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND apache 2761 2757 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND apache 2762 2757 0 04:03 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND root 2786 2369 0 04:13 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto httpd # cat /proc/2760/status Name: httpd State: S (sleeping) .............. Threads: 1 .............. #Ubuntu 18.04.3系统: root@mq-node1:~# apachectl -V Server version: Apache/2.4.29 (Ubuntu) Server built: 2019-09-16T12:58:48 Server's Module Magic Number: 20120211:68 Server loaded: APR 1.6.3, APR-UTIL 1.6.1 Compiled using: APR 1.6.3, APR-UTIL 1.6.1 Architecture: 64-bit Server MPM: event #MPM模式为event threaded: yes (fixed thread count) forked: yes (variable process count) # ps -ef | grep apache2 root 918 1 0 20:08 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start www-data 919 918 0 20:08 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start www-data 920 918 0 20:08 ? 00:00:00 /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start root 1202 1172 0 20:12 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto apache2 # cat /proc/919/status Name: apache2 Umask: 0022 State: S (sleeping) .............. Threads: 27 ..............
服务端I/O:
I/O在计算机中指Input/Output, IOPS (Input/Output Per Second)即每秒的输 入输出量(或读写次数),是衡量磁盘性能的主要指标之一。IOPS是指的是在单位 时间内系统能处理的I/O请求数量,一般以每秒处理的I/O请求数量为单位,I/O 请求通常为读或写数据操作请求。
一次完整的I/O是 用户空间的进程数据与内核空间的内核数据的报文的完整交 换过程 ,但是由于内核空间与用户空间是严格隔离的,所以其数据交换过程中 不能由用户空间的进程直接调用内核空间的内存数据,而是需要经历一次从内核 空间中的内存数据copy到用户空间的进程内存当中,所以简单说 一次 I/O就是 把数据从内核空间中的内存数据复制到用户空间中进程的内存当中的整个过程 。
Linux 的 I/O
- 磁盘 I/O
- 网络 I/O: 一切皆文件,本质为对 socket 文件的读写
磁盘 I/O
磁盘I/O是进程向内核发起系统调用,请求磁盘上的某个资源比如是文件或者是 图片,然后内核通过相应的驱动程序将目标图片加载到内核的内存空间,加载完 成之后把数据从内核内存再复制给进程内存,如果是比较大的数据也需要等待时 间。
机械磁盘的寻道时间、旋转延迟和数据传输时间:
- 寻道时间:是指磁头移动到正确的磁道上所花费的时间,寻道时间越短则I/O 处理就越快,目前磁盘的寻道时间一般在3-15毫秒左右。
- 旋转延迟:是指将磁盘片旋转到数据所在的扇区到磁头下面所花费的时间,旋 转延迟取决于磁盘的转速,通常使用磁盘旋转一周所需要时间的1/2之一表示, 比如7200转的磁盘平均训传延迟大约为60*1000/7200/2=4.17毫秒,公式的意 思为(每分钟60秒*1000毫秒每秒/7200转每分钟/2),如果是15000转的则为 60*1000/15000/2=2毫秒。
- 数据传输时间:指的是读取到数据后传输数据的时间,主要取决于传输速率, 这个值等于数据大小除以传输速率,目前的磁盘接口每秒的传输速度可以达到 600MB,因此可以忽略不计。
注意:web服务器千万不要用7200转的机械盘,最低用10000的
范例:
常见的机械磁盘平均寻道时间值: 7200转/分的磁盘平均物理寻道时间:9毫秒 10000转/分的磁盘平均物理寻道时间:6毫秒 15000转/分的磁盘平均物理寻道时间:4毫秒 常见磁盘的平均延迟时间: 7200转的机械盘平均延迟:60\*1000/7200/2 = 4.17ms 10000转的机械盘平均延迟:60\*1000/10000/2 = 3ms 15000转的机械盘平均延迟:60\*1000/15000/2 = 2ms 每秒最大IOPS的计算方法: 7200转的磁盘IOPS计算方式:1000毫秒/(9毫秒的寻道时间+4.17毫秒的平均旋转延迟时间)=1000/13.13=75.9 IOPS 10000转的磁盘的IOPS计算方式:1000毫秒/(6毫秒的寻道时间+3毫秒的平均旋转延迟时间)=1000/9=111 IOPS 15000转的磁盘的IOPS计算方式:15000毫秒/(4毫秒的寻道时间+2毫秒的平均旋转延迟时间)=1000/6=166.6 IOPS
网络 I/O
网络通信就是从网络协议栈到用户空间进程的IO,也就是网络IO。
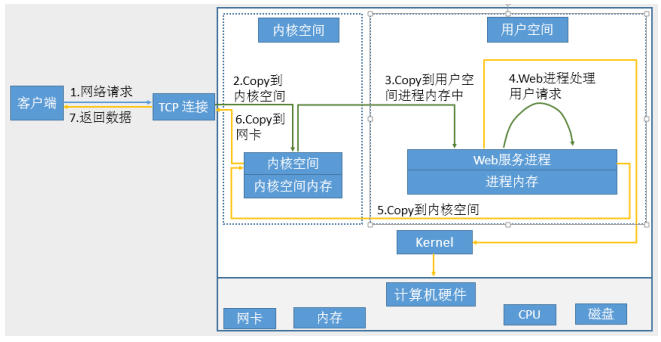
网络I/O处理过程
获取请求数据,客户端与服务器建立连接发出请求,服务器接受请求(1-3) 构建响应,当服务器接收完请求,并在用户空间处理客户端的请求,直到构建响应完成(4) 返回数据,服务器将已构建好的响应再通过内核空间的网络 I/O 发还给客户端(5-7)
不论磁盘和网络 I/O:
每次IO,都要经由两个阶段: 第一步:将数据从磁盘文件先加载至内核内存空间(缓冲区),此步骤需要等待数据准备完成,时间较长 第二步:将数据从内核缓冲区复制到用户空间的进程的内存中,时间较短
系统 I/O 模型:
I/O 模型相关概念
同步/ 异步
同步/异步:关 注的是事件处理的消息通信机制,即在等待一件事情的处理结果时,被调用者是否提供完成通知。
- 同步:synchronous,调用者等待被调用者返回消息后才能继续执行,如果被 调用者不提供消息返回则为同步,同步需要调用者主动询问事情是否处理完成。
- 异步:asynchronous,被调用者通过状态、通知或回调机制主动通知调用者, 即异步会主动返回被调用者的状态给调用者。
说明:被调用者通常是内核,调用者就是web服务(Nginx、PHP)
- 同步:进程发出请求调用后,内核不提供通知机制,即文件IO处理完成后不通 知进程,需要进程自己去问内核是否处理完成。
- 异步:进程发出请求调用后,内核会在调用处理完成后返回调用结果给进程,Nginx是异步的。

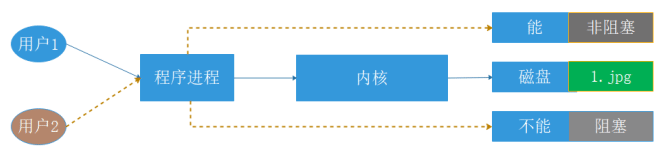
阻塞 / 非阻塞:
阻塞/非阻塞:关注调用者在等待结果返回之前所处的状态
- 阻塞:blocking,指IO操作需要彻底完成后才返回到用户空间,调用结果返回 之前,调用者被挂起,干不了别的事情。
- 非阻塞:nonblocking,指IO操作被调用后立即返回给用户一个状态值,无需 等到IO操作彻底完成,最终的调用结果返回之前,调用者不会被挂起,可以去 做别的事情。
系统IO模型组合(面试题)
以我去吃饭为例:我点了10个包子
同步与异步:
我点包子之后厨师是否告诉我:
- 同步:厨师做好包子后会放到指定位置,但是做好包子之前需要自己一次次去看包子做好没有,厨师不会在包子做好之后通知我。
- 异步:厨师做好包子后告诉我包子做好放哪了。
阻塞与非阻塞::
我点包子后的状态:
- 阻塞:在厨师做包子期间一直在包子盘子前面等着,不能干别的事情。
- 非阻塞:点完包子就可以去干别的事情,比如去逛逛街或者买买买。
- IO模型组合:
- 同步阻塞:我点完包子后不能去做别的事情,而且不知道包子有没有做好,需要自己一直等着并一次次的问厨师做好没有。
- 同步非阻塞:点完包子后可以去做别的事情,但是不能长时间做别的事情,因为我还是不知道包子有没有做好,也要自己一直等着并一次次的问厨师做好没有,只能抽空做点别的。
- 异步阻塞:我点完包子后不能去走做别的事情,但是厨师在做好包子后会告诉我,也就是我不用再一次次为厨师包子有没有做好了。
- 异步非阻塞:我点完包子后可以做别的事情,而且可以一直在做别的去事情,因为厨师在做好包子后会告诉我。
网络I/O模型(了解)
阻塞型、非阻塞型、复用型、信号驱动型、异步
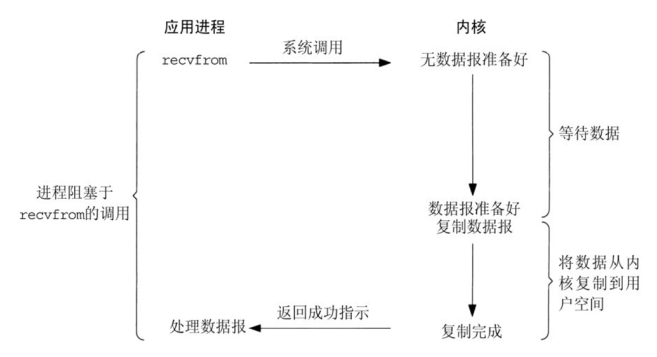
同步阻塞型IO模型(blocking IO):
阻塞IO模型是最简单的IO模型,用户线程在内核进行IO操作时被阻塞
- 用户请求到达系统服务进程,然后进程通过系统调用read向内核发起IO读操作, 即将用户请求由用户空间转到内核空间,内核接收到IO请求后开始从磁盘读取 文件到内核内存,即在等用户请求的文件从磁盘到达内核内存后,然后将接收 的数据拷贝到用户空间,然后完成read操作。
- 用户请求需要等待内核将数据读取到进程内存后,处理用户的进程才可以继续 处理该请求,整个IO请求的过程中,请求进程是被阻塞的,这导致进程在发起 IO请求时,不能做任何事情,而且对CPU的资源利用率不够。
优点:程序简单,在阻塞等待数据期间进程挂起,基本不会占用 CPU 资源
缺点:每个连接需要独立的进程单独处理,当并发请求量大时为了维护程序,内存、进程切换开销较大,apache的preforck使用的是这种模式。
同步阻塞 :程序向内核发送IO请求后一直等待内核响应,如果内核处理请求的IO操作不能立即返回,则进程将一直等待并不再接受新的请求,并由进程轮训查看IO是否完成,完成后进程将IO结果返回给Client,在IO没有返回期间进程不能接受其他客户的请求,而且是有进程自己去查看IO是否完成,这种方式简单,但是比较慢,用的比较少。
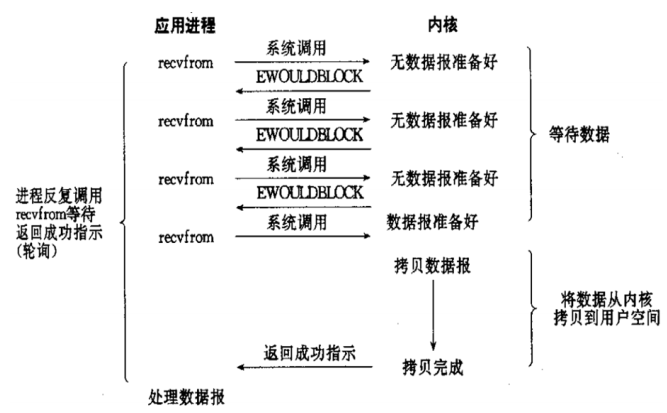
非阻塞型I/O模型(nonblocking IO):
用户请求进程向内核发起IO请求时立即返回,但并未读取到任何数据,进程需要 不断地发起IO请求,直到数据到达进程空间的内存后,才真正读取到数据并继续 执行,即前期需要一次次"轮询"去查看请求是否数据是否准备报,但是此机制存 在两个问题:
- 如果有大量文件描述符都要等,那么就得一个一个的read,这会带来大量的 Context Switch(read是系统调用,每调用一次就得在用户态和核心态切换 一次)
- 轮询的时间不好把握。这里是要猜多久之后数据才能到,等待时间设的太长, 程序响应延迟就过大,但是设的太短,就会造成过于频繁的重试,干耗CPU而 已,所以是比较浪费CPU的方式,因此一般很少直接使用这种模型,而是在 其他IO模型中使用非阻塞IO这一特性。
非阻塞 :应用进程向内核发送请IO求后一直等待内核响应,如果内核处理请求的IO操作不能立即返回IO结果,进程将不再等待,而且继续处理其他请求,但是仍然需要进程隔一段时间就要查看内核IO是否完成。
IO多路复用型(IO multiplexing):
IO multiplexing就是我们说的select,poll,epoll,有些地方也称这种IO方式 为event driven IO(事件驱动IO),select/poll/epoll的好处就在于单个 process就可以同时处理多个网络连接的IO。它的基本原理就是select,poll, epoll这个function会不断的轮询所负责的所有socket,当某个socket有数据到 达了,就通知用户进程。
当用户进程调用了select,那么整个进程会被block,而同时,kernel会“监视”所 有select负责的socket,当任何一个socket中的数据准备好了,select就会返回, 这个时候用户进程再调用read操作,将数据从kernel拷贝到用户进程。
Apache prefork是此模式的主进程+多进程/单线程+select,work是主进程+多 进程/多线程+poll模式
IO多路复用(IO Multiplexing) :是一种机制,程序注册一组socket文件描述 符给操作系统,表示“我 要监视这些fd是否有IO事件发生,有了就告诉程序处 理” IO多路复用一般和NIO一起使用的。NIO和IO多路复用是相对独立的。NIO仅仅是 指IO API总是能立刻返回,不会被Blocking;而IO多路复用仅仅是操作系统提供 的一种便利的通知机制。操作系统并不会强制这俩必须得一起用,可以只用IO多 路复用 + BIO,这时还是当前线程被卡住。IO多路复用和NIO是要配合一起使用 才有实际意义 IO多路复用是指内核一旦发现进程指定的一个或者多个IO条件准备读取,就通知该进程 多个连接共用一个等待机制,本模型会阻塞进程,但是进程是阻塞在select或者 poll这两个系统调用上,而不是阻塞在真正的IO操作上 用户首先将需要进行IO操作添加到select中,同时等待select系统调用返回。当 数据到达时,IO被激活,select函数返回。用户线程正式发起read请求,读取数 据并继续执行 从流程上来看,使用select函数进行IO请求和同步阻塞模型没有太大的区别,甚 至还多了添加监视IO,以及调用select函数的额外操作,效率更差。并且阻塞了 两次,但是第一次阻塞在select上时,select可以监控多个IO上是否已有IO操作 准备就绪,即可达到在同一个线程内同时处理多个IO请求的目的。而不像阻塞IO 那种,一次只能监控一个IO 虽然上述方式允许单线程内处理多个IO请求,但是每个IO请求的过程还是阻塞的 (在select函数上阻塞),平均时间甚至比同步阻塞IO模型还要长。如果用户线 程只是注册自己需要的IO请求,然后去做自己的事情,等到数据到来时再进行处 理,则可以提高CPU的利用率 IO多路复用是最常使用的IO模型,但是其异步程度还不够“彻底”,因它使用了 会阻塞线程的select系统调用。因此IO多路复用只能称为异步阻塞IO模型,而非 真正的异步IO
优缺点
- 优点:可以基于一个阻塞对象,同时在多个描述符上等待就绪,而不是使用多 个线程(每个文件描述符一个线程),这样可以大大节省系统资源
- 缺点:当连接数较少时效率相比多线程+阻塞 I/O 模型效率较低,可能延迟更 大,因为单个连接处j理需要 2 次系统调用,占用时间会有增加
IO多路复用适用如下场合:
- 当客户端处理多个描述符时(一般是交互式输入和网络套接口),必须使用I/O复用
- 当一个客户端同时处理多个套接字时,此情况可能的但很少出现
- 当一个服务器既要处理监听套接字,又要处理已连接套接字,一般也要用到I/O复用
- 当一个服务器即要处理TCP,又要处理UDP,一般要使用I/O复用
- 当一个服务器要处理多个服务或多个协议,一般要使用I/O复用
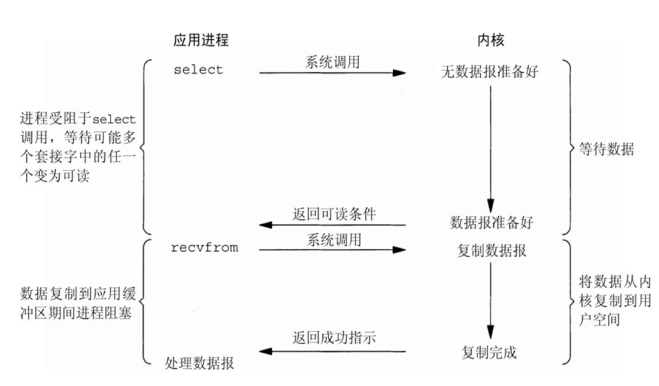
信号驱动式IO(signal-driven IO):
信号驱动IO:signal-driven I/O
信号驱动I/O的意思就是我们现在不用傻等着了,也不用去轮询。而是让内核在 数据就绪时,发送信号通知我们。
调用步骤是,通过系统调用 sigaction ,并注册一个信号处理的回调函数,该 调用会立即返回,然后主程序可以继续向下执行,当有I/O操作准备就绪,即内核 数据就绪时,内核会为该进程产生一个SIGIO 信号,并回调注册的信号回调函数, 这样就可以在信号回调函数中系统调用 recvfrom 获取数据,将用户进程所需要 的数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间
此模型的优势在于等待数据报到达期间进程不被阻塞。用户主程序可以继续执行, 只要等待来自信号处理函数的通知。
在信号驱动式 I/O 模型中,应用程序使用套接口进行信号驱动 I/O,并安装一 个信号处理函数,进程继续运行并不阻塞
当数据准备好时,进程会收到一个 SIGIO 信号,可以在信号处理函数中调用 I/O 操作函数处理数据。
优点:进程没有在等待数据时被阻塞,内核直接返回调用接收信号,不影响进程 继续处理其他请求因此可以提高资源的利用率
缺点:信号 I/O 在大量 IO 操作时可能会因为信号队列溢出导致没法通知
异步阻塞 :程序进程向内核发送IO调用后,不用等待内核响应,可以继续接 受其他请求,内核收到进程请求后进行的IO如果不能立即返回,就由内核等待结 果,直到IO完成后内核再通知进程,apache event是此模式。
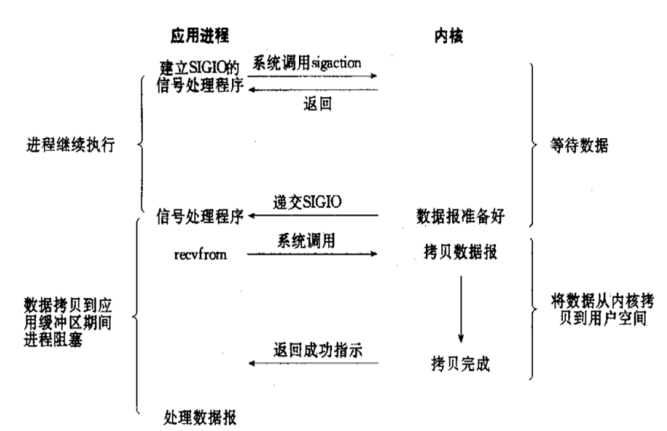
异步(非阻塞) IO(asynchronous IO):
异步I/O 与 信号驱动I/O最大区别在于,信号驱动是内核通知我们何时开始一个 I/O操作,而异步I/O是由内核通知我们I/O操作何时完成,两者有本质区别,相当 于不用去饭店场吃饭,直接点个外卖,把等待上菜的时间也给省了
相对于同步IO,异步IO不是顺序执行,用户进程进行aio_read系统调用之后,无 论内核数据是否准备好,都会直接返回给用户进程,然后用户态进程可以去做别 的事情,等到socket数据准备好了,内核直接复制数据给进程,然后从内核向进 程发送通知,异步非阻塞IO的两个阶段,进程都是非阻塞的。
异步IO与信号驱动IO最主要的区别是信号驱动IO是由内核通知应用程序何时可以 进行IO操作,而异步IO则是由内核告诉用户线程IO操作何时完成。信号驱动IO当 内核通知触发信号处理程序时,信号处理程序还需要阻塞在从内核空间缓冲区拷 贝数据到用户空间缓冲区这个阶段,而异步IO直接是在第二个阶段完成后,内核 直接通知用户线程可以进行后续操作了
优点:异步 I/O 能够充分利用 DMA 特性,让 I/O 操作与计算重叠
缺点:要实现真正的异步 I/O,操作系统需要做大量的工作。目前 Windows 下 通过 IOCP 实现了真正的异步 I/O,在 Linux 系统下,Linux 2.6才引入,目前 AIO 并不完善,因此在 Linux 下实现高并发网络编程时以 IO 复用模型模式+多 线程任务的架构基本可以满足需求
Linux提供了AIO库函数实现异步,但是用的很少,目前有很多开源的异步IO库, 例如libevent、libev、libuv等,异步过程如下图所示:
异步非阻塞 :程序进程向内核发送IO调用后,不用等待内核响应,可以继续接受其他请求,内核调用的IO如果不能立即返回,内核会继续处理其他事物,直到IO完成后将结果通知给内核,内核在将IO完成的结果返回给进程,期间进程可以接受新的请求,内核也可以处理新的事物,因此相互不影响,可以实现较大的同时并实现较高的IO复用,因此异步非阻塞使用最多的一种通信方式,nginx就是是异步非阻塞模型
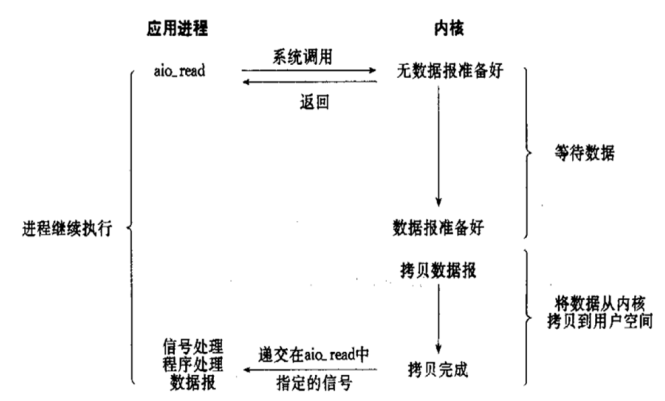
IO对比:
这五种网络 I/O模型中,越往后,阻塞越少,理论上效率也是最优前四种属于同 步I/O,因为其中真正的 I/O 操作(recvfrom)将阻塞进程/线程,只有异步 I/O 模型才与 POSIX 定义的异步 I/O 相匹配。
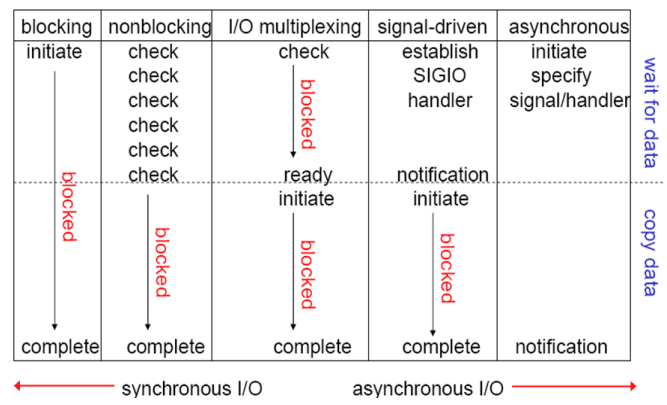
实现方式:
Nginx支持在多种不同的操作系统实现不同的事件驱动模型,但是其在不同的操 作系统甚至是不同的系统版本上面的实现方式不尽相同,主要有以下实现方式:
select:(用的较少)
select库是在linux和windows平台都基本支持的事件驱动模型库,并且在接 口的定义也基本相同,只是部分参数的含义略有差异,最大并发限制1024, 是最早期的事件驱动模型。
poll :(不推荐使用,降低性能)
在Linux的基本驱动模型,windows不支持此驱动模型,是select的升级版, 取消了最大的并发限制,在编译nginx的时候可以使 用–with-poll_module和–without-poll_module这两个指定是否编译select 库。
epoll:
epoll是库是Nginx服务器支持的最高性能的事件驱动库之一,是公认的非常 优秀的事件驱动模型,它和select和poll有很大的区别,epoll是poll的升级 版,但是与poll的效率有很大的区别.
epoll的处理方式是创建一个待处理的事件列表,然后把这个列表发给内核, 返回的时候在去轮训检查这个表,以判断事件是否发生,epoll支持一个进程 打开的最大事件描述符的上限是系统可以打开的文件的最大数,同时*epoll 库的IO效率不随描述符数目增加而线性下降*,因为它只会对内核上报的“活 跃”的描述符进行操作。
rtsig:
不是一个常用事件驱动,最大队列1024,不是很常用
kqueue
用于支持BSD系列平台的高效事件驱动模型,主要用在FreeBSD 4.1及以上版 本、OpenBSD 2.0级以上版本,NetBSD级以上版本及Mac OS X平台上,该模型 也是poll库的变种,因此和epoll没有本质上的区别,都是通过避免轮训操作 提供效率。
/dev/poll:
用于支持unix衍生平台的高效事件驱动模型,主要在Solaris平台、HP/UX, 该模型是sun公司在开发Solaris系列
平台的时候提出的用于完成事件驱动机制的方案,它使用了虚拟的/dev/poll 设备,开发人员将要见识的文件描述符加入这个设备,然后通过ioctl()调用 来获取事件通知,因此运行在以上系列平台的时候请使用/dev/poll事件驱动 机制。
eventport:
该方案也是sun公司在开发Solaris的时候提出的事件驱动库,只是Solaris 10以上的版本,该驱动库看防止内核崩溃等情况的发生。
Iocp:
Windows系统上的实现方式,对应第5种(异步I/O)模型。
常用模型通知对比
| select | poll | epoll | |
| 操作方式 | 遍历 | 遍历 | 回调 |
| 底层实现 | 数组 | 链表 | 哈希表 |
| IO效率 | 每次调用都进行线性遍历,时间复杂度为O(n) | 同左 | 时间通知方式,每当fd就绪。系统注册的回调函数就会被调用,将就绪fd放到rdllist里面,时间复杂度为O(1) |
| 最大连接数 | 1024(x86)或2048(x64) | 无上限无上限 | |
| fd拷贝 | 每次调用select,都需要把fd集合从用户态拷贝到内核态 | 每次调用poll,都需要把fd集合从用户态拷贝到内核态 | 调用epoll_ctl时拷贝进内核并保存,之后每次epoll_wait不拷贝 |
说明:
- O(1):表示算法的运行时间为常量,即无论是1000个还是10000个,耗费时间一样
- O(n): 表示该算法是线性算法
- fd: 表示事件描述符
水平触发–多次通知,需要关心数据是否取完,即数据取走之后即不再通知进程, 以避免重复多次无效通知,通知效率较低。
边缘触发–一次通知,需要关心数据是否取走,即只通知一次怎么保证数据被进 程成功取走了,以避免数据丢失,通知效率较高。
Select :
POSIX所规定,目前几乎在所有的平台上支持,其良好跨平台支持也是它的一个 优点,本质上是通过设置或者检查存放fd标志位的数据结构来进行下一步处理
缺点
- 单个进程能够监视的文件描述符的数量存在最大限制,在Linux上一般为1024, 可以通过修改宏定义FD_SETSIZE,再重新编译内核实现,但是这样也会造成效 率的降低。
- 单个进程可监视的fd数量被限制,默认是1024,修改此值需要重新编译内核。
- 对socket是线性扫描,即采用轮询的方法,效率较低。
- select 采取了内存拷贝方法来实现内核将 FD消息通知给用户空间,这样一个 用来存放大量fd的数据结构,这样会使得用户空间和内核空间在传递该结构时 复制开销大。
poll :
- 本质上和select没有区别,它将用户传入的数组拷贝到内核空间,然后查询每个fd对应的设备状态。
- 其没有最大连接数的限制,原因是它是基于链表来存储的。
- 大量的fd的数组被整体复制于用户态和内核地址空间之间,而不管这样的复制是不是有意义。
- poll特点是“水平触发”,如果报告了fd后,没有被处理,那么下次poll时会再次报告该fd。
epoll :
在Linux 2.6内核中提出的select和poll的增强版本。
支持水平触发LT和边缘触发ET,最大的特点在于边缘触发,它只告诉进程哪些fd刚刚变为就需态,并且只会通知一次
使用“事件”的就绪通知方式,通过epoll_ctl注册fd,一旦该fd就绪,内核就会采用类似callback的回调机制来激活该fd,epoll_wait便可以收到通知 。
优点:
- 没有最大并发连接的限制:能打开的FD的上限远大于1024(1G的内存能监听约 10万个端口),具体查看/proc/sys/fs/file-max,此值和系统内存大小相关
- 效率提升:非轮询的方式,不会随着FD数目的增加而效率下降;只有活跃可用的FD才会调用callback函数,即epoll
- 最大的优点就在于它只管理“活跃”的连接,而跟连接总数无关
- 内存拷贝,利用mmap(Memory Mapping)加速与内核空间的消息传递;即epoll使用mmap减少复制开销
范例: 最大并发连接数
#内存1G [root@centos8 ~]#free -h [root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 92953 #内存2G [root@centos8 ~]#free -h [root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/fs/file-max 195920
范例:内核限制
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -R FD_SETSIZE linux-5.8/* linux-5.8/Documentation/userspace-api/media/v4l/func-select.rst: ``FD_SETSIZE``. linux-5.8/include/uapi/linux/posix_types.h:#undef __FD_SETSIZE linux-5.8/include/uapi/linux/posix_types.h:#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024 #单个进程能 够监视的文件描述符的文件最大数量
范例: select 和epoll 帮助
[root@centos8 ~]#whatis epoll epoll (7) - I/O event notification facility [root@centos8 ~]#whatis select select (2) - synchronous I/O multiplexing select (3) - synchronous I/O multiplexing select (3p) - synchronous I/O multiplexing [root@centos8 ~]#whatis poll poll (2) - wait for some event on a file descriptor poll (3p) - input/output multiplexing [root@centos8 ~]#man 2 select SELECT(2) Linux Programmer's Manual SELECT(2) NAME select, pselect, FD_CLR, FD_ISSET, FD_SET, FD_ZERO - synchronous I/O multiplexing [root@centos8 ~]#man 2 poll POLL(2) Linux Programmer's Manual POLL(2) NAME poll, ppoll - wait for some event on a file descriptor
零拷贝
零拷贝介绍
传统 Linux中 I/O 的问题
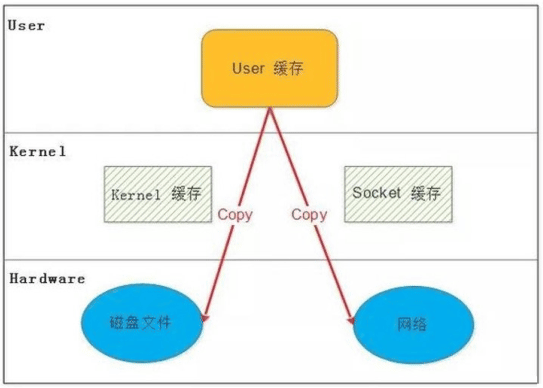
传统的 Linux 系统的标准 I/O 接口(read、write)是基于数据拷贝的,也就 是数据都是 copy_to_user或者 copy_from_user,这样做的好处是,通过中间缓 存的机制,减少磁盘 I/O 的操作,但是坏处也很明显,大量数据的拷贝,用户 态和内核态的频繁切换,会消耗大量的 CPU 资源,严重影响数据传输的性能, 统计表明,在Linux协议栈中,数据包在内核态和用户态之间的拷贝所用的时间 甚至占到了数据包整个处理流程时间的57.1%
什么是零拷贝
零拷贝就是上述问题的一个解决方案,通过尽量避免拷贝操作来缓解 CPU 的压 力。零拷贝并没有真正做到“0”拷贝,它更多是一种思想,很多的零拷贝技术 都是基于这个思想去做的优化
零拷页相关技术
- MMAP ( Memory Mapping )
- SENDFILE
- DMA 辅助的 SENDFILE
MMAP:
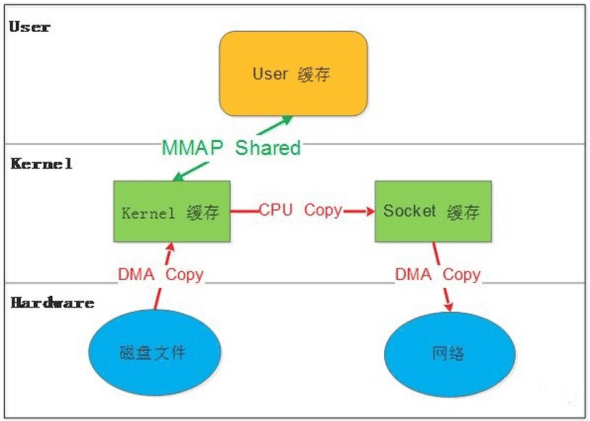
mmap(memory mapping)系统调用使得进程之间通过映射同一个普通文件实现共享 内存,普通文件被映射到进程地址空间后,进程可以像访问普通内存一样对文件 进行访问。
mmap是一种内存映射文件的方法,即将一个文件或者其它对象映射到进程的地址 空间,实现文件磁盘地址和进程虚拟地址空间中一段虚拟地址的一一对映关系。
实现这样的映射关系后,进程就可以采用指针的方式读写操作这一段内存,而系 统会自动回写脏页面到对应的文件磁盘上,即完成了对文件的操作而不必再调用 read,write等系统调用函数。相反,内核空间对这段区域的修改也直接反映用户 空间,从而可以实现不同进程间的文件共享。
内存映射减少数据在用户空间和内核空间之间的拷贝操作,适合大量数据传输
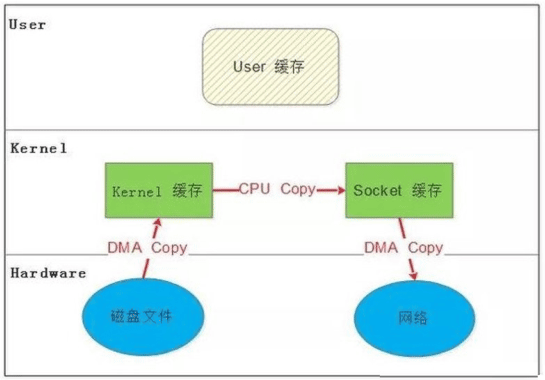
SENDFILE
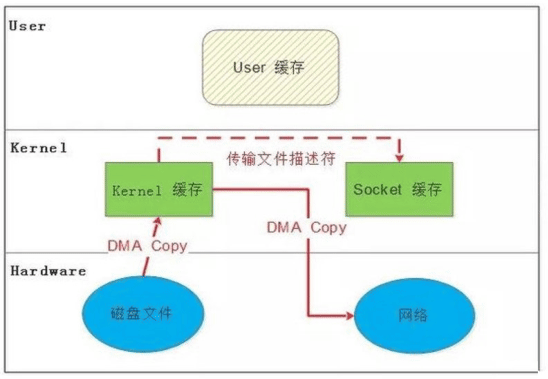
DMA 辅助的 SENDFILE
Nginx基础
Nginx:engine X ,2002年开发,分为社区版和商业版(nginx plus )
2019年3月11日 F5 Networks 6.7亿美元的价格收购
Nginx是免费的、开源的、高性能的HTTP和反向代理服务器、邮件代理服务器、 以及TCP/UDP代理服务器
解决C10K问题(10K Connections)
解决C1000K问题参考链接: http://www.ideawu.net/blog/archives/740.html
Nginx官网:https://nginx.org
nginx的其它的二次发行版:
- Tengine:由淘宝网发起的Web服务器项目。它在Nginx的基础上,针对大访问 量网站的需求,添加了很多高级功能和特性,Tengine的性能和稳定性已经在 大型的网站如淘宝网,天猫商城等得到了很好的检验,它的最终目标是打造一 个高效、稳定、安全、易用的Web平台,从2011年12月开始,Tengine成为一个 开源项目,官网http://tengine.taobao.org/
- OpenResty:基于 Nginx 与 Lua 语言的高性能 Web 平台,章亦春团队开发, 官网:http://openresty.org/cn/
Nginx功能介绍
- 静态的web资源服务器html,图片,js,css,txt等静态资源
- 结合FastCGI/uWSGI/SCGI等协议反向代理动态资源请求
- http/https协议的反向代理
- imap4/pop3协议的反向代理
- tcp/udp协议的请求转发(反向代理)
基础特性
特性 :
- 模块化设计,较好的扩展性
- 高可靠性(很少宕机)
- 支持热部署:不停机更新配置文件,升级版本,更换日志文件
- 低内存消耗: 10000个keep-alive连接模式下的非活动连接,仅需2.5M内存
- event-driven,aio,mmap,sendfile
基本功能 :
- 静态资源的web服务器
- http协议反向代理服务器
- pop3/imap4协议反向代理服务器
- FastCGI(LNMP),uWSGI(python)等协议
- 模块化(非DSO),如zip,SSL模块
和web服务相关的功能
- 虚拟主机(server)
- 支持 keep-alive 和管道连接(利用一个连接做多次请求)
- 访问日志(支持基于日志缓冲提高其性能)
- url rewirte
- 路径别名
- 基于IP及用户的访问控制
- 支持速率限制及并发数限制
- 重新配置和在线升级而无须中断客户的工作进程
Nginx组织结构
web请求处理机制:
- 多进程方式 :服务器每接收到一个客户端请求就有服务器的主进程生成一 个子进程响应客户端,直到用户关闭连接,这样的优势是处理速度快,各子 进程之间相互独立,但是如果访问过大会导致服务器资源耗尽而无法提供请 求。
- 多线程方式 :与多进程方式类似,但是每收到一个客户端请求会有服务进 程派生出一个线程来个客户方进行交互,一个线程的开销远远小于一个进程, 因此多线程方式在很大程度减轻了web服务器对系统资源的要求,但是多线程 也有自己的缺点,即当多个线程位于同一个进程内工作的时候,可以相互访 问同样的内存地址空间,所以他们相互影响,另外一旦主进程挂掉则所有子 线程都不能工作了,IIS服务器使用了多线程的方1式,需要间隔一段时间就 重启一次才能稳定。
Nginx是多进程组织模型,而且是一个由Master主进程和Worker工作进程组成。
主进程(master process)的功能:
- 读取Nginx 配置文件并验证其有效性和正确性
- 建立、绑定和关闭socket连接
- 按照配置生成、管理和结束工作进程
- 接受外界指令,比如重启、升级及退出服务器等指令
- 不中断服务,实现平滑升级,重启服务并应用新的配置
- 开启日志文件,获取文件描述符
- 不中断服务,实现平滑升级,升级失败进行回滚处理
- 编译和处理perl脚本
工作进程(woker process)的功能:
- 接受处理客户的请求
- 将请求依次送入各个功能模块进行处理
- IO调用,获取响应数据
- 与后端服务器通信,接收后端服务器的处理结果
- 缓存数据,访问缓存索引,查询和调用缓存数据
- 发送请求结果,响应客户的请求
- 接收主程序指令,比如重启、升级和退出等
进程间通信:
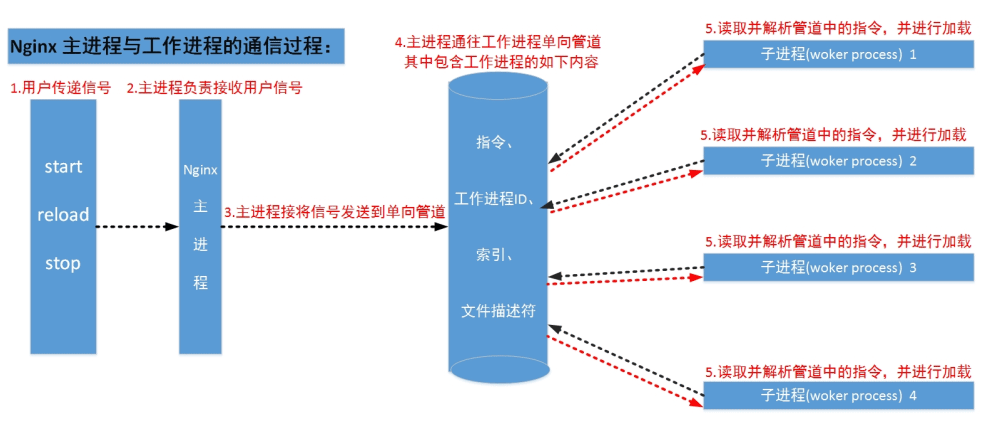
工作进程是有主进程生成的,主进程使用fork()函数,在Nginx服务器启动过程 中主进程根据配置文件决定启动工作进程的数量,然后建立一张全局的工作表用 于存放当前未退出的所有的工作进程,主进程生成工作进程后会将新生成的工作 进程加入到工作进程表中,并建立一个单向的管道并将其传递给工作进程,该管 道与普通的管道不同,它是由主进程指向工作进程的单向通道,包含了主进程向 工作进程发出的指令、工作进程ID、工作进程在工作进程表中的索引和必要的文 件描述符等信息。
主进程与外界通过信号机制进行通信,当接收到需要处理的信号时,它通过管道 向相关的工作进程发送正确的指令,每个工作进程都有能力捕获管道中的可读事 件,当管道中有可读事件的时候,工作进程就会从管道中读取并解析指令,然后 采取相应的执行动作,这样就完成了主进程与工作进程的交互。
说明:
- 工作进程之间的通信原理基本上和主进程与工作进程之间的通信是一样的, 只要工作进程之间能够取得彼此的信息,建立管道即可通信,但是由于工作 进程之间是完全隔离的,因此一个进程想要知道另外一个进程的状态信息就 只能通过主进程来设置了。
- 为了实现工作进程之间的交互,主进程在生成工作进程之后,在工作进程表 中进行遍历,将该新进程的ID以及针对该进程建立的管道句柄传递给工作进 程中的其他进程,为工作进程之间的通信做准备,当工作进程1向工作进程2 发送指令的时候,首先在主进程给它的其他工作进程工作信息中找到2的进程 ID,然后将正确的指令写入指向进程2的管道,工作进程2捕获到管道中的事 件后,解析指令并进行相关操作,这样就完成了工作进程之间的通信。
Nginx模块介绍:
- 核心模块 :是 Nginx 服务器正常运行 必不可少 的模块,提供 错误日志记录 、 配置文件解析 、 事件驱动机制 、进程管理 等核心功能
- 标准HTTP模块:提供 HTTP 协议解析相关的功能,比如: 端口配置 、 网页编码设置 、 HTTP响应头设置 等等
- 可选HTTP模块:主要用于扩展标准的 HTTP 功能,让 Nginx 能处理一些特殊的服务,比如: Flash 多媒体传输 、解析 GeoIP 请求、 网络传输压缩 、 安全协议 SSL 支持等
- 邮件服务模块:主要用于支持 Nginx 的 邮件服务 ,包括对 POP3 协议、 IMAP 协议和 SMTP协议的支持 (基本用不上)
- 第三方模块:是为了扩展 Nginx 服务器应用,完成开发者自定义功能,比如: Json 支持、 Lua 支持等
nginx高度模块化,但其模块早期不支持DSO机制;*1.9.11版本支持动态装载和卸载*
模块分类:
核心模块:core module
标准模块:
HTTP 模块: ngx_http_*
HTTP Core modules 默认功能
HTTP Optional modules 需编译时指定
Mail 模块 ngx_mail_*
Stream 模块 ngx_stream_*
第三方模块
Nginx安装
Nginx的安装版本分为Mainline version(主要开发版本,其实就是还处于开发版)、 Stable version(当前最新稳定版)和Legacy versions(旧的稳定版)
Nginx安装可以使用yum或源码安装,但是推荐使用源码,
- 是yum的版本比较旧
- 编译安装可以更方便自定义相关路径
- 是使用源码编译可以自定义相关功能,更方便业务的上的使用
源码安装需要提前准备标准的编译器,GCC的全称是(GNU Compiler collection),其有GNU开发,并以GPL即LGPL许可,是自由的类UNIX即苹果电脑 Mac OS X操作系统的标准编译器,因为GCC原本只能处理C语言,所以原名为GNU C语言编译器,后来得到快速发展,可以处理C++,Fortran,pascal, objective-C,java以及Ada等其他语言,此外还需要Automake工具,以完成自动 创建Makefile的工作,Nginx的一些模块需要依赖第三方库,比如pcre(支持 rewrite),zlib(支持gzip模块)和openssl(支持ssl模块)等。
Nginx yum安装
系统和EPEL源的中nignx版本较旧,可以安装官方源的最新版本
官方包链接: http://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html
官方提供的仓库:http://nginx.org/en/linux_packages.html#RHEL-CentOS
范例: 通过官方 yum 源安装nginx
[root@Centos7 ~]#vim /etc/yum.repos.d/nginx.repo [nginx-stable] name=nginx stable repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=1 gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key module_hotfixes=true [nginx-mainline] name=nginx mainline repo baseurl=http://nginx.org/packages/mainline/centos/$releasever/$basearch/ gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=https://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key module_hotfixes=true #列出所有版本 [root@centos8 ~]#yum list nginx --showduplicates [root@Centos7 ~]# yum install -y nginx [root@Centos7 ~]# rpm -ql nginx /etc/logrotate.d/nginx /etc/nginx/fastcgi.conf /etc/nginx/fastcgi.conf.default /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params.default /etc/nginx/koi-utf /etc/nginx/koi-win /etc/nginx/mime.types /etc/nginx/mime.types.default /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.default /etc/nginx/scgi_params /etc/nginx/scgi_params.default /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params.default /etc/nginx/win-utf /usr/bin/nginx-upgrade /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service /usr/lib64/nginx/modules /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/share/doc/nginx-1.18.0 ................. /var/lib/nginx /var/lib/nginx/tmp /var/log/nginx [root@Centos7 ~]# which nginx /usr/sbin/nginx
检查安装:
查看nginx安装包信息
[root@Centos7 ~]#rpm -qi nginx Name : nginx Epoch : 1 Version : 1.16.1 Release : 1.el7 Architecture: x86_64 Install Date: Mon 13 Jul 2020 10:37:26 PM CST Group : Unspecified Size : 1689960 License : BSD Signature : RSA/SHA256, Fri 04 Oct 2019 06:38:33 AM CST, Key ID 6a2faea2352c64e5 Source RPM : nginx-1.16.1-1.el7.src.rpm Build Date : Thu 03 Oct 2019 01:15:40 PM CST Build Host : buildvm-13.phx2.fedoraproject.org Relocations : (not relocatable) Packager : Fedora Project Vendor : Fedora Project URL : http://nginx.org/ Bug URL : https://bugz.fedoraproject.org/nginx Summary : A high performance web server and reverse proxy server Description : Nginx is a web server and a reverse proxy server for HTTP, SMTP, POP3 and IMAP protocols, with a strong focus on high concurrency, performance and low memory usage.
查看帮助
使用安装完成的二进制文件nginx
[root@Centos7 ~]# nginx -h nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 Usage: nginx [-?hvVtTq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives] Options: -?,-h : this help -v : show version and exit -V : show version and configure options then exit #显示版本和编译参数 -t : test configuration and exit #测试配置文件是否异常 -T : test configuration, dump it and exit #测试并打印 -q : suppress non-error messages during configuration testing #静默模式 -s signal : send signal to a master process: stop, quit, reopen, reload #发送信号 -p prefix : set prefix path (default: /usr/share/nginx/) #指定Nginx 目录 -c filename : set configuration file (default: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf) #配置文件路径 -g directives : set global directives out of configuration file #设置全局指令
范例: nginx 命令使用
[root@centos8 ~]#nginx -g "worker_processes 6;" nginx: [emerg] "worker_processes" directive is duplicate in /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf:3 [root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf #worker_processes 1; [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -g "worker_processes 6;" [root@centos8 ~]#ps aux|grep nginx [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -s quit [root@centos8 ~]#ps aux|grep nginx #前台运行 [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -g 'daemon off;'
验证Nginx
[root@Centos7 ~]#nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful [root@Centos7 ~]#nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.16.1 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/share/nginx --sbin-path=/usr/sbin/nginx --modules-path=/usr/lib64/nginx/modules --conf-path=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf --error-log-path=/var/log/nginx/error.log --http-log-path=/var/log/nginx/access.log --http-client-body-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/client_body --http-proxy-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/proxy --http-fastcgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/fastcgi --http-uwsgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/uwsgi --http-scgi-temp-path=/var/lib/nginx/tmp/scgi --pid-path=/run/nginx.pid --lock-path=/run/lock/subsys/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-file-aio --with-ipv6 --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-stream_ssl_preread_module --with-http_addition_module --with-http_xslt_module=dynamic --with-http_image_filter_module=dynamic --with-http_sub_module --with-http_dav_module --with-http_flv_module --with-http_mp4_module --with-http_gunzip_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_random_index_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-http_degradation_module --with-http_slice_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_perl_module=dynamic --with-http_auth_request_module --with-mail=dynamic --with-mail_ssl_module --with-pcre --with-pcre-jit --with-stream=dynamic --with-stream_ssl_module --with-google_perftools_module --with-debug --with-cc-opt='-O2 -g -pipe -Wall -Wp,-D_FORTIFY_SOURCE=2 -fexceptions -fstack-protector-strong --param=ssp-buffer-size=4 -grecord-gcc-switches -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-cc1 -m64 -mtune=generic' --with-ld-opt='-Wl,-z,relro -specs=/usr/lib/rpm/redhat/redhat-hardened-ld -Wl,-E'
Nginx启动脚本
[root@s1 ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid # Nginx will fail to start if /run/nginx.pid already exists but has the wrong # SELinux context. This might happen when running `nginx -t` from the cmdline. # https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1268621 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID KillSignal=SIGQUIT TimeoutStopSec=5 KillMode=process PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Nginx 配置文件
范例: 查看配置文件列表
[root@centos8 ~]#rpm -qc nginx /etc/logrotate.d/nginx /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf /etc/nginx/fastcgi_params /etc/nginx/koi-utf /etc/nginx/koi-win /etc/nginx/mime.types /etc/nginx/nginx.conf /etc/nginx/scgi_params /etc/nginx/uwsgi_params /etc/nginx/win-utf /etc/sysconfig/nginx /etc/sysconfig/nginx-debug [root@centos8 ~]#cat /etc/sysconfig/nginx # Configuration file for the nginx service. NGINX=/usr/sbin/nginx CONFFILE=/etc/nginx/nginx.conf [root@centos8 ~]#tree /etc/nginx/ /etc/nginx/ ├── conf.d │ └── default.conf ├── fastcgi_params ├── koi-utf ├── koi-win ├── mime.types ├── modules -> ../../usr/lib64/nginx/modules ├── nginx.conf ├── scgi_params ├── uwsgi_params └── win-utf 2 directories, 9 files
范例: 配置文件/etc/nginx/nginx.conf 默认配置
user nginx;
worker_processes auto;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80 default_server;
listen [::]:80 default_server;
server_name _;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /40x.html {
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
}
}
启动Nginx
[root@Centos7 ~]#systemctl start nginx [root@Centos7 ~]#systemctl status nginx ● nginx.service - The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: active (running) since Mon 2020-07-13 22:43:52 CST; 8s ago Process: 3141 ExecStart=/usr/sbin/nginx (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 3138 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/nginx -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Process: 3136 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 3143 (nginx) CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service ├─3143 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx ├─3144 nginx: worker process └─3145 nginx: worker process Jul 13 22:43:52 Centos7.8 systemd[1]: Starting The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server... Jul 13 22:43:52 Centos7.8 nginx[3138]: nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf ... ok Jul 13 22:43:52 Centos7.8 nginx[3138]: nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test...ful Jul 13 22:43:52 Centos7.8 systemd[1]: Started The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server. Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full. [root@Centos7 ~]#ps -ef | grep nginx root 3143 1 0 22:43 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx nginx 3144 3143 0 22:43 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process nginx 3145 3143 0 22:43 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process root 3149 3006 0 22:44 pts/1 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
访问nginx
Nginx 编译安装
官方源码包下载地址:https://nginx.org/en/download.html
[root@centos8 ~]#yum -y install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel [root@centos8 ~]#useradd -s /sbin/nologin nginx [root@centos8 ~]#cd /usr/local/src/ [root@centos8 src]#wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz [root@centos8 src]#tar xf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz [root@centos8 src]#cd nginx-1.18.0/ [root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx \ --user=nginx \ --group=nginx \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_v2_module \ --with-http_realip_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --with-pcre \ --with-stream \ --with-stream_ssl_module \ --with-stream_realip_module [root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#make && make install #修改权限 [root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#chown -R nginx.nginx /apps/nginx
nginx完成安装以后,有四个主要的目录
#生成目录 [root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#ll /apps/nginx/ total 0 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 333 Sep 22 12:49 conf drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 40 Sep 22 12:49 html drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 Sep 22 12:49 logs drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 19 Sep 22 12:49 sbin
- conf:保存nginx所有的配置文件,其中nginx.conf是nginx服务器的最核心最 主 要的配置文件,其他的.conf则是用来配置nginx相关的功能的,例如 fastcgi功 能使用的是fastcgi.conf和fastcgi_params两个文件,配置文件一 般都有个样板 配置文件,是文件名.default结尾,使用的使用将其复制为并 将default去掉即 可。
- html目录中保存了nginx服务器的web文件,但是可以更改为其他目录保存web文件,另外还有一个50x的web文件是默认的错误页面提示页面。
- logs:用来保存nginx服务器的访问日志错误日志等日志,logs目录可以放在其他路径,比如/var/logs/nginx里面。
- sbin:保存nginx二进制启动脚本,可以接受不同的参数以实现不同的功能。
验证版本及编译参数
[root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#ls /apps/nginx/sbin/ nginx [root@centos8 nginx-1.18.0]#ln -s /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/sbin/ #查看版本 [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -v nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 #查看编译参数 [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 built by gcc 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-39) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.0.2k-fips 26 Jan 2017 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --withhttp_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --withhttp_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module
访问编译安装的nginx web界面
#启动nginx [root@centos8 ~]#nginx #浏览器可以访问看到下面图示 [root@centos8 ~]#ss -ntl #关闭nginx [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -s stop [root@centos8 ~]#ss -ntl
创建Nginx自启动脚本
Nginx 1.16.1 :
[root@Centos7 ~]# cat /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=The nginx HTTP and reverse proxy server After=network.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/run/nginx.pid # Nginx will fail to start if /run/nginx.pid already exists but has the wrong # SELinux context. This might happen when running `nginx -t` from the cmdline. # https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1268621 ExecStartPre=/usr/bin/rm -f /run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID KillSignal=SIGQUIT TimeoutStopSec=5 KillMode=process PrivateTmp=true [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Nginx 1.18.0 :
cat <<\EOF> /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/ After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid ExecStartPre=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx #ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ExecReload=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload #ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID PrivateTmp=true LimitNOFILE=infinity [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOF #同时也要修改nginx的默认配置文件 [root@Centos7 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf pid /apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid; #创建pid存放目录 [root@Centos7 ~]#mkdir /apps/nginx/run/ -p
验证Nginx自启动脚本
[root@Centos7 nginx-1.18.0]# systemctl daemon-reload
[root@Centos7 nginx-1.18.0]# systemctl start nginx
[root@Centos7 nginx-1.18.0]# systemctl enable nginx
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nginx.service to
/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service.
[root@Centos7 nginx-1.18.0]# systemctl status nginx
● nginx.service - nginx - high performance web server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2020-07-14 15:20:35 CST; 32s ago
Docs: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
Process: 5048 ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 5049 (nginx)
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├─5049 nginx: master process /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
└─5050 nginx: worker process
Jul 14 15:20:35 Centos7.8 systemd[1]: Starting nginx - high performance web server...
Jul 14 15:20:35 Centos7.8 systemd[1]: Started nginx - high performance web server.
logrotate日志切割
cat <<\EOF >/etc/logrotate.d/nginx /var/log/nginx/*.log { #su root root daily rotate 5 missingok compress #size 1M delaycompress notifempty #create 644 ngnix nginx dateext #dateformat -%Y%m%d copytruncate sharedscripts postrotate if [ -f /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid ]; then kill -USR1 `cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid` fi endscript } EOF
Nginx 动态编译
参考:本章 GeoIP2
Nginx 核心配置详解
配置文件说明
nginx 官方帮助文档: http://nginx.org/en/docs/
tengine 帮助文档: http://tengine.taobao.org/nginx_docs/cn/docs/
Nginx的配置文件的组成部分:
- 主配置文件:nginx.conf
- 子配置文件 include conf.d/*.conf
- fastcgi, uwsgi,scgi等协议相关的配置文件
mime.types:支持的mime类型,MIME(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)多用途互联网邮件扩展类型,MIME消息能包含文本、图像、音频、 视频以及其他应用程序专用的数据,是设定某种扩展名的文件用一种应用程序 来打开的方式类型,当该扩展名文件被访问的时候,浏览器会自动使用指定应 用程序来打开。多用于指定一些客户端自定义的文件名,以及一些媒体文件打 开方式。
MIME参考文档:https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Basics_of_HTTP/MIME_Types
Nginx主配置文件的配置指令方式:
directive value [value2 ...];
注意:
(1) 指令必须以分号结尾
(2) 支持使用配置变量
内建变量:由Nginx模块引入,可直接引用
自定义变量:由用户使用set命令定义,格式
set variable_name value;
引用变量:$variable_name
主配置文件结构: 四部分
- main 主配置段,即全局配置段,对http,mail都有效
- event 事件驱动相关的配置
- http : http/https 协议相关配置段
- mail : mail 协议相关配置段
- stream : 4层端口服务配置段
main block:主配置段,即全局配置段,对http,mail都有效
#事件驱动相关的配置
event {
...
}
#http/https 协议相关配置段
http {
...
server {
...
server_name
root
alias
location /uri/ {
}
...
server {
...
}
}
#默认配置文件不包括下面两个块
#mail 协议相关配置段
mail {
...
}
#stream 服务器相关配置段
stream {
...
}
默认的 nginx.conf 配置文件格式说明
[root@Centos7 ~]# grep -v "#" /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf | grep -v "^$" #全局配置端,对全局生效,主要设置nginx的启动用户/组,启动的工作进程数量,工作模式,Nginx的PID路径,日志路径等。 user nginx nginx; #指定用户和组来启动nginx worker_processes 1; #启动工作进程数数量,推荐和CPU数量保持一致 events { #events设置快,主要影响nginx服务器与用户的网络连接,比如是否允许同时接受多个网络连接,使用哪种事件驱动模型处理请求,每个工作进程可以同时支持的最大连接数,是否开启对多工作进程下的网络连接进行序列化等。 worker_connections 1024; #设置单个nginx工作进程可以接受的最大并发,作为web服务器的时候最大并发数为worker_connections * worker_processes,作为反向代理的时候为(worker_connections * worker_processes)/2 } http { #http块是Nginx服务器配置中的重要部分,缓存、代理和日志格式定义等绝大多数功能和第三方模块都可以在这设置,http块可以包含多个server块,而一个server块中又可以包含多个location块,server块可以配置文件引入、MIME-Type定义、日志自定义、是否启用sendfile、连接超时时间和单个链接的请求上限等。 include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; #作为web服务器的时候打开sendfile加快静态文件传输,指定是否使用sendfile系统调用来传输文件,sendfile系统调用在两个文件描述符之间直接传递数据(完全在内核中操作),从而避免了数据在内核缓冲区和用户缓冲区之间的拷贝,操作效率很高,被称之为零拷贝,硬盘 >> kernel buffer (快速拷贝到kernelsocket buffer) >>协议栈。 keepalive_timeout 65; #长连接超时时间,单位是秒 server { #设置一个虚拟机主机,可以包含自己的全局快,同时也可以包含多个location模块。比如本虚拟机监听的端口、本虚拟机的名称和IP配置,多个server 可以使用一个端口,比如都使用80端口提供web服务、 listen 80; #配置server监听的端口 server_name localhost; #本server的名称,当访问此名称的时候nginx会调用当前serevr内部的配置进程匹配。 location / { #location其实是server的一个指令,为nginx服务器提供比较多而且灵活的指令,都是在location中体现的,主要是基于nginx接受到的请求字符串,对用户请求的UIL进行匹配,并对特定的指令进行处理,包括地址重定向、数据缓存和应答控制等功能都是在这部分实现,另外很多第三方模块的配置也是在location模块中配置。 root html; #相当于默认页面的目录名称,默认是相对路径,可以使用绝对路径配置。 index index.html index.htm; #默认的页面文件名称 } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #错误页面的文件名称 location = /50x.html { #location处理对应的不同错误码的页面定义到/50x.html,这个跟对应其server中定义的目录下。 root html; #定义默认页面所在的目录 } } #和邮件相关的配置 #mail { # ... # } mail 协议相关配置段 #tcp代理配置,1.9版本以上支持 #stream { # ... # } stream 服务器相关配置段 #导入其他路径的配置文件 #include /apps/nginx/conf.d/*.conf }
说明:
web服务器的总链接=工作进程数*单个工作进程最大并发值
七层反向代理服务器= ( 工作进程数*单个工作进程最大并发值 ) /2
main 全局配置
Main 全局配置段常见的配置指令分类
- 正常运行必备的配置
- 优化性能相关的配置
- 用于调试及定位问题相关的配置
- 事件驱动相关的配置
全局配置说明:
user nginx nginx; #启动Nginx工作进程的用户和组 worker_processes [number | auto]; #启动Nginx工作进程的数量 worker_cpu_affinity 00000001 00000010 00000100 00001000; #将Nginx工作进程绑定到指定的CPU核心,默认Nginx是不进行进程绑定的,绑定并不是意味着当前nginx进程独占以一核心CPU,但是可以保证此进程不会运行在其他核心上,这就极大减少了nginx的工作进程在不同的cpu核心上的来回跳转,减少了CPU对进程的资源分配与回收以及内存管理等,因此可以有效的提升nginx服务器的性能。 CPU MASK: 00000001:0号CPU 00000010:1号CPU 10000000:7号CPU #示例: worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;第0号---第3号CPU worker_cpu_affinity 0101 1010; #示例 worker_processes 4; worker_cpu_affinity 00000010 00001000 00100000 10000000; [root@centos8 ~]# ps axo pid,cmd,psr | grep nginx [root@Centos7 ~]#ps axo pid,cmd,psr,user | grep nginx 4106 nginx: master process /apps 1 root 4181 nginx: worker process 0 nginx 4182 nginx: worker process 1 nginx 4184 grep --color=auto nginx 0 root #错误日志记录配置,语法:error_log file [debug | info | notice | warn | error | crit |alert | emerg] #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; error_log /apps/nginx/logs/error.log error; #pid文件保存路径 pid /apps/nginx/logs/nginx.pid; worker_priority 0; #工作进程nice值,-20~19 worker_rlimit_nofile 65536; #这个数字包括Nginx的所有连接(例如与代理服务器的连接等),而不仅仅是与客户端的连接,另一个考虑因素是实际的并发连接数不能超过系统级别的最大打开文件数的限制. [root@Centos7 ~]# watch -n1 'ps -axo pid,cmd,nice | grep nginx' #验证进程优先级 daemon off; #前台运行Nginx服务用于测试、docker等环境。 master_process off|on; #是否开启Nginx的master-woker工作模式,仅用于开发调试场景。 events { #事件模型配置参数 worker_connections 65536; #设置单个工作进程的最大并发连接数 use epoll; #使用epoll事件驱动,Nginx支持众多的事件驱动,比如select、poll、epoll,只能设置在events模块中设置。 accept_mutex on; #优化同一时刻只有一个请求而避免多个睡眠进程被唤醒的设置,on为防止被同时唤醒,默认为off,全部唤醒的过程也成为"惊群",因此nginx刚安装完以后要进行适当的优化。 multi_accept on; #Nginx服务器的每个工作进程可以同时接受多个新的网络连接,但是需要在配置文件中配置,此指令默认为关闭,即默认为一个工作进程只能一次接受一个新的网络连接,打开后几个同时接受多个。建议设置为on }
范例: 实现 nginx 的高并发配置
[root@centos7 ~]#ulimit -n 102400 [root@centos7 ~]#while true;do ab -c 5000 -n 10000 http://10.0.0.8/;sleep 0.5;done #默认配置不支持高并发,会出现以下错误日志 [root@centos8 conf]#tail /apps/nginx/logs/error.log #修改配置 [root@centos8 ~]#vim /etc/security/limits.conf * - nproc 100000 [root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_rlimit_nofile 100000; [root@centos8 ~]#systemctl restart nginx
http配置块
http {
...
... #各server的公共配置
server { #每个server用于定义一个虚拟主机,第一个server为默认虚拟服务器
...
}
server {
...
server_name #虚拟主机名
root #主目录
alias #路径别名
location [OPERATOR] URL { #指定URL的特性
...
if CONDITION {
...
}
}
}
}
http 协议配置说明
http {
include mime.types; #导入支持的文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream; #设置默认的类型,会提示下载不匹配的类型文件
#日志配置部分
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#自定义优化参数
sendfile on; #实现文件零拷贝
#tcp_nopush on; #在开启了sendfile的情况下,合并请求后统一发送给客户端。
#tcp_nodelay off; #在开启了keepalived模式下的连接是否启用TCP_NODELAY选项,当为off时,延迟0.2s发送,默认On时,不延迟发送,立即发送用户相应报文。
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65; #设置会话保持时间
#gzip on; #开启文件压缩
#定义一个虚拟主机
server {
listen 80; #设置监听地址和端口
server_name localhost; #设置server name,可以以空格隔开写多个并支持正则表达式,如*.cici.com www.cici.* www.(site\d+)\.cici\.com$ default_server
#charset koi8-r; #设置编码格式,默认是俄语格式,可以改为utf-8
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; #定义错误页面
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ { #以http的方式转发php请求到指定web服务器
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ { #以fastcgi的方式转发php请求到php处理
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht { #拒绝web形式访问指定文件,如很多的网站都是通过.htaccess文件来改变自己的重定向等功能。
# deny all;
#}
location ~ /passwd.html {
deny all;
}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server { #自定义虚拟server
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm; #指定默认网页文件,此指令由ngx_http_index_module模块提供
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server { #https服务器配置
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
MIME
#在响应报文中将指定的文件扩展名映射至MIME对应的类型
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;#除mime.types中的类型外,指定其它文件的默认MIME类型,浏览器一般会提示下载
types {
text/html html;
image/gif gif;
image/jpeg jpg;
}
MIME参考文档: https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/HTTP/Basics_of_HTTP/MIME_Types
范例: 识别php文件为text/html
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /apps/nginx/html/test.php <?php phpinfo(); ?> [root@centos7 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8/test.php -I HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx/1.18.0 Date: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 13:54:39 GMT Content-Type: application/octet-stream Content-Length: 20 Last-Modified: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 13:53:26 GMT Connection: keep-alive ETag: "5f6ca4d6-14" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf http { include mime.types; default_type text/html; ...... [root@centos8 ~]#nginx -s reload [root@centos7 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8/index.html -I HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx/1.18.0 Date: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 13:56:26 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 612 Last-Modified: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 12:13:03 GMT Connection: keep-alive ETag: "5f6c8d4f-264" Accept-Ranges: bytes
指定响应报文server首部
#是否在响应报文中的Content-Type显示指定的字符集,默认off不显示 charset charset | off; #示例 charset utf-8; #是否在响应报文的Server首部显示nginx版本 server_tokens on | off | build | string;
范例: 修改server字段
如果想自定义响应报文的nginx版本信息,需要修改源码文件,重新编译 如果server_tokens on,修改 src/core/nginx.h 修改第13-14行,如下示例 #define NGINX_VERSION "1.68.9" #define NGINX_VER "cicinginx/" NGINX_VERSION 如果server_tokens off,修改 src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c 第49行,如下示例: static char ngx_http_server_string[] = "Server: nginx" CRLF; 把其中的nginx改为自己想要的文字即可,如:cicinginx
范例: 修改 Server 头部信息
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /usr/local/src/nginx-1.18.0/src/core/nginx.h #define NGINX_VERSION "1.68.9" #define NGINX_VER "cicinginx/" NGINX_VERSION [root@centos8 ~]#vim nginx-1.18.0/src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c static u_char ngx_http_server_string[] = "Server: cici-nginx" CRLF; [root@centos7 ~]#curl -I www.cici.org HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: ciciginx/1.68.9 Date: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 07:44:05 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 8 Last-Modified: Wed, 23 Sep 2020 14:39:21 GMT Connection: keep-alive ETag: "5f6b5e19-8" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf server { ...... server_tokens off; ...... [root@centos7 ~]#curl -I www.cici.org HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: cici-nginx Date: Thu, 24 Sep 2020 07:44:59 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 8 Last-Modified: Wed, 23 Sep 2020 14:39:21 GMT Connection: keep-alive ETag: "5f6b5e19-8" Accept-Ranges: bytes
核心配置示例
基于不同的IP、不同的端口以及不用得域名实现不同的虚拟主机,依赖于核心模块ngx_http_core_module实现。
新建一个PC web站点
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d
[root@s2 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
......
include /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/*.conf; #在配置文件的最后面添加此行
}
#创建PC网站配置
[root@s2 ~]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
}
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc -p
[root@s2 ~]# echo "pc web" > /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html
[root@s2 ~]# systemctl reload nginx
#访问测试
新建一个Mobile web站点
[root@s2 ~]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/mobile.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name mobile.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/mobile;
}
}
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/mobile -p
[root@s2 ~]# echo "mobile web" >> /data/nginx/html/mobile/index.html
[root@s2 ~]# systemctl reload nginx
root与alias:
root:指定web的家目录,在定义location的时候,文件的绝对路径等于 root+location
范例:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /about {
root /data/nginx/html/pc; #必须要在html目录中创建一个about目录才可以访问,否则报错。
index index.html;
}
}
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/about
[root@s2 ~]# echo about > /data/nginx/html/pc/about/index.html
#重启Nginx并访问测试
alias:定义路径别名,会把访问的路径重新定义到其指定的路径,文档映射的另一种机制;仅能用于 location上下文,此指令使用较少
范例:
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /about { #使用alias的时候uri后面如果加了斜杠则下面的路径配置必须加斜杠,否则403
alias /data/nginx/html/pc; #当访问about的时候,会显示alias定义的/data/nginx/html/pc里面的内容。
index index.html;
}
}
重启Nginx并访问测试
http://www.cici.net/about/index.html #访问指定文件资源
注意:location中使用root指令和alias指令的意义不同
root,给定的路径对应于location中的/uri 左侧的/ alias,给定的路径对应于location中的/uri 的完整路径
location的详细使用:
在一个server中location配置段可存在多个,用于实现从uri到文件系统的路径 映射;ngnix会根据用户请求的URI来检查定义的所有location,按一定的优化级 找出一个最佳匹配,而后应用其配置
在没有使用正则表达式的时候,nginx会先在server中的多个location选取匹配 度最高的一个uri,uri是用户请求的字符串,即域名后面的web文件路径,然后 使用该location模块中的正则url和字符串,如果匹配成功就结束搜索,并使用 此location处理此请求。
location 官方帮助: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#location
语法规则:
location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ { … }
= #用于标准uri前,需要请求字串与uri精确匹配,如果匹配成功就停止向下匹配并立即处理请求。
~ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且区分大小写,并且匹配
!~ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且区分大小写,并且不匹配
~* #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且不区分大写,并且匹配
!~* #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且不区分大小写,并且不匹配
^~ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且匹配以什么开头
$ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且匹配以什么结尾
\ #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且转义字符。可以转. * ?等
* #用于标准uri前,表示包含正则表达式并且代表任意长度的任意字符
#匹配优先级从高到低:
=, ^~, ~/~*, 不带符号
匹配案例-精确匹配:
=
在server部分使用location配置一个web界面,要求:当访问nginx 服务器的 /logo.jpg 的时候要显示指定html文件的内容:
精确匹配一般用于匹配组织的logo等相对固定的URL,匹配优先级最高
[root@s2 ~]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location = /1ogo.jpg {
root /var/www/nginx/images;
index index.html;
}
}
#上传图片到/var/www/nginx/images,重启Nginx并访问测试
#访问测试:http://www.cici.net/1ogo.jpg
匹配案例-区分大小写:
~
如果uri中包含大写字母,则以下location匹配Ax.jpg条件不成功,因为~为区分 大小写,那么当用户的请求被执行匹配时发现location中定义的是大写的A,则 匹配失败,即要么继续往下匹配其他的location(如果有),要么报错给客户端。
location ~ /A.?\.jpg { #匹配字母A开头的图片,后面?表示A后面零次或一个字符 index index.html; root /opt/nginx/html/image; } 重启Nginx并访问测试 将只能访问以小写字符的AX.jpg图片,不能识别大写的JPG结尾的图片 访问测试:http://www.cici.net/Aa.jpg #直接访问资源名称即可
匹配案例-不区分大小写:
~*
用来对用户请求的uri做模糊匹配,uri中无论都是大写、都是小写或者大小写混 合,此模式也都会匹配,通常使用此模式匹配用户request中的静态资源并继续 做下一步操作,此方式使用较多
注意: 此方式中,对于Linux文件系统上的文件仍然是区分大小写的,如果磁盘文件不存在,仍会提示404
正则表达式匹配: location ~* /A.?\.jpg { index index.html; root /opt/nginx/html/image; } 访问测试:http://www.cici.net/aA.jpg #直接访问资源名称即可 ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 精确匹配指定名称: # location ~ /aa.jpg { # index index.html; # root /opt/nginx/html/image; # } location ~* /aa.jpg { index index.html; root /opt/nginx/html/image; } 重启Nginx并访问测试
说明:对于不区分大小写的location,则可以访问任意大小写结尾的图片文件,如区分大小写则只能访问aa.jpg,不区分大小写则可以访问aa.jpg以外的资源比如Aa.JPG、aA.jPG这样的混合名称文件,但是要求nginx服务器的资源目录有相应的文件,比如有Aa.JPG有aA.jPG。
匹配案例-URI开始
用的相对较少
location ^~ /images {
root /data/nginx;
index index.html;
}
location /images1 {
alias /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
}
重启Nginx并访问测试,实现效果是访问images和images1返回不同的结果
[root@s2 images]# curl http://www.cici.net/images/
images
[root@s2 images]# curl http://www.cici.net/images1/
pc web
匹配案例-文件名后缀
用的比较多
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/images1 #上传一个和images目录不一样内容的的图片1.j到/data/nginx/images1 location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|bmp|png|tiff|tif|ico|wmf|js)$ { root /data/nginx/images1; index index.html; } 重启Nginx并访问测试
匹配案例-优先级
location = /1.jpg {
root /data/nginx/static1;
index index.html;
}
location /1.jpg {
root /data/nginx/static2;
index index.html;
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|bmp|png|tiff|tif|ico|wmf|js)$ {
root /data/nginx/static3;
index index.html;
}
[root@centos8 ~]# mkdir -p /data/nginx/static{1,2,3}
#上传图片到 /data/nginx/static{1,2,3} 并重启nginx访问测试
#匹配优先级:=, ^~, ~/~*,/
location优先级:(location =) > (location ^~ 路径) > (location ~,~* 正则顺序) >(location 完整路径) > (location 部分起始路径) > (/)
生产使用案例
直接匹配网站根会加速Nginx访问处理:
location = /index.html {
......;
}
location / {
......;
}
#静态资源配置:
location ^~ /static/ {
......;
}
# 或者下面写法 (用的更多)
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg|png|css|js|ico)$ {
......;
}
#多应用配置
location ~* /app1 {
......;
}
location ~* /app2 {
......;
}
Nginx 四层访问控制:
访问控制基于模块ngx_http_access_module实现,可以通过匹配客户端源IP地址进行限制。
官方帮助: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_access_module.html
location /about {
alias /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
deny 192.168.1.1;
allow 192.168.1.0/24;
allow 10.1.1.0/16;
allow 2001:0db8::/32;
deny all; #先允许小部分,再拒绝大部分
}
注意:在防火墙上拒绝效果最好
Nginx账户认证功能
#CentOS安装包 [root@centos8 ~]#yum -y install httpd-tools #Ubuntu安装包 [root@Ubuntu ~]#apt -y install apache2-utils #创建用户 #-b 非交互式方式提交密码 [root@s2 ~]# htpasswd -cbm /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd user1 123456 Adding password for user user1 [root@s2 ~]# htpasswd -bm /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd user2 123456 Adding password for user user2 [root@s2 ~]# tail /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd user1:$apr1$Rjm0u2Kr$VHvkAIc5OYg.3ZoaGwaGq/ user2:$apr1$nIqnxoJB$LR9W1DTJT.viDJhXa6wHv. [root@s2 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf location = /login/ { root /data/nginx/html/pc; index index.html; auth_basic "login password"; auth_basic_user_file /apps/nginx/conf/.htpasswd; } 重启Nginx并访问测试
自定义错误页面
定义错误页,以指定的响应状态码进行响应, 可用位置:http, server, location, if in location
error_page code ... [=[response]] uri;
范例:
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /error.html;
location = /error.html {
root html;
}
重启nginx并访问不存在的页面进行测试
范例:
error_page 404 /40x.html;
location = /40x.html {
root /data/html/ ;
}
范例: 404 转为 302
error_page 404 =302 /index.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
}
自定义错误日志
Syntax: error_log file [level]; Default: error_log logs/error.log error; Context: main, http, mail, stream, server, location level: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit, alert, emerg
范例
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/logs listen 80; server_name www.cici.net; error_page 500 502 503 504 404 /error.html; #默认目录下面创建error.html页面 access_log /data/nginx/logs/www-cici-net_access.log; error_log /data/nginx/logs/www-cici-net_error.log; location = /error.html { root html; } 重启nginx并访问不存在的页面进行测试并验证是在指定目录生成新的日志文件
检测文件是否存在:
try_files会按顺序检查文件是否存在,返回第一个找到的文件或文件夹(结尾加斜线表示为文件夹),如果所有文件或文件夹都找不到,会进行一个内部重定向到最后一个参数。只有最后一个参数可以引起一个内部重定向,之前的参数只设置内部URI的指向。最后一个参数是回退URI且必须存在,否则会出现内部500错误。 语法
Syntax: try_files file ... uri; try_files file ... =code; Default: — Context: server, location
范例: 如果不存在页面, 就转到default.html页面
location /about {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
#alias /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
#try_files $uri /about/default.html;
#try_files $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html /about/default.html;
try_files $uri $uri/index.html $uri.html =489;
}
[root@s2 ~]# echo "default" >> /data/nginx/html/pc/about/default.html
#重启nginx并测试,当访问到http://www.cici.net/about/xx.html等不存在的uri会显示default,如果是自定义的状态码则会显示在返回数据的状态码中,如:
[root@s2 about]# curl --head http://www.cici.net/about/xx.html
HTTP/1.1 489 #489就是自定义的状态返回码
Server: nginx
Date: Thu, 21 Feb 2019 00:11:40 GMT
Content-Length: 0
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=65
长连接配置:
keepalive_timeout timeout [header_timeout]; #设定保持连接超时时长,0表示禁止长连接,默认为75s,通常配置在http字段作为站点全局配置 keepalive_requests number; #在一次长连接上所允许请求的资源的最大数量,默认为100次,建议适当调大,比如:500
范例:
keepalive_requests 3; keepalive_timeout 65 65; #开启长连接后,返回客户端的会话保持时间为60s,单次长连接累计请求达到指定次数请求或65秒就会被断开,后面的60为发送给客户端应答报文头部中显示的超时时间设置为60s:如不设置客户端将不显示超时时间。 Keep-Alive:timeout=60 #浏览器收到的服务器返回的报文 #如果设置为0表示关闭会话保持功能,将如下显示: Connection:close #浏览器收到的服务器返回的报文 #使用命令测试: [root@s3 apps]# telnet www.cici.net 80 Trying 172.18.200.102... Connected to www.cici.net. Escape character is '^]'. GET / HTTP/1.1 HOST: www.cici.net #Response Headers(响应头信息): HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx/1.14.2 Date: Thu, 14 Mar 2019 17:23:46 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 7 Last-Modified: Thu, 14 Mar 2019 14:54:50 GMT Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=60 ETag: "5c8a6b3a-7" Accept-Ranges: bytes #页面内容 pc web
作为下载服务器配置
ngx_http_autoindex_module 模块处理以斜杠字符 "/" 结尾的请求,并生成目 录列表,可以做为下载服务配置使用
官方文档: http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_autoindex_module.html
相关指令:
autoindex on | off;#自动文件索引功能,默为off autoindex_exact_size on | off; #计算文件确切大小(单位bytes),off 显示大概大小(单位K、M),默认on autoindex_localtime on | off ; #显示本机时间而非GMT(格林威治)时间,默认off autoindex_format html | xml | json | jsonp; #显示索引的页面文件风格,默认html limit_rate rate; #限制响应客户端传输速率(除GET和HEAD以外的所有方法),单位B/s,即bytes/second,默认值0,表示无限制,此指令由ngx_http_core_module提供
范例: 实现下载站点
#注意:download不需要index.html文件 [root@s2 about]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/download [root@s2 about]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf location /download { autoindex on; #自动索引功能 autoindex_exact_size on; #计算文件确切大小(单位bytes),off只显示大概大小(单位kb、mb、gb) autoindex_localtime on; #显示本机时间而非GMT(格林威治)时间 limit_rate 1024k; root /data/nginx/html/pc; } [root@s2 pc]# cp /root/anaconda-ks.cfg /data/nginx/html/pc/download/ #重启Nginx并访问测试下载页面 #更新时间 ntpdate time1.aliyun.com
为了备忘,最后将apache下的配置方法也记录一下!实现效果和上面一样!
Alias / ”/data/www/file”
< Directory ”/data/www/file” >
Options Indexes //开启目录列表索引模式
Order allow,deny
IndexOptions NameWidth = 25 Charset = UTF -8 //设定文件名显示长度,文字字符编码
Allow from all
</ Directory >
作为上传服务器
以下指令控制上传数据
client_max_body_size 1m; #设置允许客户端上传单个文件的最大值,默认值为1m client_body_buffer_size size; #用于接收每个客户端请求报文的body部分的缓冲区大小;默认16k;超出此大小时,其将被暂存到磁盘上的由下面client_body_temp_path指令所定义的位置 client_body_temp_path path [level1 [level2 [level3]]]; #设定存储客户端请求报文的body部分的临时存储路径及子目录结构和数量,目录名为16进制的数字,使用hash之后的值从后往前截取1位、2位、2位作为文件名: [root@s3 ~]# md5sum /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html 95f6f65f498c74938064851b1bb 96 3d 4 /data/nginx/html/pc/index.html 1级目录占1位16进制,即2^4=16个目录 0-f 2级目录占2位16进制,即2^8=256个目录 00-ff 3级目录占2位16进制,即2^8=256个目录 00-ff #配置示例: client_max_body_size 100m; #如果太大,上传时会出现下图的413错误,注意:如果php上传,还需要修改php.ini的相关配置 client_body_buffer_size 1024k; client_body_temp_path /apps/nginx/temp 1 2 2; #reload Nginx会自动创建temp目录
上传超过nginx指定client_max_body_size值会出413错误
其他配置
keepalive_disable none | browser ...; #对哪种浏览器禁用长连接
limit_except method ... { ... },仅用于location
#限制客户端使用除了指定的请求方法之外的其它方法
method:GET, HEAD, POST, PUT, DELETE,MKCOL, COPY, MOVE, OPTIONS, PROPFIND,PROPPATCH, LOCK, UNLOCK, PATCH
limit_except GET {
allow 192.168.0.0/24;
allow 192.168.7.101;
deny all;
}
#除了GET和HEAD 之外其它方法仅允许192.168.1.0/24网段主机使用
[root@s2 about]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/pc/upload
[root@s2 about]# echo "upload" > /data/nginx/html/pc/upload/index.html
[root@s2 about]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
location /upload {
root /data/cici/pc;
index index.html;
limit_except GET {
allow 172.18.200.101;
deny all;
}
}
#重启Nginx并进行测试上传文件
[root@s2 pc]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@s2 pc]#
[root@s2 pc]# curl -XPUT /etc/issue http://www.cici.net/about
curl: (3) <url> malformed
<html>
<head><title>405 Not Allowed</title></head> #Nginx已经允许但是程序未支持上传功能
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>405 Not Allowed</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
[root@s1 ~]# curl -XPUT /etc/issue http://www.cici.net/upload
curl: (3) <url> malformed
<html>
<head><title>403 Forbidden</title></head> #Nginx拒绝上传
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>403 Forbidden</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
aio on | off #是否启用asynchronous file I/O(AIO)功能,需要编译开启 linux 2.6以上内核提供以下几个系统调用来支持aio: 1、SYS_io_setup:建立aio 的context 2、SYS_io_submit: 提交I/O操作请求 3、SYS_io_getevents:获取已完成的I/O事件 4、SYS_io_cancel:取消I/O操作请求 5、SYS_io_destroy:毁销aio的context
directio size | off; #directio是直接读写文件到磁盘,启用直接I/O,默认为关闭,当文件大于等于给定大小时,例如directio 4m,可以和sebdfile结合使用,比如当大于此值使用AIO,当小于此值使用sendfile。 open_file_cache off; #是否缓存打开过的文件信息,一般加到主配置文件 open_file_cache max=N [inactive=time]; nginx可以缓存以下三种信息: (1) 文件元数据:文件的描述符、文件大小和最近一次的修改时间 (2) 打开的目录结构 (3) 没有找到的或者没有权限访问的文件的相关信息 max=N:可缓存的缓存项上限数量;达到上限后会使用LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法实现管理 inactive=time:缓存项的非活动时长,在此处指定的时长内未被命中的或命中的次数少于open_file_cache_min_uses指令所指定的次数的缓存项即为非活动项,将被删除 open_file_cache_errors on | off; 是否缓存查找时发生错误的文件一类的信息 默认值为off open_file_cache_min_uses number; open_file_cache指令的inactive参数指定的时长内,至少被命中此处指定的次数方可被归类为活动项默认值为1 open_file_cache_valid time; 缓存项有效性的检查验证频率,默认值为60s open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=60s; #最大缓存10000个文件,非活动数据超时时长60s open_file_cache_valid 60s; #每间隔60s检查一下缓存数据有效性 open_file_cache_min_uses 5; #60秒内至少被命中访问5次才被标记为活动数据 open_file_cache_errors on; #缓存错误信息 server_tokens off; #隐藏Nginx server版本。
范例:
open_file_cache max=10000 inactive=60s; #最大缓存10000个文件,非活动数据超时时长60s open_file_cache_valid 60s; #每间隔60s检查一下缓存数据有效性 open_file_cache_min_uses 5; #60秒内至少被命中访问5次才被标记为活动数据 open_file_cache_errors on; #缓存错误信息
Nginx 高级配置
Nginx 状态页
基于nginx模块ngx_http_stub_status_module实现,在编译安装nginx的时候需要添加编译参数–with-http_stub_status_module,否则配置完成之后监测会是提示语法错误。
注意: 状态页显示的是整个服务器的状态,而非虚拟主机的状态
#配置示例: location /nginx_status { stub_status; allow 192.168.0.0/16; allow 127.0.0.1; deny all; } #状态页用于输出nginx的基本状态信息: #输出信息示例: Active connections: 291 server accepts handled requests 16630948 16630948 31070465 上面三个数字分别对应accepts,handled,requests三个值 Reading: 6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106 Active connections: 当前处于活动状态的客户端连接数,包括连接等待空闲连接数。 accepts:统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经接受的客户端请求的总数。 handled:统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经处理完成的客户端请求的总数,通常等于accepts,除非有因为worker_connections限制等被拒绝的连接。 requests:统计总值,Nginx自启动后客户端发来的总的请求数。 Reading:当前状态,正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接的连接数。越小越好 Writing:当前状态,正在向客户端发送响应报文过程中的连接数。越小越好 Waiting:当前状态,正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲连接数,开启 keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于 active – (reading+writing),
说明:Active connections,Reading,Writing,Waiting这几个值很重要!
范例:分析网站当前访问量
[root@centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.com/nginx_status 2> /dev/null |awk '/Reading/{print $2,$4,$6}'
0 1 1
Nginx 第三方模块:
第三模块是对nginx 的功能扩展,第三方模块需要在编译安装Nginx 的时候使用参数–add-module=PATH指定路径添加,有的模块是由公司的开发人员针对业务需求定制开发的,有的模块是开源爱好者开发好之后上传到github进行开源的模块,nginx支持第三方模块需要从源码重新编译支持,比如开源的echo模块 https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module:
[root@s2 pc]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@s2 pc]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
location /main {
index index.html;
default_type text/html;
echo "hello world,main-->";
echo_reset_timer;
echo_location /sub1;
echo_location /sub2;
echo "took $echo_timer_elapsed sec for total.";
}
location /sub1 {
echo_sleep 1;
echo sub1;
}
location /sub2 {
echo_sleep 1;
echo sub2;
}
[root@s2 pc]# /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: [emerg] unknown directive "echo_reset_timer" in
/apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf:86
nginx: configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test failed
#解决以上报错问题
[root@s2 src]# yum install git -y
[root@s2 src]# git clone https://github.com/openresty/echo-nginx-module.git
[root@s2 src]# cd nginx-1.12.2/
[root@s2 src]# ./configure \
--prefix=/apps/nginx \
--user=nginx --group=nginx \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_v2_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-pcre \
--with-stream \
--with-stream_ssl_module \
--with-stream_realip_module \
--with-http_perl_module \
--add-module=/usr/local/src/echo-nginx-module
[root@s2 src]# make && make install
#确认语法检测通过
[root@s2 pc]# /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
#重启nginx访问测试:
[root@s2 pc]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@s2 pc]# curl http://www.cici.net/main
hello world,main-->
sub1
sub2
took 2.010 sec for total.
Nginx 变量使用
nginx的变量可以在配置文件中引用,作为功能判断或者日志等场景使用,变量可以分为内置变量和自定义变量,内置变量是由nginx模块自带,通过变量可以获取到众多的与客户端访问相关的值。
内置变量
常用内置变量
日志配置常用变量:
log_format用来设置日志格式,也就是日志文件中每条日志的格式,具体如下:
log_format name(格式名称) type(格式样式)
举例说明如下:
log_format main '$server_name remote_addr $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $uptream_status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for" $ssl_protocol $ssl_cipher $upstream_addr $request_time $upstream_response_time';
$server_name: 请求的服务器的主机名。$remote_addr: 存放了客户端的地址,注意是客户端的公网IP。变量值为 "-"时,表示空白,历史原因导致还存在
$remote_user: 已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名。$time_local: 访问的时间与时区,比如18/Jul/2012:17:00:01 +0800,时 间信息最后的"+0800"表示服务器所处时区位于UTC之后的8小时。$time_iso8601: 2017-03-30T14:23:21+08:00$request:请求的URI和HTTP协议,这是整个PV日志记录中最有用的信息,记录服务器收到一个什么样的请求$status:记录请求返回的http状态码,比如成功是200$uptream_status:upstream状态,比如成功是200$body_bytes_sent:发送给客户端的文件主体内容的大小,比如899,可以将日志每条记录中的这个值累加起来以粗略估计服务器吞吐量。$http_referer:记录从哪个页面链接访问过来的。$http_user_agent: 客户端浏览器的详细信息$proxy_add_x_forwarded_for: 此变量表示将客户端IP追加请求报文中 X-Forwarded-For首部字段,多个IP之间用逗号分隔,如果请求中没有 X-Forwarded-For,就使用$remote_addrthe “X-Forwarded-For” client request header field with the $remote_addr variable appended to it, separated by a comma. If the “X-Forwarded-For” field is not present in the client request header, the $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for variable is equal to the $remote_addr variable
$ssl_protocol:SSL协议版本,比如TLSv1。$ssl_cipher: 交换数据中的算法,比如RC4-SHA$upstream_addr: upstream 的地址,即真正提供服务的主机地址 。$request_time:整个请求的总时间。$request_body: 即可打出post的数据$upstream_response_time:请求过程中,upstream的响应时间。
其他常用变量 :
$args: 变量中存放了URL中的指令例如http://www.cici.net/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search中的id=20190221&partner=search
$document_root: 保存了针对当前资源的请求的系统根目录,如/apps/nginx/html。$document_uri: 保存了当前请求中不包含指令的URI,注意是不包含请求的指令比如 http://www.cici.net/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search会被定义为/main/index.do 。 返回结果为:/main/index.do
$host: 存放了请求的host名称$limit_rate:limit_rate 10240; echo $limit_rate;
如果nginx服务器使用limit_rate配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置, 则显示0。
$remote_port: 客户端请求Nginx服务器时随机打开的端口,这是每个客户端自己的端口。request_body_file: 做反向代理时发给后端服务器的本地资源的名称。$request_method: 请求资源的方式,GET/PUT/DELETE等$request_filename: 当前请求的资源文件的路径名称,由root或alias指 令与URI请求生成的文件绝对路径,如/apps/nginx/html/main/index.html$request_uri: 包含请求参数的原始URI,不包含主机名,相当 于:$document_uri?$args,例如: /main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=searc$scheme: 请求的协议,如ftp,https,http等。$server_protocol: 保存了客户端请求资源使用的协议的版本,如HTTP/1.0,HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2.0等。$server_addr: 保存了服务器的IP地址。$server_port: 请求的服务器的端口号。$http_<name>: name为任意请求报文首部字段,表示记录请求报文的首部字段arbitrary request header field; the last part of a variable name is the field name converted to lower case with dashes replaced by underscores #用下划线代替横线
示例: echo $http_User_Agent;
$http_cookie: 客户端的cookie信息。$cookie_<name>: name为任意请求报文首部字部cookie的key名
范例:
[root@centos8 conf.d]#vim www.conf
.....
location /echo {
echo $request;
echo $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
echo $args;
echo $document_uri;
echo $request_uri;
echo $document_root;
echo $host;
echo $request_method;
echo $request_filename;
echo $scheme;
set $test $http_host;
echo $test;
echo $http_User_Agent;
echo $http_cookie;
echo $cookie_key1;
}
}
[root@centos7 ~]#curl -b 'key1=v1;key2=v2' "http://www.cici.org/echo/index.html?id=123456&partner=search"
GET /echo/index.html?id=123456&partner=search HTTP/1.1
10.0.0.7
id=123456&partner=search
/echo/index.html
/echo/index.html?id=123456&partner=search
/data/nginx/html/pc
www.cici.org
GET
/data/nginx/html/pc/echo/index.html
http
www.cici.org
curl/7.29.0
key1=v1;key2=v2
v1
自定义变量:
假如需要自定义变量名称和值,使用指令 set $variable value; ,则方法如下:
Syntax: set $variable value; Default: — Context: server, location, if
范例:
set $name cici; echo $name; set $my_port $server_port; echo $my_port; echo "$server_name:$server_port";
Nginx 自定义访问日志
访问日志是记录客户端即用户的具体请求内容信息,全局配置模块中的error_log是记录nginx服务器运行时的日志保存路径和记录日志的level,因此有着本质的区别,而且Nginx的错误日志一般只有一个,但是访问日志可以在不同server中定义多个,定义一个日志需要使用access_log指定日志的保存路径,使用log_format指定日志的格式,格式中定义要保存的具体日志内容。
访问日志由 ngx_http_log_module 模块实现
语法格式:
Syntax: access_log path [format [buffer=size] [gzip[=level]] [flush=time] [if=condition]]; access_log off; Default: access_log logs/access.log combined; Context: http, server, location, if in location, limit_except
自定义默认格式日志
如果是要保留日志的源格式,只是添加相应的日志内容,则配置如下:
log_format nginx_format1 '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" ' '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" ' '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"' '$server_name:$server_port'; access_log logs/access.log nginx_format1; #重启nginx并访问测试日志格式 ==> /apps/nginx/logs/access.log <== 192.168.0.1 - - [22/Feb/2019:08:44:14 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 162 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:65.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/65.0" "-"www.cici.net:80
自定义json格式日志
Nginx的默认访问日志记录内容相对比较单一,默认的格式也不方便后期做日志 统计分析,生产环境中通常将nginx日志转换为json日志,然后配合使用ELK做日 志收集-统计-分析。
log_format access_json '{"@timestamp":"$time_iso8601",' '"host":"$server_addr",' '"clientip":"$remote_addr",' '"size":$body_bytes_sent,' '"responsetime":$request_time,' #总的处理时间 '"upstreamtime":"$upstream_response_time",' '"upstreamhost":"$upstream_addr",' #后端应用服务器处理时间 '"http_host":"$host",' '"uri":"$uri",' '"domain":"$host",' '"xff":"$http_x_forwarded_for",' '"referer":"$http_referer",' '"tcp_xff":"$proxy_protocol_addr",' '"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",' '"status":"$status"}'; access_log /apps/nginx/logs/access_json.log access_json; #重启Nginx并访问测试日志格式 {"@timestamp":"2019-02-22T08:55:32+08:00","host":"192.168.7.102","clientip":"192.168.0.1","size":162,"response time":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"- ","http_host":"www.cici.net","uri":"/favicon.ico","domain":"www.cici.net","xff":"-","referer":"-","tcp_xff":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:65.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/65.0","status":"404"}
其他
log_format json escape=json '{"client_ip":"$remote_addr",' '"client_user":"$remote_user",' '"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",' '"request_uri":"$request_uri",' '"status":"$status",' '"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",' '"http_referer":"$http_referer",' '"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",' '"http_x_forwarded_for":"$http_x_forwarded_for",' '"client_port":"$remote_port",' '"host":"$host",' '"http_host":"$http_host",' '"tcp_xff":"$proxy_protocol_addr",' '"request_length":"$request_length",' '"request_method":"$request_method",' '"request_time":"$request_time",' '"request_body":"$request_body",' '"scheme":"$scheme",' '"server_protocol":"$server_protocol",' '"ssl_cipher":"$ssl_cipher",' '"ssl_protocol":"$ssl_protocol",' '"time_local":"$time_local",' '"upstream_addr":"$upstream_addr",' '"upstream_response_time":"$upstream_response_time",' '"upstream_status":"$upstream_status",' '"url":"$scheme://$host$request_uri"}';
json格式的日志访问统计
#!/usr/bin/env python #coding:utf-8 status_200= [] status_404= [] with open("access_json.log") as f: for line in f.readlines(): line = eval(line) if line.get("status") == "200": status_200.append(line.get) elif line.get("status") == "404": status_404.append(line.get) else: print("状态码 ERROR") f.close() print "状态码200的有--:",len(status_200) print "状态码404的有--:",len(status_404) #保存日志文件到指定路径并进测试: [root@s2 ~]# python nginx_json.py 状态码200的有--: 1910 状态码404的有--: 13
Nginx 压缩功能
Nginx支持对指定类型的文件进行压缩然后再传输给客户端,而且压缩还可以设置压缩比例,压缩后的文件大小将比源文件显著变小,这样有助于降低出口带宽的利用率,降低企业的IT支出,不过会占用相应的CPU资源。
Nginx对文件的压缩功能是依赖于模块ngx_http_gzip_module
官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_gzip_module.html,
配置指令如下:
#启用或禁用gzip压缩,默认关闭 gzip on | off; #压缩比由低到高从1到9,默认为1 gzip_comp_level level; #禁用IE6 gzip功能 gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\."; #gzip压缩的最小文件,小于设置值的文件将不会压缩 gzip_min_length 1k; #启用压缩功能时,协议的最小版本,默认HTTP/1.1 gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1; #指定Nginx服务需要向服务器申请的缓存空间的个数*大小,默认32 4k|16 8k; gzip_buffers number size; #指明仅对哪些类型的资源执行压缩操作;默认为gzip_types text/html,不用显示指定,否则出错 gzip_types mime-type ...; #如果启用压缩,是否在响应报文首部插入“Vary: Accept-Encoding” gzip_vary on | off;
范例:开启json压缩
#重启nginx并进行访问测试压缩功能 [root@s2 pc]# cp /apps/nginx/logs/access.log /data/nginx/html/pc/test.html [root@s2 pc]# echo "test1" > /data/nginx/html/pc/test1.html #小于1k的文件测试是否会压缩 [root@s2 pc]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf gzip on; gzip_min_length 1k; gzip_buffers 64 16k; gzip_comp_level 9; gzip_types text/xml text/plain text/css application/javascript application/x-javascript application/rss+xml application/atom+xml application/xml application/json text/event-stream; gzip_vary on; #重启Nginx并访问测试: [root@s2 pc]# curl --head --compressed http://www.cici.net HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Thu, 21 Feb 2019 13:06:18 GMT Content-Type: text/html Content-Length: 7 Last-Modified: Tue, 19 Feb 2019 04:09:32 GMT Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=65 ETag: "5c6b817c-7" Accept-Ranges: bytes [root@s2 ~]# curl --head --compressed http://www.cici.net/test.html HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Fri, 22 Feb 2019 01:52:23 GMT Content-Type: text/html Last-Modified: Thu, 21 Feb 2019 10:31:18 GMT Connection: keep-alive Keep-Alive: timeout=65 Vary: Accept-Encoding ETag: W/"5c6e7df6-171109" Content-Encoding: gzip #压缩传输
浏览器 f12 访问前后对比验证不压缩与压缩访问的文件大小。
参考:
浏览器解压 Content-Encoding: gzip 的原理
整个过程是 HTTP 协议内容协商和压缩技术的一个典型应用,其核心目的是为了节省网络带宽、加快页面加载速度。
基本原理概述 当浏览器(客户端)向服务器请求一个资源(如 HTML、CSS、JS 文件)时,它会在请求头中告知服务器自己支持哪些压缩算法。如果服务器也支持其中一种算法,就会选择该算法对响应 body 进行压缩,并在响应头中声明使用了哪种压缩算法。浏览器收到响应后,会根据响应头的指示,用对应的解压算法将数据还原,然后再进行后续处理(如解析 HTML、执行 JS)。
步骤分解
1.请求:客户端(浏览器)声明支持压缩 (Request)
GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 Host: www.example.com Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br, zstd User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0...
#gzip: GNU zip 格式,是目前最广泛支持的压缩格式。 #deflate: 另一种压缩格式(注意:它通常指 zlib 封装,而非原始的 deflate 流)。 #br: Brotli,一种由 Google 开发的现代压缩算法,比 GZIP 有更高的压缩率。
2.响应:服务器压缩并声明 (Response)
服务器收到请求后,会执行以下逻辑:
- 检查 Accept-Encoding:查看浏览器支持哪些压缩格式。
- 选择算法:服务器根据自己的配置和支持情况,选择一种压缩算法(例如,选择 gzip)。通常服务器会有一个压缩优先级列表(如优先用 br,然后 gzip)。
- 压缩内容:服务器读取原始的、未压缩的资源文件(如 index.html),使用选定的算法(如 GZIP)在内存中对其进行实时压缩。注意:对于静态文件(如 .js, .css),服务器通常会预先压缩好(如生成一个 script.js.gz 文件)并缓存起来,以节省每次请求时的 CPU 开销。
- 设置响应头:服务器在返回响应时,必须添加 Content-Encoding: gzip 头,明确告知浏览器 body 的压缩格式。同时,它还会包含 Vary: Accept-Encoding 头,这指示缓存系统(如 CDN、浏览器缓存)根据不同的 Accept-Encoding 来分别缓存压缩和未压缩的版本,避免向不支持 gzip 的客户端误发压缩内容。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 Content-Encoding: gzip # 告知浏览器 body 的压缩格式 Vary: Accept-Encoding #可选 Content-Length: 1024 #压缩后的数据大小 ...
响应 Body 此时已经是压缩后的二进制数据流,而不是可读的文本。
3.解压:浏览器识别并处理 (Processing)
浏览器收到响应后:
- 检查响应头:浏览器解析响应头,发现 Content-Encoding: gzip。
- 启动对应解压器:浏览器内核(如 Chrome 的 Blink、Firefox 的 Gecko)中的网络栈会自动识别这个头,并启动内置的 GZIP 解压算法。
- 透明解压:解压器读取压缩的二进制 Body 数据流,将其解压还原为原始的、未压缩的格式(纯文本的 HTML、CSS 等)。这个过程对开发者是完全透明的,你无法在 JavaScript 中直接接触到压缩后的数据。
4.交付:将解压后的内容交给渲染引擎 (Delivery) 解压完成后,浏览器会将解压得到的原始文本内容交给相应的处理器:
- 如果是 text/html,则交给 HTML 解析器构建 DOM 树。
- 如果是 application/javascript,则交给 JavaScript 引擎执行。
- 如果是 text/css,则交给 CSS 解析器构建 CSSOM。
范例:Nginx
# 1.将JSON文件压缩为gzip格式 gzip -9 -k data.json #压缩并保留原文件 # 2压缩后的.json.gz文件上传到Nginx的Web目录 # 3配置nginx,浏览访问gzip格式文件,自动解压并以json方式展示 location ~* \.json\.gz$ { add_header Content-Type application/json; # 告知浏览器body类型,浏览器可以使用对应类型解析器 add_header Content-Encoding gzip; # 告知浏览body的压缩格式 root /usr/local/nginx/html/; }
http_gzip_static_module 预压缩
| 特性 | http_gzip_module (动态压缩) | http_gzip_static_module (预压缩) |
|---|---|---|
| CPU 使用率 | 高(每次请求都压缩) | 极低(直接发送现成文件) |
| 响应速度 | 较快(有压缩时间开销) | 极快(无压缩开销,纯磁盘读取) |
| 压缩比 | 一般(为性能平衡,级别较低) | 可最大化(可离线用最高级别压缩) |
| 适用场景 | 所有内容(静态+动态) | 仅限静态文件(如 .js, .css, .html, .txt) |
| 配置难度 | 简单(默认) | 需额外启用模块和配置 |
| 文件管理 | 无需管理 | 需预生成并维护 .gz 文件 |
这个模块需要单独启用,它采用了一种“预编译”的思路来优化性能。
- 需要编译时增加
--with-http_gzip_static_module
工作原理:
- 你提前使用命令行工具(如 gzip)将静态文件(如 style.css)压缩好,生成一个对应的 .gz 文件(style.css.gz),并放在原始文件所在的同一目录下。
- 当客户端请求 style.css 时,Nginx 会先检查客户端是否支持 Gzip(通过 Accept-Encoding 头)。
- 如果支持,Nginx 不会去读 style.css,而是直接去寻找磁盘上是否已经存在 style.css.gz 这个预压缩文件。
- 如果找到,则直接发送这个 .gz 文件给客户端,并添加 Content-Encoding: gzip 头。
优点:
- 极致性能,接近零 CPU 开销:省去了实时压缩的计算过程,大大降低了服务器 CPU 负载。Nginx 只需要进行简单的磁盘 I/O 读取并发送即可,这是它的强项。
- 最佳压缩比:你可以使用最高级别(最慢)的压缩算法(如 gzip -9)在离线时压缩文件,从而得到比 Nginx 默认常规压缩级别(通常为 gzip_comp_level 6)更小的文件体积,而完全不影响服务器运行时性能。
- 避免坏请求:如果客户端不支持 Gzip(请求头中没有 Accept-Encoding: gzip),Nginx 会自动回退到发送原始的 .css 文件。行为与动态压缩完全一致。
句法: gzip_static on | off | always;
默认: gzip_static off;
语境: http,server,location
'on':优先使用预压缩文件(.gz),如果不存在且客户端支持gzip,则可能进行动态压缩(版本依赖)
范例:json文件的gzip压缩文件展示
# 1.将JSON文件压缩为gzip格式 # 2压缩后的.json.gz文件上传到Nginx的Web目录 # 3配置nginx # 启用动态gzip压缩 (作为回退方案) gzip on; # 设置动态压缩的最小文件大小,小于该值的文件不压缩(单位字节) gzip_min_length 1024; # 设置动态压缩的压缩级别(1-9)。级别越高压缩比越好,但CPU消耗越大。 # 注意:此设置不影响预压缩文件,预压缩文件的级别在生成时确定。 gzip_comp_level 6; # 设置哪些MIME类型的文件需要被压缩(动态和静态都参考此值) # 对于预压缩模块,如果请求的文件类型不在此列表,即使有.gz文件也不会发送。 gzip_types text/plain text/css text/xml text/javascript application/javascript application/xml+rss application/json application/xml application/xhtml+xml image/svg+xml; # 配置代理请求的压缩行为。建议设置为“任何” gzip_proxied any; # 禁用对IE6等古老浏览器的gzip压缩(它们对Gzip支持很差) gzip_disable "msie6"; # 建议添加:告知代理服务器根据Accept-Encoding头缓存不同版本 # 避免将gzip版本缓存后发给不支持gzip的客户端 gzip_vary on; location ~* \.json$ { # 启用 gzip_static 模块。推荐使用 'on' # 'on':优先使用预压缩文件(.gz),如果不存在且客户端支持gzip,则可能进行动态压缩(版本依赖) # 'always':无论客户端是否支持gzip,都只发送.gz文件(风险高,不推荐) gzip_static on; # 告知客户端(浏览器)解析类型 add_header Content-Type application/json; root /usr/local/nginx/html/; } # 可选,支持压缩文件直接展示 location ~* \.json\.gz$ { # 告知客户端(浏览器)解析类型,及gzip压缩算法 add_header Content-Type application/json; add_header Content-Encoding gzip; root /usr/local/nginx/html/; # 移除.gz扩展名以便浏览器正确保存文件 #if ($request_uri ~ ^/(.*)\.gz$) { # add_header Content-Disposition "inline; filename=$1"; #} }
访问 https://xxx.com/data.json, 会优先使用预压缩文件data.json.gz,如果不存在,则使用动态压缩。
https 功能
Web网站的登录页面都是使用https加密传输的,加密数据以保障数据的安全,
HTTPS能够加密信息,以免敏感信息被第三方获取,所以很多银行网站或电子邮
箱等等安全级别较高的服务都会采用HTTPS协议,HTTPS其实是有两部分组成:
HTTP + SSL / TLS ,也就是在HTTP上又加了一层处理加密信息的模块。服务
端和客户端的信息传输都会通过TLS进行加密,所以传输的数据都是加密后的数
据。
https 实现过程如下:
客户端发起HTTPS请求:
客户端访问某个web端的https地址,一般都是443端口
服务端的配置:
采用https协议的服务器必须要有一套证书,可以通过一些组织申请,也可以 自己制作,目前国内很多网站都自己做的,当你访问一个网站的时候提示证 书不可信任就表示证书是自己做的,证书就是一个公钥和私钥匙,就像一把 锁和钥匙,正常情况下只有你的钥匙可以打开你的锁,你可以把这个送给别 人让他锁住一个箱子,里面放满了钱或秘密,别人不知道里面放了什么而且 别人也打不开,只有你的钥匙是可以打开的。
传送证书:
服务端给客户端传递证书,其实就是公钥,里面包含了很多信息,例如证书得到颁发机构、过期时间等等。
客户端解析证书:
这部分工作是有客户端完成的,首先回验证公钥的有效性,比如颁发机构、 过期时间等等,如果发现异常则会弹出一个警告框提示证书可能存在问题, 如果证书没有问题就生成一个随机值,然后用证书对该随机值进行加密,就 像2步骤所说把随机值锁起来,不让别人看到。
传送4步骤的加密数据:
就是将用证书加密后的随机值传递给服务器,目的就是为了让服务器得到这 个随机值,以后客户端和服务端的通信就可以通过这个随机值进行加密解密 了。
服务端解密信息:
服务端用私钥解密5步骤加密后的随机值之后,得到了客户端传过来的随机值 (私钥),然后把内容通过该值进行对称加密,对称加密就是将信息和私钥通 过算法混合在一起,这样除非你知道私钥,不然是无法获取其内部的内容, 而正好客户端和服务端都知道这个私钥,所以只要机密算法够复杂就可以保 证数据的安全性。
传输加密后的信息:
服务端将用私钥加密后的数据传递给客户端,在客户端可以被还原出原数据内容。
客户端解密信息:
客户端用之前生成的私钥获解密服务端传递过来的数据,由于数据一直是加密的,因此即使第三方获取到数据也无法知道其详细内容。
https 配置参数:
nginx 的https 功能基于模块ngx_http_ssl_module实现,因此如果是编译安装的nginx要使用参数ngx_http_ssl_module开启ssl功能,但是作为nginx的核心功能,yum安装的nginx默认就是开启的,编译安装nginx需要指定编译参数–with-http_ssl_module开启
官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_ssl_module.html
配置参数如下:
ssl on | off; #为指定的虚拟主机配置是否启用ssl功能,此功能在1.15.0废弃,使用listen [ssl]替代。 ssl_certificate /path/to/file; #当前虚拟主机使用使用的公钥文件,一般是crt文件 ssl_certificate_key /path/to/file; #当前虚拟主机使用的私钥文件,一般是key文件 ssl_protocols [SSLv2] [SSLv3] [TLSv1] [TLSv1.1] [TLSv1.2]; #支持ssl协议版本,早期为ssl,现在是TSL,默认为后三个 ssl_session_cache off | none | [builtin[:size]] [shared:name:size]; #配置ssl缓存 off: 关闭缓存 none: 通知客户端支持ssl session cache,但实际不支持 builtin[:size]:使用OpenSSL内建缓存,为每worker进程私有 [shared:name:size]:在各worker之间使用一个共享的缓存,需要定义一个缓存名称和缓存空间大小,一兆可以存储4000个会话信息,多个虚拟主机可以使用相同的缓存名称。 ssl_session_timeout time;#客户端连接可以复用ssl session cache中缓存的有效时长,默认5m
自签名证书
#自签名CA证书 [root@s2 ~]# cd /apps/nginx/ [root@s2 nginx]# mkdir certs [root@s2 nginx]# cd certs/ [root@s2 nginx]# openssl req -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -sha256 -keyout ca.key -x509 -days 3650 -out ca.crt #自签名CA证书 Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key .................++ ..... Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN #国家代码,https://country-code.cl/ State or Province Name (full name) []:BeiJing #省份 Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:Beijing #城市名称 Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:cici.Ltd #公司名称 Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:cici #部门 Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:cici.ca #通用名称 Email Address []:[email protected] #邮箱 [root@s2 certs]# ll ca.crt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2118 Feb 22 12:10 ca.crt #自制key和csr文件 [root@s2 certs]# openssl req -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -sha256 -keyout www.cici.net.key -out www.cici.net.csr Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key ........................................................................++...... Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN State or Province Name (full name) []:BeiJing Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BeiJing Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:cici.net Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:cici.net Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:www.cici.net Email Address []:[email protected] Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []: An optional company name []: [root@s2 certs]# ll total 16 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2118 Feb 22 12:10 ca.crt -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3272 Feb 22 12:10 ca.key -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1760 Feb 22 12:18 www.cici.net.csr -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 3272 Feb 22 12:18 www.cici.net.key #签发证书 [root@s2 certs]# openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in www.cici.net.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out www.cici.net.crt Signature ok subject=/C=CN/ST=BeiJing/L=BeiJing/O=cici.net/OU=cici.net/CN=www.cici.net/emailAd dress[email protected] Getting CA Private Key #验证证书内容 [root@s2 certs]# openssl x509 -in www.cici.net.crt -noout -text Certificate: Data: Version: 1 (0x0) Serial Number: bb:76:ea:fe:f4:04:ac:06 Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: C=CN, ST=BeiJing, L=Beijing, O=cici.Ltd, OU=cici, CN=cici.ca/[email protected] Validity Not Before: Feb 22 06:14:03 2019 GMT Not After : Feb 22 06:14:03 2020 GMT Subject: C=CN, ST=BeiJing, L=BeiJing, O=cici.net, OU=cici.net, CN=www.cici.net/[email protected] Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption Public-Key: (4096 bit)
https 配置
listen 80; listen 443 ssl; ssl_certificate /apps/nginx/certs/www.cici.net.crt; ssl_certificate_key /apps/nginx/certs/www.cici.net.key; ssl_session_cache shared:sslcache:20m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; #重启Nginx并访问验证
访问
实现多域名HTTPS
Nginx支持基于单个IP实现多域名的功能,并且还支持单IP多域名的基础之上实 现HTTPS,其实是基于Nginx的SNI(Server Name Indication)功能实现,SNI是 为了解决一个Nginx服务器内使用一个IP绑定多个域名和证书的功能,其具体功 能是客户端在连接到服务器建立SSL链接之前先发送要访问站点的域名 (Hostname),这样服务器再根据这个域名返回给客户端一个合适的证书。
范例: SNI功能
[root@centos8 ~]#nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.18.0 built by gcc 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5) (GCC) built with OpenSSL 1.1.1c FIPS 28 May 2019 TLS SNI support enabled configure arguments: --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with- http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with- http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module --add-module=../echo-nginx- module/
范例:
#制作key和csr文件 [root@s2 certs]# openssl req -newkey rsa:4096 -nodes -sha256 -keyout mobile.cici.net.key -out mobile.cici.net.csr Generating a 4096 bit RSA private key .......... Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:CN State or Province Name (full name) []:BeiJing Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:BeiJing Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:cici Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:cici Common Name (eg, your name or your server's hostname) []:mobile.cici.net Email Address []:[email protected] Please enter the following 'extra' attributes to be sent with your certificate request A challenge password []: An optional company name []: #签名证书 [root@s2 certs]# openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -in mobile.cici.net.csr -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial -out mobile.cici.net.crt Signature ok subject=/C=CN/ST=BeiJing/L=BeiJing/O=cici/OU=cici/CN=mobile.cici.net/emailAddress [email protected] Getting CA Private Key #验证证书内容 [root@s2 certs]# openssl x509 -in mobile.cici.net.crt -noout -text Certificate: Data: Version: 1 (0x0) Serial Number: bb:76:ea:fe:f4:04:ac:07 Signature Algorithm: sha256WithRSAEncryption Issuer: C=CN, ST=BeiJing, L=Beijing, O=cici.Ltd, OU=cici, CN=cici.ca/[email protected] Validity Not Before: Feb 22 13:50:43 2019 GMT Not After : Feb 19 13:50:43 2029 GMT Subject: C=CN, ST=BeiJing, L=BeiJing, O=cici, OU=cici, CN=mobile.cici.net/[email protected] Subject Public Key Info: Public Key Algorithm: rsaEncryption Public-Key: (4096 bit) .............. #合并证书文件 [root@centos8 certs]#cat mobile.cici.net.crt ca.crt > mobile.cici.net.pem #Nginx 配置 [root@s2 certs]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/mobile.conf server { listen 80; server_name mobile.cici.net; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } location /linux38 { root /data/nginx/mobile/html; index index.html index.htm; } location /python { root /data/nginx/mobile/html; index index.html index.htm; } } server { listen 443 ssl; server_name mobile.cici.net; ssl_certificate /apps/nginx/certs/mobile.cici.net.pem; ssl_certificate_key /apps/nginx/certs/mobile.cici.net.key; ssl_session_cache shared:sslcache:20m; ssl_session_timeout 10m; location / { root html; index index.html index.htm; } }
关于favicon.ico:
favicon.ico 文件是浏览器收藏网址时显示的图标,当客户端使用浏览器问页面时,浏览器会自己主动发起请求获取页面的favicon.ico文件,但是当浏览器请求的favicon.ico文件不存在时,服务器会记录404日志,而且浏览器也会显示404报错。
解决办法:
#一:服务器不记录访问日志: #location = /favicon.ico { #log_not_found off; #access_log off; #} #二:将图标保存到指定目录访问: #location ~ ^/favicon\.ico$ { location = /favicon.ico { root /data/nginx/html/pc/images; expires 90d; #设置文件过期时间 }
安全选项
隐藏Nginx版本号
更改nginx源码信息并重新编译Nginx
# vim src/http/ngx_http_header_filter_module.c 49 static u_char ngx_http_server_string[] = "Server: linux38" CRLF; #定义响应报文中的server字段信息
升级OpenSSL版本
心脏出血(英语:Heartbleed),也简称为心血漏洞,是一个出现在加密程序库 OpenSSL的安全漏洞,该程序库广泛用于实现互联网的传输层安全(TLS)协议。 它于2012年被引入了软件中,2014年4月首次向公众披露。只要使用的是存在缺 陷的OpenSSL实例,无论是服务器还是客户端,都可能因此而受到攻击。此问题 的原因是在实现TLS的心跳扩展时没有对输入进行适当验证(缺少边界检查), 因此漏洞的名称来源于“心跳”(heartbeat)。该程序错误属于缓冲区过读, 即可以读取的数据比应该允许读取的还多。
范例:
#准备OpenSSL源码包: cd /usr/local/src wget https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz tar xvf openssl-1.1.1h.tar.gz #编译安装Nginx并制定新版本OpenSSL路径: # cd /usr/local/src/nginx-1.16.1/ #./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --withhttp_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --withstream_realip_module --with-select_module --with-file-aio --addmodule=/usr/local/src/echo-nginx-module --with-openssl=/usr/local/src/openssl-1.1.1h # make && make install 验证并启动Nginx: # /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful #systemctl restart nginx #nginx -V
实现 HSTS
官方文档: https://www.nginx.com/blog/http-strict-transport-security-hsts-and-nginx/
注意: 配置rewrite才能实现http跳转到https
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.cici.org;
add_header Strict-Transport-Security "max-age=31536000; includeSubDomains" always;
location / {
if ( $scheme = http ) {
rewrite ^/(.*)$ https://www.cici.org/$1 redirect;
}
.....
}
}
其他
自动刷新 Dns 缓存
nginx 中 proxy_pass 使用的是域名,域名解析的 ip 会被固定到 nginx 内部,一但发生解析记录变化就访问不了,这里添加 resover 来解决此问题。
server {
listen 8080;
server_name localhost;
resolver 114.114.114.114 223.5.5.5 valid=3600s;
resolver_timeout 3s;
location / {
proxy_pass http://mydomain.com;
}
}
nginx开启IPV6支持配置
IPV4日益稀缺,ipv6已经慢慢走上日程,待ipv6在国内普及,使用nginx配置ipv6那是肯定的,看看如何让nginx支持ipv6以及配置.
查看nginx是否支持ipv6
# /usr/local/nginx-1.7.0/sbin/nginx -V nginx version: nginx/1.7.0 built by gcc 4.4.7 20120313 (Red Hat 4.4.7-3) (GCC) configure arguments: --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.7.0 --with-http_stub_status_module
没有出现–with-ipv6,说明当前的nginx不支持ipv6,所以我们需要重新编译nginx,配置里面增加–with-ipv6,具体怎么安装,我不在啰嗦了。
同时监听IPV4和IPV6
server {
....
listen [::]:80;
...
}
只监听IPV6
server {
....
listen [::]:80 default ipv6only=on;
...
}
监听指定IPV6地址
server {
....
listen [3608:f0f0:3002:31::1]:80;
...
}
重启nginx
/usr/local/nginx-1.7.0/sbin/nginx -s reload
nginx添加自定义header
location / {
add_header X-UA-Compatible 'IE=Edge,chrome=1'; # 这里是自定义头
root www/htdocs;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
其中,X-UA-Compatible是名称,IE=Edge,chrome=1是值,可以随意自定义。在html的<head></head>标签中可以添加http请求: <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=Edge,chrome=1">
添加完之后重启nginx和浏览器,然后打开添加了自定义head的页面查看效果
nginx 日志 打印自定 header 头
在nginx.conf 中的格式化日志时在 自已的header 名字前加 http_ 如,以 mac 为自定义的 header 需要在配置文件中写成 http_mac
Nginx Rewrite相关功能:
Nginx服务器利用ngx_http_rewrite_module模块解析和处理rewrite请求,此功 能依靠 PCRE(perl compatible regularex pression),因此编译之前要安装 PCRE库,rewrite是nginx服务器的重要功能之一,用于实现URL的重写,URL的重 写是非常有用的功能,比如它可以在我们改变网站结构之后,不需要客户端修改 原来的书签,也无需其他网站修改我们的链接,就可以设置为访问,另外还可以 在一定程度上提高网站的安全性。
ngx_http_rewrite_module模块指令
if指令
用于条件匹配判断,并根据条件判断结果选择不同的Nginx配置,可以配置在 server或location块中进行配置,Nginx的if语法仅能使用if做单次判断,不支 持使用if else或者if elif这样的多重判断,用法如下:
if (条件匹配) {
action
}
使用正则表达式对变量进行匹配,匹配成功时if指令认为条件为true,否则认为false,变量与表达式之间使用以下符号链接:
=: #比较变量和字符串是否相等,相等时if指令认为该条件为true,反之为false。 !=: #比较变量和字符串是否不相等,不相等时if指令认为条件为true,反之为false。 ~: #表示在匹配过程中区分大小写字符,(可以通过正则表达式匹配),满足匹配条件为真,不满足为假。 !~:#为区分大小写字符且匹配结果不匹配,不满足为真,满足为假。 ~*: #表示在匹配过程中不区分大小写字符,(可以通过正则表达式匹配),满足匹配条件为真,不满足为假。 !~*: #为不区分大小字符且匹配结果不匹配,满足为假,不满足为真。 -f 和 ! -f: #判断请求的文件是否存在和是否不存在 -d 和 ! -d: #判断请求的目录是否存在和是否不存在。 -x 和 ! -x: #判断文件是否可执行和是否不可执行。 -e 和 ! -e: #判断请求的文件或目录是否存在和是否不存在(包括文件,目录,软链接)。 #注意: #如果$变量的值为空字符串或0,则if指令认为该条件为false,其他条件为true。 #nginx 1.0.1之前$变量的值如果以0开头的任意字符串会返回false #实例-1: location /main { index index.html; default_type text/html; if ( $scheme = http ){ echo "if-----> $scheme"; } if ( $scheme = https ){ echo "if ----> $scheme"; } #if (-f $request_filename) { # echo "file is exist"; #} if (!-f $request_filename) { echo "file is not exist"; #return 409; } }
set指令
指定key并给其定义一个变量,变量可以调用Nginx内置变量赋值给key,另外set 定义格式为set $key value,value可以是text, variables和两者的组合。
location /main {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
default_type text/html;
set $name cici;
echo $name;
set $my_port $server_port;
echo $my_port;
}
break 指令:
用于中断当前相同作用域(location)中的其他Nginx配置,与该指令处于同一作 用域的Nginx配置中,位于它前面的配置生效,位于后面的 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块中指令就不再执行,Nginx服务器在根据配置处 理请求的过程中遇到该指令的时候,回到上一层作用域继续向下读取配置,该指 令可以在server块和locationif块中使用
注意: 如果break指令在location块中后续指令还会继续执行,只是不执行 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块的指令,其它指令还会执行
使用语法如下:
if ($slow) { limit_rate 10k; break; } location /main { root /data/nginx/html/pc; index index.html; default_type text/html; set $name cici; echo $name; break; #location块中break后面指令还会执行 set $my_port $server_port; echo $my_port; }
return 指令
return用于完成对请求的处理,并直接向客户端返回响应状态码,比如:可以指 定重定向URL(对于特殊重定向状态码,301/302等) 或者是指定提示文本内容(对 于特殊状态码403/500等),处于此指令后的所有配置都将不被执行,return可以 在server、if 和 location块进行配置
语法格式:
return code; #返回给客户端指定的HTTP状态码 return code [text]; #返回给客户端的状态码及响应报文的实体内容,可以调用变量,其中text如果有空格,需要用单或双引号 return code URL; #返回给客户端的URL地址
范例:
location /main {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
default_type text/html;
index index.html;
if ( $scheme = http ){
#return 666;
#return 666 "not allow http";
#return 301 http://www.baidu.com;
return 500 "service error";
echo "if-----> $scheme"; #return后面的将不再执行
}
if ( $scheme = https ){
echo "if ----> $scheme";
}
}
rewrite_log 指令:
设置是否开启记录ngx_http_rewrite_module模块日志记录到error_log日志文件当中,可以配置在http、server、location或if当中,需要日志级别为notice 。
location /main {
index index.html;
default_type text/html;
set $name cici;
echo $name;
rewrite_log on;
break;
set $my_port $server_port;
echo $my_port;
}
#重启nginx,访问并验证error_log:
[root@s2 ~]# tail -f /apps/nginx/logs/error.log
2019/02/27 15:10:02 [warn] 5815#0: *3 using uninitialized "my_port" variable, client:192.168.0.1, server: www.cici.net, request: "GET /main HTTP/1.1", host:"www.cici.net"
rewrite 指令:
通过正则表达式的匹配来改变URI,可以同时存在一个或多个指令,按照顺序依次对URI进行匹配,rewrite主要是针对用户请求的URL或者是URI做具体处理
官方文档: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_rewrite_module.html#rewrite
rewrite可以配置在 server、location、if
语法格式 :
rewrite regex replacement [flag];
rewrite将用户请求的URI基于regex所描述的模式进行检查,匹配到时将其替换为表达式指定的新的URI
以下是URL和URI的具体介绍:
- URI(universal resource identifier):通用资源标识符,标识一个资源的路 径,可以不带协议。
URL(uniform resource location):统一资源定位符,是用于在Internet中描 述资源的字符串,是URI的子集,主要包括传输协议(scheme)、主机(IP、端口 号或者域名)和资源具体地址(目录和文件名)等三部分
一般格式为scheme://主机名[:端口号][/资源路径],如: http://www.a.com:8080/path/file/index.html就是一个URL路径,URL必须带 访问协议。
每个URL都是一个URI,但是URI不都是URL。
范例:
http://example.org:8080/path/to/resource.txt #URI/URL ftp://example.org/resource.txt #URI/URL /absolute/path/to/resource.txt #URI
注意:如果在同一级配置块中存在多个rewrite规则,那么会自上而下逐个检查; 被某条件规则替换完成后,会重新一轮的替换检查,隐含有循环机制,但不超过 10次;如果超过,提示500响应码,[flag]所表示的标志位用于控制此循环机制
如果替换后的URL是以http://或https://开头,则替换结果会直接以重定向 返回给客户端, 即永久重定向 301
正则表达式格式
. #匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 \w #匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字 \s #匹配任意的空白符 \d #匹配数字 \b #匹配单词的开始或结束 ^ #匹配字付串的开始 $ #匹配字符串的结束 * #匹配重复零次或更多次 + #匹配重复一次或更多次 ? #匹配重复零次或一次 (n) #匹配重复n次 {n,} #匹配重复n次或更多次 {n,m} #匹配重复n到m次 *? #匹配重复任意次,但尽可能少重复 +? #匹配重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复 ?? #匹配重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复 {n,m}? #匹配重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复 {n,}? #匹配重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复 \W #匹配任意不是字母,数字,下划线,汉字的字符 \S #匹配任意不是空白符的字符 \D #匹配任意非数字的字符 \B #匹配不是单词开头或结束的位置 [^x] #匹配除了x以外的任意字符 [^cici] #匹配除了cici 这几个字母以外的任意字符
rewrite flag使用介绍
利用nginx的rewrite的指令,可以实现url的重新跳转,rewrtie有四种不同的 flag,分别是redirect(临时重定向302)、permanent(永久重定向301)、break和 last。其中前两种是跳转型的flag,后两种是代理型
- 跳转型指由客户端浏览器重新对新地址进行请求
- 代理型是在WEB服务器内部实现跳转
rewrite 格式
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag]; #通过正则表达式处理用户请求并返回替换后的数据包。 Default: — Context: server, location, if
flag说明
- redirect;
- 临时重定向,重写完成后以临时重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端,由客户端重新发起请求;
- 使用相对路径,或者
http://或https://开头,状态码:302
- permanent;
- 重写完成后以永久重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端,由客户端重新发起请求,状态码:301
- break;
- 重写完成后,停止对当前URL在当前location中后续的其它重写操作,而后直接跳转至重写规则配置块之后的其它配置;结束循环
- 建议在location中使用
- 适用于一个URL一次重写
- last;
- 重写完成后,停止对当前URI在当前location中后续的其它重写操作,而后对新的URL启动新一轮重写检查
- 不建议在location中使用
- 适用于一个URL多次重写,要注意避免出现超过十次以及URL重写后返回错误的给用户
rewrite案例-域名永久与临时重定向
要求:因业务需要,将访问源域名 www.cici.net的请求永久重定向到 www.cici.com 。
临时重定向不会缓存域名解析记录(A记录),但是永久重定向会缓存。
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
rewrite / http://www.cici.com permanent;
#rewrite / http://www.cici.com redirect;
}
#重启Nginx并访问域名www.cici.net进行测试
永久重定向301
域名永久重定向,京东早期的域名 www.360buy.com由于与360公司类似,于是后 期永久重定向到了 www.jd.com,永久重定向会缓存DNS解析记录。
临时重定向302
域名临时重定向,告诉浏览器域名不是固定重定向到当前目标域名,后期可能随 时会更改,因此浏览器不会缓存当前域名的解析记录,而浏览器会缓存永久重定 向的DNS解析记录,这也是临时重定向与永久重定向最大的本质区别。
rewrite案例 break 与 last
大部分场合下,break单次重写就足够了
要求:访问about的请求被转发至images,而访问images传递请求再次被转发至images1,以此测试last和break分别有什么区别:
break案例
break测试案例:
- 当客户端访问break的时候,测试通过rewrite将URL重写为test1,然后再通过rewrite将test1重写为test2,测试两条write规则最终哪一条生效,并且测试重写后的URL会不会到其他 location重新匹配。
#Nginx配置: location /break { #return 666 "break"; root /data/nginx; index index.html; rewrite ^/break/(.*) /test1/$1 break; #break匹配成功后不再向下匹配,也不会跳转到其他的location,即直接结束匹配并给客户端返回结果数据。 rewrite ^/test1/(.*) /test2/$1 break; #break不会匹配后面的rewrite规则也不匹配其他location } location = /test1 { return 999 "new test1"; #index index.html; #root /data/nginx; } location = /test2 { return 666 "new test2"; #root /opt/nginx; #index index.html; } 创建资源路径: # mkdir /data/nginx/break # mkdir /data/nginx/test1 # mkdir /data/nginx/test2 # cat /data/nginx/break/index.html break # cat /data/nginx/test1/index.html test1 # cat /data/nginx/test2/index.html test2 # /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t # /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload break访问测试: [root@s3 ~]# curl -L http://www.cici.net/break/index.html test1 #最终的结果不会超出break的location而且不会继续匹配当前location后续的write规则,而且直接返回数据给客户端。
break适用于不改变客户端访问方式,但是要将访问的目的URL做单次重写的场景,比如有V1/V2两个版本的网站前端页面并存,旧版本的网站数据已经保存到了statics不能丢失,但是要将访问新版本的资源重写到新的静态资源路径到新的目录static:
location /statics {
root /data/nginx;
index index.html;
rewrite ^/statics/(.*) /static/$1 break;
}
last案例
last:对某个location的URL匹配成功后会停止当前location的后续rewrite规则,并结束当前location,然后将匹配生成的新URL跳转至其他location继续匹配,直到没有location可匹配后将最后一次location的数据返回给客户端。
last适用于要不改变客户端访方式但是需做多次目的URL重写的场景,场景不是很多。
location /test1 {
#return 999 "new test1";
index index.html;
root /data/nginx;
rewrite ^/test1/(.*) /test2/$1 last;
}
location /test2 {
return 666 "new test2";
#root /opt/nginx;
#index index.html;
}
location /last {
root /data/nginx;
index index.html;
rewrite ^/last/(.*) /test1/$1 last;
#rewrite ^/test1/(.*) /test2/$1 last; #如果第一条rewrite规则匹配成功则不执行本条,否则执行本条rewrite规则。
}
last访问测试:
[root@s3 ~]# curl -L http://www.cici.net/last/index.html
new test2 #会匹配多个location,直到最终全部匹配完成,返回最后一个location的匹配结果给客户端。
rewrite案例-自动跳转https
要求:基于通信安全考虑公司网站要求全站https,因此要求将在不影响用户请求的情况下将http请求全部自动跳转至https,另外也可以实现部分location跳转
server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen 80;
ssl_certificate /apps/nginx/certs/www.cici.net.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /apps/nginx/certs/www.cici.net.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:sslcache:20m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
if ($scheme = http ){ #未加条件判断,会导致死循环
rewrite / https://www.cici.net permanent;
}
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
[root@s3 ~]# curl -L -k -i https://www.cici.net/
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx
Date: Fri, 15 Mar 2019 19:53:07 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 7
Last-Modified: Thu, 14 Mar 2019 14:54:50 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Keep-Alive: timeout=60
ETag: "5c8a6b3a-7"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
pc web
rewrite案例-判断文件是否存在
要求:当用户访问到公司网站的时输入了一个错误的URL,可以将用户重定向至官网首页。
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
if (!-e $request_filename) {
#return 404 "linux35";
rewrite (.*) http://www.cici.net/index.html; #实现客户端浏览器的302跳转
#rewrite .* /index.html; #web服务器内部跳转
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
其他案例
#案例1:如果客户端浏览器包含MSIE,则rewrite客户端请求到/msie目录下 if ( $http_user_agent ~ MSIE){ rewrite ^(.*)$ /msie/$1 break; } #案例2: 更换目录访问方式,目录转换为对象存储形式 #要求: #/20200106/static ->/static?id=20200106 #/20200123/image ->/image?id=20200123 rewrite ^/(\d+)/(.+)/ /$2?id=$l last; #案例3:多目录转换访问方式 #要求: www.cici.com/images/20200106/1.jpg => www.cici.com/index.do?name=images&dir=20200106=&file=1.jpg #规则配置: if ($host ~* (.*)\.cici\.com) { rewrite ^/(.*)/(\d+)/(.*)$ /index.do?name=$1&dir=$2&file=$3 last;
Nginx防盗链
防盗链基于客户端携带的referer实现,referer是记录打开一个页面之前记录是从哪个页面跳转过来的标记信息,如果别人只链接了自己网站图片或某个单独的资源,而不是打开了网站的整个页面,这就是盗链。
referer就是之前的那个网站域名,正常的referer信息有以下几种:
- none:请求报文首部没有referer首部,比如用户直接在浏览器输入域名访问web网站,就没有referer信息。
- blocked:请求报文有referer首部,但无有效值,比如为空。
- server_names:referer首部中包含本主机名及即nginx 监听的server_name。
- arbitrary_string:自定义指定字符串,但可使用*作通配符。
- regular expression:被指定的正则表达式模式匹配到的字符串,要使用~开头,例如: ~.*\.cici\.com。
正常通过搜索引擎搜索web 网站并访问该网站的referer信息如下:
#通过搜索引擎访问web网站的referer信息: ==> /apps/nginx/logs/access_json.log <== {"@timestamp":"2019-02-28T13:58:46+08:00","host":"192.168.7.102","clientip":"192.168.0.1","siz e":0,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"www.cici.net","uri":"/index.html","domain":"www.cici.net","xff":"-","referer":"https://www.baidu.com/s?ie=utf- 8&f=8&rsv_bp=1&rsv_idx=1&tn=baidu&wd=www.cici.net&oq=www.ncici.net&rsv_pq=d63060680002eb69&rsv_t=de01TWnmyTdcJqph7SfI1hXgXLJxSSfUPcQ3QkWdJk%2FLNrN95ih3XOhbRs4&rqlang=cn&rsv_enter=1&inputT=321&rsv_sug3=41&rsv_sug2=0&rsv_sug4=1626","tcp_xff":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36","status":"304"}
实现 web 盗链:
在一个web 站点盗链另一个站点的资源信息,比如图片、视频等。
[root@s2 conf.d]# pwd
/apps/nginx/conf/conf.d
[root@s2 conf.d]# cat ncici.net.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.ncici.net;
location / {
index index.html;
root "/data/nginx/html/ncici";
access_log /apps/nginx/logs/www.ncici.net.log access_json;
}
}
#准备盗链web页面:
[root@s2 conf.d]# mkdir /data/nginx/html/ncici
[root@s2 conf.d]# cat /data/nginx/html/ncici/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>盗链页面</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://www.cici.net">测试盗链</a>
<img src="http://www.cici.net/images/1.jpg">
</body>
</html>
#重启Nginx并访问http://www.ncici.net/测试
#验证两个域名的日志,是否会在被盗连的web站点的日志中出现以下盗链日志信息:
==> /apps/nginx/logs/access_json.log <==
{"@timestamp":"2019-02-28T13:27:37+08:00","host":"192.168.7.102","clientip":"192.168.0.1","size":0,"responsetime":0.000,"upstreamtime":"-","upstreamhost":"-","http_host":"www.cici.net","uri":"/images/1.jpg","domain":"www.cici.net","xff":"-","referer":"http://www.ncici.net/","tcp_xff":"","http_user_agent":"Mozilla/5.0(Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; rv:65.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/65.0","status":"304"}
实现防盗链:
基于访问安全考虑,nginx支持通过ungx_http_referer_module模块,检查访问请求的referer信息是否有效实现防盗链功能
官方文档: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_referer_module.html
定义方式如下:
[root@s2 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
location /images {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
valid_referers none blocked server_names
*.example.com example.* www.example.org/galleries/
~\.google\.;
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
}
范例:定义防盗链:
location ^~ /images {
root /data/nginx;
index index.html;
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.cici.com www.cici.* api.online.test/v1/hostlist ~\.google\. ~\.baidu\.; #定义有效的referer
if ($invalid_referer) { #假如是使用其他的无效的referer访问:
return 403; #返回状态码403
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
使用浏览器访问盗链网站 www.ncici.net, 验证是否提前状态码403:
map
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_map_module.html
#创建一个新变量,其值取决于第一个参数中指定的一个或多个源变量的值。 Syntax: map string $variable { ... } Default: — Context: http
匹配模式类型:
- "精确字符串" 完全匹配字符串(大小写敏感)
- ~ 开头,表示这个正则表达式对大小写敏感。
- ~* 开头,表示这个正则表达式对大小写不敏感
还支持以下特殊参数:
- default value 如果源值与任何指定的变体都不匹配,则设置结果值。如果default未指定,则默认结果值为空字符串。
- include file 包含一个带有值的文件。
基本语法
http {
map $源变量 $目标变量 {
匹配模式1 结果值1;
匹配模式2 结果值2;
...
default 默认值;
}
}
注意事项
- 性能优化:将高频匹配项放在顶部,减少无效匹配。
- 默认值:务必设置 default 防止空值。
- 作用域:map 块在 http{} 内全局有效。
- 变量依赖:目标变量未被使用时,映射不会执行。
map 指令是 Nginx 中强大的变量处理工具,适用于:
- 简化复杂的 if 条件判断
- 动态路由(如根据域名、路径分配后端)
- 请求头/URI 内容处理
- 配置逻辑抽象化
示例:根据 User-Agent 设置变量
#当客户端为移动设备时,重定向到移动版页面。 http { map $http_user_agent $is_mobile { default 0; "~*android" 1; # 匹配 Android "~*iphone|ipod" 1; # 匹配 iPhone/iPod } server { location / { if ($is_mobile) { rewrite ^ /mobile redirect; } # 其他配置... } } }
示例:使用正则捕获组
#请求 /image.png → $file_extension = "png" http { map $uri $file_extension { ~*\.(?<ext>\w+)$ $ext; # 提取 URI 中的扩展名 default ""; } }
示例:域名到后端服务的映射
http {
map $host $backend {
hostnames; # 启用通配符匹配
api.example.com api_server;
*.example.com web_server;
default default_backend;
}
upstream api_server { ... }
upstream web_server { ... }
server {
location / {
proxy_pass http://$backend;
}
}
}
示例:嵌套映射(通过多次调用)
map $status_code $error_type { 404 "Not Found"; 500 "Server Error"; } map $error_type $log_level { "Not Found" "warn"; "Server Error" "error"; }
流量切分
限制
限制连接数ngx_http_limit_conn_module模块
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_conn_module.html
#设置共享内存区域以及指定键值的最大允许连接数 Syntax: limit_conn zone number; Default: — Context: http, server, location
#设置共享内存区域的参数,该区域将保存各种键的状态 Syntax: limit_conn_zone key zone=name:size; Default: — Context: http
#设置响应被拒绝的请求而返回的状态代码 Syntax: limit_conn_status code; Default: limit_conn_status 503; Context: http, server, location
范例
#设置共享内存区域以及指定键值的最大允许连接数。当超出此限制时,服务器将返回 错误 以响应请求。 limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=perip:10m; limit_conn_zone $server_name zone=perserver:10m; server { ... limit_conn perip 10; #每个 IP 地址每次只允许10个连接 limit_conn perserver 100; #同时限制到虚拟服务器的总连接数 }
范例:针对爬虫限速
http {
map $http_user_agent $agent {
default "";
~curl $http_user_agent;
~*apachebench $http_user_agent;
~*spider $http_user_agent;
~*bot $http_user_agent;
~*slurp $http_user_agent;
}
limit_conn_zone $agent zone=conn_xxx_com:10m;
limit_req_zone $agent zone=req_xxx_com:10m rate=1r/s;
server {
listen 8080;
server_name test.xxx.com;
root /data/webroot/www.xxx.com/
location / {
limit_req zone=conn_xxx_com burst=5;
limit_conn req_xxx_com 1;
}
}
}
范例:限速白名单
http {
geo $whiteiplist {
default 1;
127.0.0.1 0;
10.0.0.0/8 0;
121.207.242.0/24 0;
}
map $whiteiplist $limit {
1 $binary_remote_addr;
0 "";
}
limit_conn_zone $limit zone=limit:10m;
server {
listen 8080;
server_name test.xxx.com;
location ^~ /xxx.com/ {
limit_conn limit 4;
limit_rate 200k;
alias /data/www.xxx.com/data/download/;
}
}
说明
- geo指令定义一个白名单$whiteiplist, 默认值为1, 所有都受限制。 如果客户端IP与白名单列出的IP相匹配,则$whiteiplist值为0也就是不受限制。
- map指令是将$whiteiplist值为1的,也就是受限制的IP,映射为客户端IP。将$whiteiplist值为0的,也就是白名单IP,映射为空的字符串。
- limit_conn_zone和limit_req_zone指令对于键为空值的将会被忽略,从而实现对于列出来的IP不做限制。
测试方法:
ab -c 100 -n 300 http://test.xxx.com:8080/xxx.com/docs/pdf/nginx_guide.pdf
限制请求数ngx_http_limit_req_module模块
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_limit_req_module.html
Syntax: limit_req zone=name [burst=number] [nodelay | delay=number]; Default: — Context: http, server, location limit_req zone=one burst=5 nodelay; #在峰值burst=5以内的并发请求,会被挂起,延迟处理。超过5个直接返回503 #如果不希望在限制请求的同时延迟过多的请求,nodelay
Syntax: limit_req_zone key zone=name:size rate=rate [sync]; Default: — Context: http limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=one:10m rate=1r/s; #状态被保存在一个10MB的区域one中,平均请求处理率不能超过每秒1个请求 #1 兆字节的区域可以保存大约 16,000 个IP
范例
#多种限制,域名server_name、单个 IP 地址的请求处理速率 http { limit_req_status 555; limit_req_zone $server_name zone=abcserver:10m rate=2000r/s; limit_req_zone $server_name zone=defserver:10m rate=1500r/s; limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=abc:10m rate=1r/s; limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr$uri zone=abc_uri:10m rate=1r/s; limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=def:10m rate=1r/s; server { ... ... #速率qps=1,延迟请求, 超过返回453 location /cdp/distributor/api/batch_data { proxy_read_timeout 60; limit_req_status 453; limit_req zone=abc_uri nodelay; proxy_pass http://xxx; } } }
GeoIP2
Nginx需要安装GeoIP2模块才能使用MaxMind的数据库
1、获取MaxMind GeoIP2数据库
- 官方:需要提前注册,进入下载页 https://dev.maxmind.com/geoip/geolite2-free-geolocation-data/,下载 GeoLite2-Country.mmdb 文件
- 第三方免费文件: https://github.com/P3TERX/GeoLite.mmdb
2、安装Nginx GeoIP2模块
安装依赖
#sudo apt-get install libmaxminddb0 libmaxminddb-dev mmdb-bin yum install -y libmaxminddb libmaxminddb-devel
手动查询ip归属
]# mmdblookup --file GeoLite2-City.mmdb --ip 103.121.182.139
{
"city":
{
"geoname_id":
1642911 <uint32>
"names":
{
"de":
"Jakarta" <utf8_string>
"en":
"Jakarta" <utf8_string>
......
"zh-CN":
"雅加达" <utf8_string>
}
}
"continent":
{
"code":
"AS" <utf8_string>
"geoname_id":
6255147 <uint32>
"names":
{
"de":
"Asien" <utf8_string>
"en":
"Asia" <utf8_string>
.....
"ru":
"Азия" <utf8_string>
"zh-CN":
"亚洲" <utf8_string>
}
}
"country":
{
"geoname_id":
1643084 <uint32>
"iso_code":
"ID" <utf8_string>
"names":
{
"de":
"Indonesien" <utf8_string>
"en":
"Indonesia" <utf8_string>
......
"zh-CN":
"印度尼西亚" <utf8_string>
}
}
"location":
{
"accuracy_radius":
20 <uint16>
"latitude":
-6.211400 <double>
"longitude":
106.844600 <double>
"time_zone":
"Asia/Jakarta" <utf8_string>
}
"postal":
{
"code":
"11730" <utf8_string>
}
"registered_country":
{
"geoname_id":
1643084 <uint32>
"iso_code":
"ID" <utf8_string>
"names":
{
"de":
"Indonesien" <utf8_string>
"en":
"Indonesia" <utf8_string>
......
"zh-CN":
"印度尼西亚" <utf8_string>
}
}
"subdivisions":
[
{
"geoname_id":
1642907 <uint32>
"iso_code":
"JK" <utf8_string>
"names":
{
"en":
"Jakarta" <utf8_string>
}
}
]
}
GeoIP]# mmdblookup --file GeoLite2-City.mmdb --ip 103.121.182.139 country names zh-CN
"印度尼西亚" <utf8_string>
GeoIP]# mmdblookup --file GeoLite2-City.mmdb --ip 103.121.182.139 city names zh-CN
"雅加达" <utf8_string>
下载GeoIP2模块
cd /usr/local/src/ git clone https://github.com/leev/ngx_http_geoip2_module.git 动态编译Nginx with GeoIP2模块 wget https://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.27.3.tar.gz tar -xzf nginx-1.27.3.tar.gz cd nginx-1.27.3 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx-1.27.3 \ --with-compat --add-dynamic-module=/usr/local/src/ngx_http_geoip2_module \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-stream \ --with-http_realip_module \ --add-module=/usr/local/src/echo-nginx-module-master make #make install #已安装nginx就不要覆盖,默认会把geoip文件放在 /usr/local/nginx-1.27.3/modules 目录中. ngx_http_geoip2_module.so ngx_stream_geoip2_module.so #ln -svf /usr/local/nginx-1.27.3 /usr/local/nginx #ln -svf /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/bin/nginx mkdir -p /usr/local/nginx/modules \cp objs/nginx /usr/local/nginx/sbin #更新nginx二进制文件 \cp objs/{ngx_http_geoip2_module,ngx_http_geoip_module,ngx_stream_geoip2_module,ngx_stream_geoip_module}.so /usr/local/nginx/modules/
配置nginx,加载模块
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf sed -ri '/events/i\include modules.conf;' nginx.conf cat > modules.conf <<eof load_module modules/ngx_http_geoip2_module.so; #load_module modules/ngx_http_geoip_module.so; load_module modules/ngx_stream_geoip2_module.so; #load_module modules/ngx_stream_geoip_module.so; eof nginx -s reload
3、配置Nginx使用GeoIP2数据库
编辑Nginx配置文件,加载GeoIP2数据库
- http 块中添加以下内容
#在 http 块中添加以下内容 ## 加载GeoIP2数据库 #geoip2 /usr/local/nginx/conf/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb { # $geoip2_data_country_code source=$http_x_forwarded_for country iso_code; #} #geoip2模块加载ip数据库 geoip2 /usr/local/nginx/conf/GeoLite2-Country.mmdb { $geoip2_data_country_code source=$http_x_forwarded_for country iso_code; #国家英文名 $geoip2_data_country_name_en source=$http_x_forwarded_for country names en; #国家中文名 $geoip2_data_country_name_cn source=$http_x_forwarded_for country names zh-CN; } geoip2 /usr/local/nginx/conf/GeoLite2-City.mmdb { #城市英文名,大多是拼音,有重复情况 $geoip2_data_city_name_en source=$http_x_forwarded_for city names en; #城市中文名,部分城市没有中文名 $geoip2_data_city_name_cn source=$http_x_forwarded_for city names zh-CN; #经度,longitude $geoip2_longitude source=$http_x_forwarded_for location longitude ; #维度,latitude $geoip2_latitude source=$http_x_forwarded_for location latitude ; } # 定义变量:如果IP来自中国,则设置为1 map $geoip2_data_country_code $is_china { default 0; CN 1; # CN是中国的国家代码 }
设置屏蔽规则:
- 在 server 块中添加以下内容:
server {
listen 80;
server_name yourdomain.com;
access_log /var/log/nginx/geoip.access.log json;
# 如果IP来自中国,返回688
charset utf8;
#default_type text/plain;
if ($is_china = 1) {
#return 688 "$http_x_forwarded_for $is_china $geoip2_data_country_name_en $geoip2_data_city_name_en $geoip2_data_city_name_cn | $geoip2_data_city_name_en $geoip2_longitude,$geoip2_latitude";
return 688;
}
location / {
root /usr/local/nginx/html;
index index.html;
}
}
重启Nginx
sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t # 测试配置文件
sudo /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload # 重启Nginx
日志格式化
log_format json escape=json '{"client_ip":"$remote_addr",' '"client_user":"$remote_user",' '"@timestamp": "$time_iso8601",' '"request_uri":"$request_uri",' '"status":"$status",' '"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent",' '"http_referer":"$http_referer",' '"http_user_agent":"$http_user_agent",' '"http_x_forwarded_for":"$http_x_forwarded_for",' '"client_port":"$remote_port",' '"host":"$host",' '"http_host":"$http_host",' '"tcp_xff":"$proxy_protocol_addr",' '"request_length":"$request_length",' '"request_method":"$request_method",' '"request_time":"$request_time",' '"request_body":"$request_body",' '"scheme":"$scheme",' '"server_protocol":"$server_protocol",' '"ssl_cipher":"$ssl_cipher",' '"ssl_protocol":"$ssl_protocol",' '"time_local":"$time_local",' '"upstream_addr":"$upstream_addr",' '"upstream_response_time":"$upstream_response_time",' '"upstream_status":"$upstream_status",' '"url":"$scheme://$host$request_uri",' '"client_country_name":"$geoip2_data_country_name_cn | $geoip2_data_country_name_en",' '"client_city_name":"$geoip2_data_city_name_cn | $geoip2_data_city_name_en",' '"longitude_latitude":"$geoip2_longitude,$geoip2_latitude"}';
参考:nginx动态加载模块
Nginx 反向代理功能
反向代理:反向代理也叫reverse proxy,指的是代理外网用户的请求到内部的 指定web服务器,并将数据返回给用户的一种方式,这是用的比较多的一种方式。
Nginx除了可以在企业提供高性能的web服务之外,另外还可以将本身不具备的请 求通过某种预定义的协议转发至其它服务器处理,不同的协议就是Nginx服务器 与其他服务器进行通信的一种规范,主要在不同的场景使用以下模块实现不同的 功能
逻辑调用关系:
ngx_http_proxy_module: 将客户端的请求以http协议转发至指定服务器进行处理。 ngx_stream_proxy_module:将客户端的请求以tcp协议转发至指定服务器处理。 ngx_http_fastcgi_module:将客户端对php的请求以fastcgi协议转发至指定服务器助理。 ngx_http_uwsgi_module:将客户端对Python的请求以uwsgi协议转发至指定服务器处理。
实现 http 反向代理
要求:将用户对域 www.nagedu.net 的请求转发值后端服务器处理,
官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_proxy_module.html
环境准备:
192.168.7.102 #Nginx 代理服务器 192.168.7.103 #后端web A,Apache部署 192.168.7.104 #后端web B,Apache部署
访问逻辑图:
部署后端 Apache服务器
[root@s3 ~]# yum install httpd -y [root@s3 ~]# echo "web1 192.168.7.103" > /var/www/html/index.html [root@s3 ~]# systemctl start httpd && systemctl enable httpd [root@s4 ~]# yum install httpd -y [root@s4 ~]# echo "web2 192.168.7.104" >> /var/www/html/index.html [root@s4 ~]# systemctl start httpd && systemctl enable httpd #访问测试 [root@s4 ~]# curl http://192.168.7.103 web1 192.168.7.103 [root@s3 ~]# curl http://192.168.7.104 web2 192.168.7.104
Nginx http 反向代理入门
反向代理配置参数
proxy_pass; #用来设置将客户端请求转发给的后端服务器的主机,可以是主机名、IP地址:端口的方式,也可以代理到预先设置的主机群组,需要模块gx_http_upstream_module支持。 #示例: location /web { index index.html; proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80; #不带斜线将访问的/web,等于访问后端服务器 http://192.168.7.103:80/web/index.html,即后端服务器配置的站点根目录要有web目录才可以被访问,这是一个追加/web到后端服务器http://servername:port/WEB/INDEX.HTML的操作 proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80/; #带斜线,等于访问后端服务器的http://192.168.7.103:80/index.html 内容返回给客户端 } #重启Nginx测试访问效果: # curl -L http://www.cici.net/web/index.html proxy_hide_header field; #用于nginx作为反向代理的时候,在返回给客户端http响应的时候,隐藏后端服务版本相应头部的信息,可以设置在http/server或location块, location /web { index index.html; proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80/; proxy_hide_header ETag; } proxy_pass_header field; #默认nginx在响应报文中不传递后端服务器的首部字段Date, Server, X-Pad, X-Accel等参数,如果要传递的话则要使用 proxy_pass_header field声明将后端服务器返回的值传递给客户端。 proxy_pass_request_body on | off; #是否向后端服务器发送HTTP包体部分,可以设置在http/server或location块,默认即为开启 proxy_pass_request_headers on | off; #是否将客户端的请求头部转发给后端服务器,可以设置在http/server或location块,默认即为开启 proxy_set_header; #可以更改或添加客户端的请求头部信息内容并转发至后端服务器,比如在后端服务器想要获取客户端的真实IP的时候,就要更改每一个报文的头部,如下: #proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; #添加HOST到报文头部,如果客户端为NAT上网那么其值为客户端的共用的公网IP地址,常用于在日之中记录客户端的真实IP地址。 #在后端httpd服务器修改配置,添加日志记录X-Forwarded-For字段 LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" \"%{X- Real-IP}i\"" combined proxy_connect_timeout time; #配置nginx服务器与后端服务器尝试建立连接的超时时间,默认为60秒,用法如下: proxy_connect_timeout 60s; #60s为自定义nginx与后端服务器建立连接的超时时间 proxy_read_time time; #配置nginx服务器向后端服务器或服务器组发起read请求后,等待的超时时间,默认60s proxy_send_time time; #配置nginx项后端服务器或服务器组发起write请求后,等待的超时时间,默认60s proxy_http_version 1.0; #用于设置nginx提供代理服务的HTTP协议的版本,默认http 1.0 proxy_ignore_client_abort off; #当客户端网络中断请求时,nginx服务器中断其对后端服务器的请求。即如果此项设置为on开启,则服务器会忽略客户端中断并一直等着代理服务执行返回,如果设置为off,则客户端中断后Nginx也会中断客户端请求并立即记录499日志,默认为off。 proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 128; #当配置了 proxy_hide_header和proxy_set_header的时候,用于设置nginx保存HTTP报文头的hash表的上限。 proxy_headers_hash_max_size 512; #设置proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size的最大可用空间 server_names_hash_bucket_size 512; #server_name hash表申请空间大小 server_names_hash_max_szie 512; #设置服务器名称hash表的上限大小
反向代理单台web服务器
[root@s2 conf.d]# mv pc.conf pc.conf.bak0304
[root@s2 conf.d]# cp mobile.conf pc.conf
[root@s2 conf.d]# cat pc.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80/;
}
}
#重启Nginx 并访问测试
反向代理示例–指定location
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
index index.html index.php;
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /web {
#proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80/; #注意有后面的/,
proxy_pass http://192.168.7.104:80/;
}
}
#后端web服务器必须要有相对于的访问URL
[root@s3 ~]# mkdir /var/www/html/web
[root@s3 ~]# echo "web1 page for apache" > /var/www/html/web/index.html
[root@s4 ~]# mkdir /var/www/html/web
[root@s4 ~]# echo "web2 page for apache" > /var/www/html/web/index.html
#重启Nginx并访问测试:
[root@s2 ~]# curl -L http://www.cici.net/
pc web
[root@s2 ~]# curl -L http://www.cici.net/web
web2 page for apache
#Apache的访问日志:
[root@s4 ~]# tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log
192.168.7.102 - - [04/Mar/2019:18:52:00 +0800] "GET /web/ HTTP/1.1" 200 21 "-""curl/7.29.0"
192.168.7.102 - - [04/Mar/2019:18:52:00 +0800] "GET /web HTTP/1.0" 301 233 "-""curl/7.29.0"
192.168.7.102 - - [04/Mar/2019:18:52:00 +0800] "GET /web/ HTTP/1.1" 200 21 "-""curl/7.29.0"
反向代理示例-缓存功能
缓存功能默认关闭状态
proxy_cache zone | off; 默认off #指明调用的缓存,或关闭缓存机制;Context:http, server, location proxy_cache_key string; #缓存中用于“键”的内容,默认值:proxy_cache_key $scheme$proxy_host$request_uri; proxy_cache_valid [code ...] time; #定义对特定响应码的响应内容的缓存时长,定义在http{...}中 示例: proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m; proxy_cache_valid 404 1m; proxy_cache_path; #定义可用于proxy功能的缓存;Context:http proxy_cache_path path [levels=levels] [use_temp_path=on|off] keys_zone=name:size [inactive=time] [max_size=size][manager_files=number] [manager_sleep=time] [manager_threshold=time] [loader_files=number] [loader_sleep=time] [loader_threshold=time] [purger=on|off] [purger_files=number] [purger_sleep=time] [purger_threshold=time]; 示例:在http配置定义缓存信息 proxy_cache_path /var/cache/nginx/proxy_cache #定义缓存保存路径,proxy_cache会自动创建 levels=1:2:2 #定义缓存目录结构层次,1:2:2可以生成2^4x2^8x2^8=1048576个目录 keys_zone=proxycache:20m #指内存中缓存的大小,主要用于存放key和metadata(如:使用次数) inactive=120s; #缓存有效时间 max_size=1g; #最大磁盘占用空间,磁盘存入文件内容的缓存空间最大值 #调用缓存功能,需要定义在相应的配置段,如server{...};或者location等 proxy_cache proxycache; proxy_cache_key $request_uri; proxy_cache_valid 200 302 301 10m; #指定的状态码返回的数据缓存多长时间 proxy_cache_valid any 1m; proxy_cache_use_stale error http_502 http_503; #在被代理的后端服务器出现哪种情况下,可直接使用过期的缓存响应客户端, proxy_cache_use_stale error | timeout | invalid_header | updating | http_500 | http_502 | http_503 | http_504 | http_403 | http_404 | off ; #默认是off proxy_cache_methods GET | HEAD | POST ...; #对哪些客户端请求方法对应的响应进行缓存,GET和HEAD方法总是被缓存
非缓存场景压测
[root@s3 app1]# pwd /var/www/html/app1 [root@s3 app1]# cp /var/log/messages ./log.html #准备测试页面 [root@s2 pc]# ab -n 2000 -c200 http://www.cici.net/web/log.html Total transferred: 3059318000 bytes HTML transferred: 3058760000 bytes Requests per second: 155.14 [#/sec] (mean) Time per request: 1289.166 [ms] (mean) Time per request: 6.446 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) Transfer rate: 231747.94 [Kbytes/sec] received
准备缓存配置
[root@s2 pc]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf proxy_cache_path /data/nginx/proxycache levels=1:1:1 keys_zone=proxycache:20m inactive=120s max_size=1g; #配置在nginx.conf http配置段 [root@s2 pc]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf location /web { #要缓存的URL 或者放在server配置项对所有URL都进行缓存 proxy_pass http://192.168.7.104:80/; proxy_set_header clientip $remote_addr; proxy_cache proxycache; proxy_cache_key $request_uri; proxy_cache_valid 200 302 301 1h; proxy_cache_valid any 1m; } [root@s2 pc]# /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t nginx: the configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful [root@s2 pc]# systemctl start nginx
访问并验证缓存文件
#访问web并验证缓存目录 [root@s2 pc]# curl http://www.cici.net/web/log.html [root@s2 pc]# ab -n 2000 -c200 http://www.cici.net/web/log.html Total transferred: 3059318000 bytes HTML transferred: 3058760000 bytes Requests per second: 1922.78 [#/sec] (mean) Time per request: 104.016 [ms] (mean) Time per request: 0.520 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests) Transfer rate: 2872259.55 [Kbytes/sec] received #验证缓存目录结构及文件大小 [root@s2 pc]# tree /data/nginx/proxycache/ /data/nginx/proxycache/ └── f └── 0 └── 6 └── 50b643197ae7d66aaaa5e7e1961b060f 3 directories, 1 file [root@s2 pc]# ll -h /data/nginx/proxycache/f/0/6/50b643197ae7d66aaaa5e7e1961b060f -rw------- 1 nginx nginx 1.5M Mar 7 14:30 /data/nginx/proxycache/f/0/6/50b643197ae7d66aaaa5e7e1961b060f #验证文件内容: [root@s2 pc]# head -n100 /data/nginx/proxycache/f/0/6/50b643197ae7d66aaaa5e7e1961b060f #会在文件首部添加相应码 HTTP/1.1 200 OK Date: Thu, 07 Mar 2019 18:35:37 GMT Server: Apache/2.4.6 (CentOS) Last-Modified: Thu, 07 Mar 2019 14:14:47 GMT ETag: "175624-58381ba95ac05" Accept-Ranges: bytes Content-Length: 1529380 Connection: close Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 192.168.0.1 - - [18/Feb/2019:10:26:33 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 612
添加头部报文信息
nginx基于模块ngx_http_headers_module可以实现对头部报文添加指定的key与值, https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_headers_module.html
Syntax: add_header name value [always]; Default: — Context: http, server, location, if in location #添加自定义首部,如下: add_header name value [always]; #示例 add_header X-Via $server_addr; #当前nginx主机的IP add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status; #是否缓存命中 add_header X-Accel $server_name; #客户访问的FQDN #添加自定义响应信息的尾部, 1.13.2版后支持 add_trailer name value [always];
Nginx配置
location /web {
proxy_pass http://192.168.7.103:80/;
proxy_set_header clientip $remote_addr;
proxy_cache proxycache;
proxy_cache_key $request_uri;
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 301 1h;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
add_header X-Via $server_addr;
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
add_header X-Accel $server_name;
}
验证头部信息 :
Nginx http 反向代理高级应用
在上一个章节中Nginx可以将客户端的请求转发至单台后端服务器但是无法转发至特定的一组的服务器,而且不能对后端服务器提供相应的服务器状态监测,但是Nginx可以基于ngx_http_upstream_module模块提供服务器分组转发、权重分配、状态监测、调度算法等高级功能
官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_upstream_module.html
http upstream配置参数
upstream name {
server .....
......
}
#示例
upstream backend {
server backend1.example.com weight=5;
server 127.0.0.1:8080 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
server backup1.example.com backup;
}
upstream name {
}
#自定义一组服务器,配置在http内
server address [parameters];
#配置一个后端web服务器,配置在upstream内,至少要有一个server服务器配置。
#server支持的parameters如下:
weight=number #设置权重,默认为1。
max_conns=number #给当前server设置最大活动链接数,默认为0表示没有限制。
fail_timeout=time #对后端服务器的单次监测超时时间,默认为10秒。
max_fails=number #在fail_timeout时间对后端服务器连续监测失败多少次就标记为不可用。
backup #设置为备份服务器,当所有服务器不可用时将重新启用次服务器。
down #标记为down状态。
resolve #当server定义的是主机名的时候,当A记录发生变化会自动应用新IP而不用重启Nginx。
hash KEY consistent;
#基于指定key做hash计算,使用consistent参数,将使用ketama一致性hash算法,适用于后端是Cache服务器(如varnish)时使用,consistent定义使用一致性hash运算,一致性hash基于取模运算。
hash $request_uri consistent; #基于用户请求的uri做hash
hash $cookie_sessionid #基于cookie中的sessionid这个key进行hash调度,实现会话绑定
ip_hash;
#源地址hash调度方法,基于的客户端的remote_addr(源地址)做hash计算,以实现会话保持,
least_conn;
#最少连接调度算法,优先将客户端请求调度到当前连接最少的后端服务器
反向代理示例-多台web服务器
upstream webserver {
#hash $request_uri consistent;
#ip_hash;
#least_conn;
server 192.168.7.103:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=15s max_fails=3; #后端服务器状态监测
server 192.168.7.104:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=15s max_fails=3;
server 192.168.7.101:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=15s max_fails=3 backup;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
index index.html index.php;
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /web {
index index.html;
proxy_pass http://webserver/;
}
}
#重启Nginx 并访问测试
[root@s2 ~]# curl http://www.cici.net/web
web1 192.168.7.103
[root@s2 ~]# curl http://www.cici.net/web
web2 192.168.7.104
关闭192.168.7.103和192.168.7.104,测试nginx backup服务器可用性:
[root@s4 ~]# while true;do curl http://www.cici.net/web;sleep 1;done
反向代理示例 - 客户端 IP 透传
[root@s2 conf.d]# cat pc.conf
upstream webserver {
#hash $request_uri consistent; #consistent 一致性hash算法
#server 192.168.7.103:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=5s max_fails=3;
server 192.168.7.104:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=5s max_fails=3;
server 192.168.7.101:80 weight=1 fail_timeout=5s max_fails=3 backup;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.cici.net;
location / {
index index.html index.php;
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
}
location /web {
index index.html;
proxy_pass http://webserver/;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; #添加客户端IP到报文头部
}
}
#重启nginx
#后端web服务器配置
1、Apache:
[root@s4 ~]# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
LogFormat "%{X-Forwarded-For}i %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{UserAgent}i\"" combined
#重启apache访问web界面并验证apache日志:
192.168.7.104 192.168.7.102 - - [05/Mar/2019:00:36:03 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 200 19 "-" "curl/7.29.0"
192.168.0.1 192.168.7.102 - - [05/Mar/2019:00:40:46 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 200 19 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36"
2、Nginx:
[root@s1 conf.d]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
"$http_x_forwarded_for"' #默认日志格式就有此配置
重启nginx访问web界面并验证日志格式:
192.168.7.102 - - [04/Mar/2019:16:33:24 +0800] "GET // HTTP/1.0" 200 24 "-" "curl/7.29.0" "192.168.7.104"
192.168.7.102 - - [04/Mar/2019:16:40:51 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.0" 200 24 "-" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/72.0.3626.119 Safari/537.36" "192.168.0.1"
实战案例: 基于Cookie 实现会话绑定
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
upstream websrvs {
hash $cookie_hello; #hello是cookie的key的名称
server 10.0.0.101:80 weight=2;
server 10.0.0.102:80 weight-1;
}
}
[root@centos8 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf
server {
location /{
#proxy_cache mycache;
proxy_pass http://websrvs;
}
}
实现Nginx tcp负载均衡
支持的时间太晚,导致目前用的较少
Nginx在1.9.0版本开始支持tcp模式的负载均衡,在1.9.13版本开始支持udp协议 的负载,udp主要用于DNS的域名解析,其配置方式和指令和http代理类似,其基 于ngx_stream_proxy_module模块实现tcp负载,另外基于模块 ngx_stream_upstream_module实现后端服务器分组转发、权重分配、状态监测、 调度算法等高级功能。
官方文档:
https://nginx.org/en/docs/stream/ngx_stream_proxy_module.html
http://nginx.org/en/docs/stream/ngx_stream_upstream_module.html
tcp负载均衡配置参数
stream { #定义stream
upstream backend { #定义后端服务器
hash $remote_addr consistent; #定义调度算法
server backend1.example.com:12345 weight=5; #定义具体server
server 127.0.0.1:12345 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
server unix:/tmp/backend3;
}
upstream dns { #定义后端服务器
server 192.168.0.1:53535; #定义具体server
server dns.example.com:53;
}
server { #定义server
listen 12345; #监听IP:PORT
proxy_connect_timeout 1s; #连接超时时间
proxy_timeout 3s; #转发超时时间
proxy_pass backend; #转发到具体服务器组
}
server {
listen 127.0.0.1:53 udp reuseport;
proxy_timeout 20s;
proxy_pass dns;
}
server {
listen [::1]:12345;
proxy_pass unix:/tmp/stream.socket;
}
}
负载均衡实例-Redis
服务器安装redis
[root@s4 ~]# yum install redis -y
[root@s4 ~]# vim /etc/redis.conf
bind 0.0.0.0
......
[root@s4 ~]# systemctl start redis
[root@s4 ~]# systemctl enable redis
[root@s4 ~]# ss -tnl | grep 6379
LISTEN 0 128 *:6379 *:*
nginx配置:
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /apps/nginx/conf/tcp
[root@s2 ~]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/tcp/tcp.conf
stream {
upstream redis_server {
#hash $remote_addr consistent;
server 192.168.7.104:6379 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
}
server {
listen 192.168.7.102:6379;
proxy_connect_timeout 3s;
proxy_timeout 3s;
proxy_pass redis_server;
}
}
[root@s2 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
21 include /apps/nginx/conf/tcp/tcp.conf; #注意此处的include与http模块平级
#重启nginx并访问测试
[root@s2 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
[root@s2 ~]# ss -tnl | grep 6379
LISTEN 0 128 192.168.7.102:6379 *:*
#测试通过nginx 负载连接redis:
[root@s4 ~]# redis-cli -h 192.168.7.102
192.168.7.102:6379> set name jack
OK
192.168.7.102:6379> get name
"jack"
192.168.7.102:6379>
负载均衡实例:MySQL
服务器安装MySQL:
[root@s4 ~]# yum install mariadb mariadb-server -y [root@s4 ~]# systemctl start mariadb [root@s4 ~]# mysql_secure_installation #安全初始化 [root@s4 ~]# systemctl enable mariadb [root@s4 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456 MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'root'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456' WITH GRANT OPTION; MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> exit
nginx配置:
[root@s2 ~]# cat /apps/nginx/conf/tcp/tcp.conf
stream {
upstream redis_server {
server 192.168.7.104:6379 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
}
upstream mysql_server {
least_conn;
server 192.168.7.104:3306 max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s;
}
###################################################################
server {
listen 192.168.7.102:3306;
proxy_connect_timeout 6s;
proxy_timeout 15s;
proxy_pass mysql_server;
}
server {
listen 192.168.7.102:6379;
proxy_connect_timeout 3s;
proxy_timeout 3s;
proxy_pass redis_server;
}
}
#重启nginx并访问测试:
[root@s2 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
#测试通过nginx负载连接MySQL:
[root@s4 ~]# mysql -uroot -p123456 -h 192.168.7.102
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 32
Server version: 5.5.60-MariaDB MariaDB Server
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database linux34;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| linux34 |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.01 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]>
实现FastCGI
CGI的由来:
最早的Web服务器只能简单地响应浏览器发来的HTTP请求,并将存储在服务器上 的HTML文件返回给浏览器,也就是静态html文件,但是后期随着网站功能增多网 站开发也越来越复杂,以至于出现动态技术,比如像php(1995年)、java(1995)、 python(1991)语言开发的网站,但是nginx/apache服务器并不能直接运行 php、 java这样的文件,apache实现的方式是打补丁,但是nginx缺通过与第三方基于 协议实现,即通过某种特定协议将客户端请求转发给第三方服务处理,第三方服 务器会新建新的进程处理用户的请求,处理完成后返回数据给Nginx并回收进程, 最后nginx在返回给客户端,那这个约定就是通用网关接口(common gateway interface,简称CGI),CGI(协议) 是web服务器和外部应用程序之间的接口标 准,是cgi程序和web服务器之间传递信息的标准化接口。
为什么会有FastCGI?
CGI协议虽然解决了语言解析器和 Web Server 之间通讯的问题,但是它的效率 很低,因为 Web Server每收到一个请求都会创建一个CGI进程,PHP解析器都会 解析php.ini文件,初始化环境,请求结束的时候再关闭进程,对于每一个创建 的CGI进程都会执行这些操作,所以效率很低,而FastCGI是用来提高CGI性能的, FastCGI每次处理完请求之后不会关闭掉进程,而是保留这个进程,使这个进程 可以处理多个请求。这样的话每个请求都不用再重新创建一个进程了,大大提升 了处理效率。
什么是PHP-FPM?
PHP-FPM(FastCGI Process Manager:FastCGI进程管理器)是一个实现了Fastcgi 的管理程序,并且提供进程管理的功能,进程包括master进程和worker进程, master进程只有一个,负责监听端口,接受来自web server的请求。worker进程 一般会有多个,每个进程中会嵌入一个PHP解析器,进行PHP代码的处理。
FastCGI 配置指令
Nginx基于模块ngx_http_fastcgi_module实现通过fastcgi协议将指定的客户端请求转发至php-fpm处理,其配置指令如下:
fastcgi_pass address; #转发请求到后端服务器,address为后端的fastcgi server的地址,可用位置:location, if in location fastcgi_index name; #fastcgi默认的主页资源,示例:fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param parameter value [if_not_empty]; #设置传递给FastCGI服务器的参数值,可以是文本,变量或组合,可用于将Nginx的内置变量赋值给自定义key fastcgi_param REMOTE_ADDR $remote_addr; #客户端源IP fastcgi_param REMOTE_PORT $remote_port; #客户端源端口 fastcgi_param SERVER_ADDR $server_addr; #请求的服务器IP地址 fastcgi_param SERVER_PORT $server_port; #请求的服务器端口 fastcgi_param SERVER_NAME $server_name; #请求的server name Nginx默认配置示例: location ~ \.php$ { root html; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name; #默认脚本路径 include fastcgi_params; }
缓存定义指令: 注意使用fastcgi缓存, 可能会导致源代码更新失败,生产慎用
fastcgi_cache_path path [levels=levels] [use_temp_path=on|off] keys_zone=name:size [inactive=time] [max_size=size] [manager_files=number] [manager_sleep=time] [manager_threshold=time] [loader_files=number] [loader_sleep=time] [loader_threshold=time] [purger=on|off] [purger_files=number] [purger_sleep=time] [purger_threshold=time]; 定义fastcgi的缓存; path #缓存位置为磁盘上的文件系统路径 max_size=size #磁盘path路径中用于缓存数据的缓存空间上限 levels=levels:#十六进制的缓存目录的层级数量,以及每一级的目录数量,levels=ONE:TWO:THREE,示例:leves=1:2:2 keys_zone=name:size #设置缓存名称及k/v映射的内存空间的名称及大小 inactive=time #缓存有效时间,默认10分钟,需要在指定时间满足fastcgi_cache_min_uses 次数被视为活动缓存。
缓存调用指令:
fastcgi_cache zone | off; #调用指定的缓存空间来缓存数据,可用位置:http, server, location fastcgi_cache_key string; #定义用作缓存项的key的字符串,示例:fastcgi_cache_key $request_uri; fastcgi_cache_methods GET | HEAD | POST ...; #为哪些请求方法使用缓存 fastcgi_cache_min_uses number; #缓存空间中的缓存项在inactive定义的非活动时间内至少要被访问到此处所指定的次数方可被认作活动项 fastcgi_keep_conn on | off; #收到后端服务器响应后,fastcgi服务器是否关闭连接,建议启用长连接 fastcgi_cache_valid [code ...] time; #不同的响应码各自的缓存时长 fastcgi_hide_header field; #隐藏响应头指定信息 fastcgi_pass_header field; #返回响应头指定信息,默认不会将Status、X-Accel-...返回
FastCGI示例–Nginx与php-fpm在同一服务器
php安装可以通过yum或者编译安装,使用yum安装相对比较简单,编译安装更方便自定义参数或选项。
说明:服务器压力不大时,nginx通常与php-fpm在同一服务器
php环境准备
使用base源自带的php版本,https://www.php.net/docs.php
#yum安装默认版本php [root@s2 ~]# yum install php-fpm php-mysql -y #默认版本 [root@s2 ~]# systemctl start php-fpm && systemctl enable php-fpm [root@s2 ~]# ps -ef | grep php-fpm root 4925 1 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: master process (/etc/phpfpm.conf) apache 4927 4925 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www apache 4928 4925 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www apache 4929 4925 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www apache 4930 4925 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www apache 4931 4925 0 17:13 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www root 4933 3235 0 17:13 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto php-fpm
php相关配置优化
[root@s2 ~]# grep "^[a-Z]" /etc/php-fpm.conf include=/etc/php-fpm.d/*.conf pid = /run/php-fpm/php-fpm.pid error_log = /var/log/php-fpm/error.log daemonize = yes #是否后台启动 [root@s2 ~]# cat /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf [www] listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 #监听地址及IP listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1 #允许客户端从哪个源IP地址访问,要允许所有行首加 ;注释即可 user = nginx #php-fpm启动的用户和组,会涉及到后期文件的权限问题 group = nginx pm = dynamic #动态模式进程管理 pm.max_children = 500 #静态方式下开启的php-fpm进程数量,在动态方式下他限定php-fpm的最大进程数 pm.start_servers = 100 #动态模式下初始进程数,必须大于等于pm.min_spare_servers和小于等于 pm.max_children的值。 pm.min_spare_servers = 100 #最小空闲进程数 pm.max_spare_servers = 200 #最大空闲进程数 pm.max_requests = 500000 #进程累计请求回收值,会回收并重新生成新的子进程 pm.status_path = /pm_status #状态访问URL ping.path = /ping #ping访问动地址 ping.response = ping-pong #ping返回值 slowlog = /var/log/php-fpm/www-slow.log #慢日志路径 php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/php-fpm/www-error.log #错误日志 php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on php_value[session.save_handler] = files #phpsession保存方式及路径 php_value[session.save_path] = /var/lib/php/session #当时使用file保存session的文件路径
修改配置文件后记得重启php-fpm
[root@s2 ~]# systemctl restart php-fpm
准备php测试页面
[root@s2 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/php [root@s2 ~]# cat /data/nginx/php/index.php #php测试页面 <?php phpinfo(); ?>
Nginx配置转发
Nginx安装完成之后默认生成了与fastcgi的相关配置文件,一般保存在nginx的安装路径的conf目录当中,比如/apps/nginx/conf/fastcgi.conf、/apps/nginx/conf/fastcgi_params。
[root@s2 ~]# vim /apps/nginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf #在指定文件配置fastcgi location ~ \.php$ { root /data/nginx/php; #$document_root调用root目录 fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; #fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /data/nginx/php$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; #如果SCRIPT_FILENAME是绝对路径则可以省略root /data/nginx/php; include fastcgi_params; } #重启Nginx并访问web测试 systemctl restart nginx
访问验证php测试页
浏览器访问
fastcgi_pass常见的错误: File not found. #路径不对 502: php-fpm处理超时、服务停止运行等原因导致的无法连接或请求超时
php-fpm 的运行状态页面
访问配置文件里面指定的路径,会返回php-fpm的当前运行状态。
Nginx配置:
location ~ ^/(pm_status|ping)$ {
#access_log off;
#allow 127.0.0.1;
#deny all;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
}
重启Nginx并测试:
[root@Centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.net/pm_status pool: www process manager: dynamic start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 42 accepted conn: 2 listen queue: 0 max listen queue: 0 listen queue len: 128 idle processes: 4 active processes: 1 total processes: 5 max active processes: 1 max children reached: 0 slow requests: 0 [root@Centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.net/ping pong [root@Centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.net/pm_status?full pool: www process manager: dynamic start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 accepted conn: 4 listen queue: 0 max listen queue: 0 listen queue len: 128 idle processes: 4 active processes: 1 total processes: 5 max active processes: 1 max children reached: 0 slow requests: 0 ************************ pid: 2099 state: Idle start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 requests: 1 request duration: 393 request method: GET request URI: /pm_status content length: 0 user: - script: - last request cpu: 0.00 last request memory: 262144 ************************ pid: 2100 state: Idle start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 requests: 0 request duration: 0 request method: - request URI: - content length: 0 user: - script: - last request cpu: 0.00 last request memory: 0 ************************ pid: 2101 state: Idle start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 requests: 1 request duration: 301 request method: GET request URI: /pm_status content length: 0 user: - script: - last request cpu: 0.00 last request memory: 262144 ************************ pid: 2102 state: Running start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 requests: 1 request duration: 477 request method: GET request URI: /pm_status?full content length: 0 user: - script: - last request cpu: 0.00 last request memory: 0 ************************ pid: 2103 state: Idle start time: 21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800 start since: 85 requests: 1 request duration: 242 request method: GET request URI: /ping content length: 0 user: - script: - last request cpu: 0.00 last request memory: 262144 [root@Centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.net/pm_status?html <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd"> <html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en"> <head><title>PHP-FPM Status Page</title></head> <body> <table> <tr><th>pool</th><td>www</td></tr> <tr><th>process manager</th><td>dynamic</td></tr> <tr><th>start time</th><td>21/Jul/2020:16:58:35 +0800</td></tr> <tr><th>start since</th><td>116</td></tr> <tr><th>accepted conn</th><td>5</td></tr> <tr><th>listen queue</th><td>0</td></tr> <tr><th>max listen queue</th><td>0</td></tr> <tr><th>listen queue len</th><td>128</td></tr> <tr><th>idle processes</th><td>4</td></tr> <tr><th>active processes</th><td>1</td></tr> <tr><th>total processes</th><td>5</td></tr> <tr><th>max active processes</th><td>1</td></tr> <tr><th>max children reached</th><td>0</td></tr> <tr><th>slow requests</th><td>0</td></tr> </table> </body></html> [root@Centos7 ~]#curl http://www.cici.net/pm_status?json {"pool":"www","process manager":"dynamic","start time":1595321915,"start since":147,"accepted conn":6,"listen queue":0,"max listen queue":0,"listen queue len":128,"idle processes":4,"active processes":1,"total processes":5,"max active processes":1,"max children reached":0,"slow requests":0}
FastCGI示例–Nginx与php不在同一个服务器
nginx会处理静态请求,但是会转发动态请求到后端指定的php-fpm服务器,因此代码也需要放在后端的php-fpm服务器,即静态页面放在Nginx上而动态页面放在后端php-fpm服务器,正常情况下,一般都是采用6.3.2的部署方式。
yum安装较新版本php-fpm
[root@s4 ~]# rpm -ivh https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/remi/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm [root@nginx-web2 ~]#yum install https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/remi/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm #包含较新的PHP等软件包 #[root@s4 ~]# yum install php56-php-fpm php56-php-mysql -y #安装指定版本的php [root@nginx-web2 ~]#yum install php72-php-fpm php72-php-mysql -y 验证安装路径: [root@nginx-web2 ~]#rpm -ql php72-php-fpm /etc/logrotate.d/php72-php-fpm /etc/opt/remi/php72/php-fpm.conf /etc/opt/remi/php72/php-fpm.d /etc/opt/remi/php72/php-fpm.d/www.conf /etc/opt/remi/php72/sysconfig/php-fpm /etc/systemd/system/php72-php-fpm.service.d /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/sbin/php-fpm ...... /var/opt/remi/php72/run/php-fpm 生成php72配置文件: [root@s4 ~]# cp /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/share/doc/php72-php-common-7.2.24/php.iniproduction /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/etc/php.ini [root@s4 ~]# cp /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/share/doc/php72-php-fpm-7.2.24/phpfpm.conf.default /opt/remi/php72/root/usr/etc//php-fpm.conf
修改php-fpm监听配置
php-fpm默认监听在127.0.0.1的9000端口,也就是无法远程连接,因此要做相应的修改。
#php56修改监听配置 [root@s4 ~]# vim /opt/remi/php56/root/etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf listen = 10.0.0.27:9000 #指定监听IP #listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1 #注释运行的客户端 #php72修改监听配置 [root@nginx-web2 ~]#vim /etc/opt/remi/php72/php-fpm.d/www.conf user = nginx group = nginx listen = 10.0.0.27:9000 ; listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1
准备php测试页面
#准备php数据目录 [root@s4 ~]# mkdir /data/nginx/php -p [root@s4 ~]# vim /data/nginx/php/index.php <?php phpinfo(); ?>
启动并验证php-fpm
#启动php-fpm56 [root@s4 ~]# systemctl start php56-php-fpm [root@s4 ~]# systemctl enable php56-php-fpm #启动php-fpm72 [root@s4 ~]# systemctl start php72-php-fpm [root@s4 ~]# systemctl enable php56-php-fpm #验证php-fpm进程及端口: [root@s4 ~]# ps -ef | grep php-fpm [root@nginx-web2 ~]#ps -ef |grep php root 1910 1 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: master process (/etc/opt/remi/php72/php-fpm.conf) nginx 1911 1910 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www nginx 1912 1910 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www nginx 1913 1910 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www nginx 1914 1910 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www nginx 1915 1910 0 20:24 ? 00:00:00 php-fpm: pool www root 1917 1009 0 20:24 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto php [root@s4 ~]# ss -tnl | grep 9000 LISTEN 0 128 127.0.0.1:9000 *:* [root@s4 ~]# netstat -tuanlp | grep 9000 tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 5339/php-fpm: maste
Nginx配置转发
location ~ \.php$ { root /data/nginx/php; fastcgi_pass 10.0.0.27:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; #fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /data/php$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } #重启nginx [root@s2 ~]# systemctl restart nginx
访问验证php测试页面:
php 56:
php72:
http 499 问题
查看 HTTP status code 并没有发现 499 定义。
在 nginx 源代码 src/http/ngx_http_special_response.c 文件中对 499 状态码进行了定义:
#define NGX_HTTP_OFF_5XX (NGX_HTTP_LAST_4XX - 400 + NGX_HTTP_OFF_4XX)
ngx_string(ngx_http_error_494_page), /* 494, request header too large */
ngx_string(ngx_http_error_495_page), /* 495, https certificate error */
ngx_string(ngx_http_error_496_page), /* 496, https no certificate */
ngx_string(ngx_http_error_497_page), /* 497, http to https */
ngx_string(ngx_http_error_404_page), /* 498, canceled */
ngx_null_string, /* 499, client has closed connection */
看到 499 表示 客户端主动断开连接 。
而在实际业务中,当出现 HTTP 499 状态码时,大部分都是由于服务端请求时间过长,导致客户端等待超时,因此断开了连接。
服务端接口请求超时
如请求接口时 sql 全表扫描,客户端超时等待。
解决:优化接口
nginx 主动断开连接
如 nginx 认为过快的 post 请求不安全,主动断开连接。
解决: 配置文件追加
proxy_ignore_client_abort on;。意思是 proxy 忽略客户端的中断,一直等待着代理服务器的返回,如果没有执行错误,则记录的日志是 200 日志,如果执行超时,记录的日志是 504 日志。缺点:当客户端断开连接之后,服务器仍然会继续执行,存在着拖垮服务器的风险。所以线上业务要根据情况合理使用。固定时间出现 499 问题
可能某一资源被拖垮的连锁反应。排查 crontab 脚本、服务器、数据库、error.lg、SQL slow.log
nginx 二次开发版本
Tengine
继承Nginx-1.16.0的所有特性,兼容nginx的配置 支持HTTP的CONNECT方法,可用于正向代理场景 支持异步OpenSSL,可使用硬件如:QAT进行HTTPS的加速与卸载 增强相关运维、监控能力,比如异步打印日志及回滚,本地DNS缓存,内存监控等 Stream模块支持server_name指令 更加强大的负载均衡能力,包括一致性hash模块、会话保持模块,还可以对后端的服务器进行主动健康检查, 根据服务器状态自动上线下线,以及动态解析upstream中出现的域名 输入过滤器机制支持。通过使用这种机制Web应用防火墙的编写更为方便 支持设置proxy、memcached、fastcgi、scgi、uwsgi在后端失败时的重试次数 动态脚本语言Lua支持。扩展功能非常高效简单 支持按指定关键字(域名,url等)收集Tengine运行状态 组合多个CSS、JavaScript文件的访问请求变成一个请求 自动去除空白字符和注释从而减小页面的体积 自动根据CPU数目设置进程个数和绑定CPU亲缘性; 监控系统的负载和资源占用从而对系统进行保护 显示对运维人员更友好的出错信息,便于定位出错机器 更强大的防攻击(访问速度限制)模块 更方便的命令行参数,如列出编译的模块列表、支持的指令等 可以根据访问文件类型设置过期时间
动态模块
http://tengine.taobao.org/document_cn/dso_cn.html
这个模块主要是用来运行时动态加载模块,而不用每次都要重新编译Tengine.
如果你想要编译官方模块为动态模块,你需要在configure的时候加上类似这样 的指令(–withhttp_xxx_module),./configure –help可以看到更多的细节.
如果只想要安装官方模块为动态模块(不安装Nginx),那么就只需要configure之 后,执行make dso_install命令.动态加载模块的个数限制为128个.
如果已经加载的动态模块有修改,那么必须重起Tengine才会生效.
只支持HTTP模块.
模块 在Linux/FreeeBSD/MacOS下测试成功.
编译安装 tengine-2.1.2 注意: 不支持CentOS8
[root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel [root@centos7 ~]#useradd -r nginx [root@centos7 ~]#cd /usr/local/src [root@centos7 src]#wget http://tengine.taobao.org/download/tengine-2.1.2.tar.gz [root@centos7 src]#tar xf tengine-2.1.2.tar.gz [root@centos7 src]#cd tengine-2.1.2/ [root@nginx-web1 tengine-2.1.2]#./configure --prefix=/apps/tengine-2.1.2 --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --add-module=/usr/local/src/echo-nginx-module # make && make install
在tengine-2.1.2中添加 lua 动态模块
# yum install lua lua-devel # ./configure --help | grep shared # ./configure --prefix=/apps/tengine-2.1.2 --user=nginx --group=nginx --withhttp_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --withhttp_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --withhttp_lua_module=shared # make dso_install # ll /apps/tengine-2.1.2/modules/ngx_http_lua_module.so # vim /apps/tengine-2.1.2/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; dso { load ngx_http_lua_module.so; } #/apps/tengine-2.1.2/sbin/nginx -t the configuration file /apps/tengine-2.1.2/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok configuration file /apps/tengine-2.1.2/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
编译安装 tengine-2.3.2 centos8
# wget http://tengine.taobao.org/download/tengine-2.3.2.tar.gz # tar xvf tengine-2.3.2.tar.gz # cd tengine-2.3.2/ # /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -V #如果需要兼容Nginx则使用之前Nginx的编译参数 # ./configure --prefix=/apps/tengine-2.3.2 --user=nginx --group=nginx --withhttp_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --withhttp_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module # make # make install [root@centos8 tengine-2.3.2]#ln -s /apps/tengine-2.3.2/sbin/* /usr/sbin/ [root@centos8 tengine-2.3.2]#nginx -v
concat模块使用:
网站中的css、js等文件都是小文件,单个文件大小几k甚至几个字节,所以文件的特点是小而多,会造成网站加载时http请求较多,且网络传输时间比较短,甚至有时候请求时间比传输时间还长,当公司网站中的这类小文件很多时,大量的http请求就会造成传输效率低,影响网站的访问速度和客户端体验,这时合并http请求就非常有必要了,concat模块就提供了合并文件http请求的功能,这个模块由淘宝开发,功能和apache的mod_concat模块类似。
Tengine-2.1.2 concat模块使用: https://tengine.taobao.org/document_cn/http_concat_cn.html
访问方式
请求参数需要用两个问号('??')例如: http://example.com/??style1.css,style2.css,foo/style3.css 参数中某位置只包含一个‘?’,则'?'后表示文件的版本,例如: http://example.com/??style1.css,style2.css,foo/style3.css?v=102234
编译安装 concat 模块
#tengine-2.1.2有此模块 #./configure --help |grep http_concat #./configure --prefix=/apps/tengine --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-file-aio --with-http_concat_module=shared --withhttp_lua_module=shared #make dso_install #通过动态模块实现concat功能: # vim /apps/tenginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log info; #pid logs/nginx.pid; dso { load ngx_http_lua_module.so; load ngx_http_concat_module.so; } #/apps/tengine/sbin/nginx -t # /apps/tengine/sbin/nginx -s reload #通过重新编译tengine实现concat功能: #直接编译至tengine --with-http_concat_module
tengine配置文件:
兼容Nginx指定版本的配置参数
pc.conf配置文件: # cat /apps/tenginx/conf/conf.d/pc.conf server { listen 80; server_name www.cici.net *.www.cici.net pc.cici.net; aio on; location / { concat on; root html; index index.html index.htm; } location ~ \.php$ { root /data/nginx/php; fastcgi_pass 172.18.0.202:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; #fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /data/nginx/php$fastcgi_script_name; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } }
基于tengine的wordpress站点:
openresty
Nginx 是俄罗斯人发明的, Lua 是巴西几个教授发明的,中国人章亦春把 LuaJIT VM 嵌入到 Nginx中,实现了 OpenResty 这个高性能服务端解决方案
OpenResty® 是一个基于 Nginx 与 Lua 的高性能 Web平台,其内部集成了大量 精良的 Lua库、第三方模块以及大多数的依赖项。用于方便地搭建能够处理超高 并发、扩展性极高的动态Web 应用、Web 服务和动态网关。
OpenResty® 通过汇聚各种设计精良的 Nginx 模块(主要由 OpenResty团队自主 开发),从而将 Nginx 有效地变成一个强大的通用 Web应用平台。这样,Web 开发人员和系统工程师可以使用 Lua 脚本语言调动 Nginx支持的各种 C 以及 Lua 模块,快速构造出足以胜任 10K 乃至 1000K以上单机并发连接的高性能 Web 应用系统。
OpenResty® 的目标是让你的Web服务直接跑在 Nginx 服务内部,充分利用 Nginx的非阻塞 I/O 模型,不仅仅对HTTP 客户端请求,甚至于对远程后端诸如 MySQL、PostgreSQL、Memcached 以及 Redis 等都进行一致的高性能响应。
编译安装 openresty
[root@centos8 ~]#dnf -yq install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel [root@centos8 ~]#useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin nginx # cd /usr/local/src # wget https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.15.8.2.tar.gz # tar xf openresty-1.15.8.2.tar.gz # cd openresty-1.15.8.2/ # ./configure --prefix=/apps/openresty --user=nginx --group=nginx --withhttp_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --withhttp_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module # make && make install # ll /apps/openresty/ total 280 drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 ./ drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 ../ drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 bin/ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 22924 Jan 8 08:44 COPYRIGHT drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 luajit/ drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 lualib/ drwxr-xr-x 6 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 nginx/ drwxr-xr-x 47 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 pod/ -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 226755 Jan 8 08:44 resty.index drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jan 8 08:44 site/ # /apps/openresty/bin/openresty
如果编译时,有 undefined reference to `SSL_get_client_random' 报错,通过如下方法解决
#下载openssl源码到 /path 目录下 ./configure --with-openssl=/path/openssl-3.0.15
系统参数优化
系统参数优化
默认的Linux内核参数考虑的是最通用场景,不符合用于支持高并发访问的Web服务器的定义,根据业务特点来进行调整,当Nginx作为静态web内容服务器、反向代理或者提供压缩服务器的服务器时,内核参数的调整都是不同的,此处针对最通用的、使Nginx支持更多并发请求的TCP网络参数做简单的配置
优化内核参数
修改/etc/sysctl.conf
fs.file-max = 1000000 #表示单个进程较大可以打开的句柄数 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_reuse = 1 #参数设置为 1 ,表示允许将TIME_WAIT状态的socket重新用于新的TCP链接,这对于服务器来说意义重大,因为总有大量TIME_WAIT状态的链接存在 net.ipv4.tcp_keepalive_time = 600 #当keepalive启动时,TCP发送keepalive消息的频度;默认是2小时,将其设置为10分钟,可更快的清理无效链接 net.ipv4.tcp_fin_timeout = 30 #当服务器主动关闭链接时,socket保持在FIN_WAIT_2状态的较大时间 net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_buckets = 5000 #表示操作系统允许TIME_WAIT套接字数量的较大值,如超过此值,TIME_WAIT套接字将立刻被清除并打印警告信息,默认为8000,过多的TIME_WAIT套接字会使Web服务器变慢 net.ipv4.ip_local_port_range = 1024 65000 #定义UDP和TCP链接的本地端口的取值范围 net.ipv4.tcp_rmem = 10240 87380 12582912 #定义了TCP接受缓存的最小值、默认值、较大值 net.ipv4.tcp_wmem = 10240 87380 12582912 #定义TCP发送缓存的最小值、默认值、较大值 net.core.netdev_max_backlog = 8096 #当网卡接收数据包的速度大于内核处理速度时,会有一个列队保存这些数据包。这个参数表示该列队的较大值 net.core.rmem_default = 6291456 #表示内核套接字接受缓存区默认大小 net.core.wmem_default = 6291456 #表示内核套接字发送缓存区默认大小 net.core.rmem_max = 12582912 #表示内核套接字接受缓存区较大大小 net.core.wmem_max = 12582912 #表示内核套接字发送缓存区较大大小 注意:以上的四个参数,需要根据业务逻辑和实际的硬件成本来综合考虑 net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies = 1 #与性能无关。用于解决TCP的SYN攻击 net.ipv4.tcp_max_syn_backlog = 8192 #这个参数表示TCP三次握手建立阶段接受SYN请求列队的较大长度,默认1024,将其设置的大一些可使出现Nginx繁忙来不及accept新连接时,Linux不至于丢失客户端发起的链接请求 net.ipv4.tcp_tw_recycle = 1 #这个参数用于设置启用timewait快速回收 net.core.somaxconn=262114 #选项默认值是128,这个参数用于调节系统同时发起的TCP连接数,在高并发的请求中,默认的值可能会导致链接超时或者重传,因此需要结合高并发请求数来调节此值。 net.ipv4.tcp_max_orphans=262114 #选项用于设定系统中最多有多少个TCP套接字不被关联到任何一个用户文件句柄上。如果超过这个数字,孤立链接将立即被复位并输出警告信息。这个限制指示为了防止简单的DOS攻击,不用过分依靠这个限制甚至认为的减小这个值,更多的情况是增加这个值
PAM 资源限制优化
在/etc/security/limits.conf 最后增加:
* soft nofile 65535 * hard nofile 65535 * soft nproc 65535 * hard nproc 65535
LNMP项目实战-WordPress站点搭建
LNMP项目实战环境说明
L:Linux(CentOS7)https://mirrors.aliyun.com/centos/7/isos/x86_64/ N:Nginx(1.18.0) https://nginx.org/en/download.html M:MySQL(8.0.19) https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/ P:PHP(7.4.10) http://php.net/downloads.php Wordpress(5.4.2):https://cn.wordpress.org/download/ #部署规划: 10.0.0.7:Nginx php-fpm 运行web服务 10.0.0.17:运行MySQL数据库,Redis服务
部署数据库
在10.0.0.17主机部署MySQL服务
二进制部署MySQL数据库
#一键安装脚本 [root@centos7 ~]#cat install_mysql5.7or8.0_for_centos.sh #!/bin/bash #MySQL Download URL: https://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.29-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.gz . /etc/init.d/functions SRC_DIR=`pwd` MYSQL='mysql-8.0.19-linux-glibc2.12-x86_64.tar.xz' COLOR='echo -e \E[01;31m' END='\E[0m' MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=cici check (){ if [ $UID -ne 0 ]; then action "当前用户不是root,安装失败" false exit 1 fi cd $SRC_DIR if [ ! -e $MYSQL ];then $COLOR"缺少${MYSQL}文件"$END $COLOR"请将相关软件放在${SRC_DIR}目录下"$END exit elif [ -e /usr/local/mysql ];then action "数据库已存在,安装失败" false exit else return fi } install_mysql(){ $COLOR"开始安装MySQL数据库..."$END yum -y -q install libaio numactl-libs libaio &> /dev/null cd $SRC_DIR tar xf $MYSQL -C /usr/local/ MYSQL_DIR=`echo $MYSQL| sed -nr 's/^(.*[0-9]).*/\1/p'` ln -s /usr/local/$MYSQL_DIR /usr/local/mysql chown -R root.root /usr/local/mysql/ id mysql &> /dev/null || { useradd -s /sbin/nologin -r mysql ; action "创建mysql用户"; } echo 'PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin/:$PATH' > /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh . /etc/profile.d/mysql.sh ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/* /usr/bin/ cat > /etc/my.cnf <<-EOF [mysqld] server-id=`hostname -I|cut -d. -f4` log-bin datadir=/data/mysql socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock log-error=/data/mysql/mysql.log pid-file=/data/mysql/mysql.pid [client] socket=/data/mysql/mysql.sock EOF mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --datadir=/data/mysql cp /usr/local/mysql/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld chkconfig --add mysqld chkconfig mysqld on service mysqld start [ $? -ne 0 ] && { $COLOR"数据库启动失败,退出!"$END;exit; } MYSQL_OLDPASSWORD=`awk '/A temporary password/{print $NF}' /data/mysql/mysql.log` mysqladmin -uroot -p$MYSQL_OLDPASSWORD password $MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD &>/dev/null action "数据库安装完成" } check install_mysql #运行脚本安装数据库
创建wordpress数据库和用户并授权
[root@centos7 ~]#mysql -uroot -pcici mysql> create database wordpress; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec) mysql> create user wordpress@'10.0.0.%' identified by '123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec) mysql> grant all on wordpress.* to wordpress@'10.0.0.%'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
验证MySQL账户权限
在WordPress服务器使用授权的MySQL账户远程登录测试权限
[root@centos7 ~]#mysql -uwordpress -p123456 -h10.0.0.17 mysql> show databases; +--------------------+ | Database | +--------------------+ | information_schema | | wordpress | +--------------------+
部署PHP
在10.0.0.7主机部署php-fpm服务
编译安装 php
[root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install gcc openssl-devel libxml2-devel bzip2-devel libmcrypt-devel sqlite-devel oniguruma-devel [root@centos7 ~]#cd /usr/local/src [root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#./configure --prefix=/apps/php74 --enable-mysqlnd --with-mysqli=mysqlnd --with-pdo-mysql=mysqlnd --with-openssl --with-zlib --with-config-file-path=/etc --with-config-file-scan-dir=/etc/php.d --enable-mbstring --enable-xml --enable-sockets --enable-fpm --enable-maintainer-zts --disable-fileinfo [root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#make -j 8 && make install
准备PHP配置文件
#生成配置文件 [root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#cp /usr/local/src/php-7.4.11/php.ini-production /etc/php.ini [root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#cd /apps/php74/etc [root@centos7 etc]#cp php-fpm.conf.default php-fpm.conf [root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#cd php-fpm.d/ [root@centos7 php-fpm.d]#cp www.conf.default www.conf [root@centos7 php-fpm.d]#vim www.conf [root@centos7 php-fpm.d]#grep '^[^;]' www.conf [www] user = www group = www listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 pm = dynamic pm.max_children = 5 pm.start_servers = 2 pm.min_spare_servers = 1 pm.max_spare_servers = 3 pm.status_path = /pm_status ping.path = /ping access.log = log/$pool.access.log slowlog = log/$pool.log.slow #创建用户 [root@centos7 php-fpm.d]#useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin www #创建访问日志文件路径 [root@centos7 php-fpm.d]#mkdir /apps/php74/log
启动并验证 php-fpm服务
[root@centos7 ~]#/apps/php74/sbin/php-fpm -t
[22-Oct-2020 10:55:19] NOTICE: configuration file /apps/php74/etc/php-fpm.conf
test is successful
[root@centos7 ~]#cp /usr/local/src/php-7.4.11/sapi/fpm/php-fpm.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/
[root@centos7 ~]#systemctl daemon-reload
[root@centos7 ~]#systemctl enable --now php-fpm
[root@centos7 php-7.4.11]#ss -ntl
[root@centos7 ~]#pstree -p |grep php
[root@centos7 ~]#ps -ef |grep php
部署 Nginx
在10.0.0.7主机部署nginx服务
编译安装 nginx
root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install gcc pcre-devel openssl-devel zlib-devel [root@centos7 ~]#cd /usr/local/src/ [root@centos7 src]#wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz [root@centos7 src]#tar xf nginx-1.18.0.tar.gz [root@centos7 src]#cd nginx-1.18.0/ [root@centos7 nginx-1.18.0]#./configure --prefix=/apps/nginx \ --user=www \ --group=www \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_v2_module \ --with-http_realip_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module \ --with-http_gzip_static_module \ --with-pcre \ --with-stream \ --with-stream_ssl_module \ --with-stream_realip_module [root@centos7 nginx-1.18.0]#make && make install
准备服务文件并启动 nginx
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service [Unit] Description=nginx - high performance web server Documentation=http://nginx.org/en/docs/ After=network-online.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target Wants=network-online.target [Service] Type=forking PIDFile=/apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid ExecStart=/apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID ExecStop=/bin/kill -s TERM $MAINPID [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target #创建目录 [root@centos8 ~]#mkdir /apps/nginx/run/ #修改配置文件 [root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf pid /apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid; [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl daemon-reload [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl enable --now nginx [root@centos7 ~]#ss -ntl
配置 Nginx 支持 fastcgi
[root@centos7 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf [root@centos7 ~]#grep -Ev '#|^$' /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; pid /apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen 80; server_name www.cici.org; #指定主机名 location / { root /data/nginx/wordpress; #指定数据目录 index index.php index.html index.htm; #指定默认主页 } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } location ~ \.php$ { #实现php-fpm root /data/nginx/wordpress; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; } location ~ ^/(ping|pm_status)$ { #实现状态页 include fastcgi_params; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; } } } [root@centos7 ~]# /apps/nginx/sbin/nginx -t [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl reload nginx
准备 php 测试页
准备测试页
[root@centos7 ~]#mkdir -p /data/nginx/wordpress
[root@centos7 ~]#vim /data/nginx/wordpress/test.php
[root@centos7 ~]#cat /data/nginx/wordpress/test.php
<?php
phpinfo();
?>
访问验证 php 测试页
部署 WordPress
在10.0.0.7主机部署 wordpress
准备 WordPress 文件
[root@centos7 ~]#tar xf wordpress-5.4.2-zh_CN.tar.gz [root@centos7 ~]#cp -r wordpress/* /data/nginx/wordpress [root@centos7 ~]#chown -R www.www /data/nginx/wordpress/
web页面
- 初始化web页面
- 打开浏览器访问
- 登录后台管理界面并发表文章
验证发表的文章
#可以看到上传的图片 [root@centos7 ~]#tree /data/nginx/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/
配置允许上传大文件
#注意:默认只支持1M以下文件上传,要上传大图片,需要修改下面三项配置,最大上传由三项值的最小值决定 #直接上传大于1M文件,会出现下面413错误 [root@centos7 ~]#tail -f /apps/nginx/logs/access.log 10.0.0.1 - - [27/Nov/2020:12:21:16 +0800] "POST /wp-admin/async-upload.php HTTP/1.1" 413 585 "http://10.0.0.7/wp-admin/upload.php" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/87.0.4280.67 Safari/537.36 Edg/87.0.664.47" [root@centos7 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf server { client_max_body_size 10m; #默认值为1M ..... [root@centos7 ~]#vim /etc/php.ini post_max_size = 30M #默认值为8M upload_max_filesize = 20M #默认值为2M [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl restart nginx php-fpm
安全加固
[root@centos7 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf [root@centos7 ~]#grep -Ev '#|^$' /apps/nginx/conf/nginx.conf worker_processes 1; pid /apps/nginx/run/nginx.pid; events { worker_connections 1024; } http { include mime.types; default_type application/octet-stream; sendfile on; keepalive_timeout 65; server { listen 80; server_name www.cici.org; server_tokens off; #添加此行 location / { root /data/nginx/wordpress; index index.php index.html index.htm; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } location ~ \.php$ { root /data/nginx/wordpress; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_index index.php; fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; include fastcgi_params; fastcgi_hide_header X-Powered-By; #添加此行 } location ~ ^/(ping|pm_status)$ { include fastcgi_params; fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000; fastcgi_param PATH_TRANSLATED $document_root$fastcgi_script_name; } } } [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl reload nginx
配置 php 开启 opcache 加速
在10.0.0.7主机进行以下修改配置
#编辑php.ini配置文件 [root@centos7 ~]#vim /etc/php.ini [opcache] ; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled zend_extension=opcache.so opcache.enable=1 ..... [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl restart php-fpm #访问测试页确认开启opcache加速
PHP 扩展session模块支持redis
PECL是 PHP 扩展的存储库,提供用于下载和开发 PHP 扩展的所有已知扩展和托管功能的目录
官方链接: http://pecl.php.net/package-stats.php
github: https://github.com/phpredis/phpredis
github安装文档: https://github.com/phpredis/phpredis/blob/develop/INSTALL.markdown
开始在 PHP 中使用 Redis 前, 需要确保已经安装了 redis 服务及 PHP redis 驱动
PHP redis 驱动下载地址为:https://github.com/phpredis/phpredis/releases
编译安装PHP redis
在10.0.0.7主机进行以下编译安装
[root@centos7 ~]#cd /usr/local/src [root@centos7 src]#ls [root@centos7 src]#wget http://pecl.php.net/get/redis-5.3.1.tgz [root@centos7 src]#tar xf redis-5.3.1.tgz [root@centos7 src]#cd redis-5.3.1/ #如果是yum安装php,需要执行yum -y install php-cli php-devel #以下为编译安装php的对应方式 [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#/apps/php74/bin/phpize Configuring for: PHP Api Version: 20190902 Zend Module Api No: 20190902 Zend Extension Api No: 320190902 Cannot find autoconf. Please check your autoconf installation and the #报错提示 $PHP_AUTOCONF environment variable. Then, rerun this script. [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#yum -y install autoconf #重新执行成功 [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#/apps/php74/bin/phpize Configuring for: PHP Api Version: 20190902 Zend Module Api No: 20190902 Zend Extension Api No: 320190902 #查看生成configure脚本 [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#ls #yum安装php,无需指定--with-php-config [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#./configure --with-php-config=/apps/php74/bin/php-config [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#make -j 8 && make install ..... See any operating system documentation about shared libraries for more information, such as the ld(1) and ld.so(8) manual pages. ---------------------------------------------------------------------- Build complete. Don't forget to run 'make test'. Installing shared extensions: /apps/php74/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-zts- 20190902/ #验证redis模块 #yum安装php,模块文件默认存放在 /usr/lib64/php/modules/redis.so [root@centos7 redis-5.3.1]#ll /apps/php74/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-zts-20190902/ total 9584 -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4647668 Oct 22 10:44 opcache.a -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2509416 Oct 22 10:44 opcache.so -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 2651320 Oct 22 12:10 redis.so
编辑php配置文件支持redis
在10.0.0.7主机进行以下修改配置
#编辑php.ini配置文件,扩展redis.so模块 [root@centos7 ~]#vim /etc/php.ini ..... #extension=/apps/php74/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-zts-20190902/redis.so extension=redis.so #文件最后一行添加此行,路径可省略 [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl restart php-fpm
验证加载 redis 模块
访问测试页确认redis模块开启
安装和配置 redis 服务
在10.0.0.17主机进行安装redis 服务
#在10.0.0.17主机安装redis服务 [root@centos7 ~]#yum -y install redis [root@centos7 ~]#vim /etc/redis.conf bind 0.0.0.0 requirepass 123456 [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl enable --now redis [root@centos7 ~]#ss -tnl
配置 php 支持 redis 保存 session
在10.0.0.7 主机进行以下配置
#在10.0.0.7主机配置php的session保存在redis服务 [root@centos7 ~]#vim /etc/php.ini [Session] ; Handler used to store/retrieve data. ; http://php.net/session.save-handler session.save_handler = redis session.save_path = "tcp://10.0.0.17:6379?auth=123456" [root@centos7 ~]#systemctl restart php-fpm
准备 php实现 session 的测试页面
在10.0.0.7主机进行准备相关文件
[root@centos7 ~]#cat /data/nginx/wordpress/session.php <?php session_start(); //redis用session_id作为key 并且是以string的形式存储 $redisKey = 'PHPREDIS_SESSION:' . session_id(); // SESSION 赋值测试 $_SESSION['message'] = "Hello, I'm in redis"; $_SESSION['arr'] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]; echo $_SESSION["message"] , "<br/>"; echo "Redis key = " . $redisKey . "<br/>"; echo "以下是从Redis获取的数据", "<br/>"; // 取数据' $redis = new Redis(); $redis->connect('10.0.0.17', 6379); $redis->auth('123456'); echo $redis->get($redisKey); ?>
访问 web 页面测试实现session保存在redis服务
redis 主机验证 session 数据
在10.0.0.17主机进行验证
[root@centos7 ~]#redis-cli -h 10.0.0.17 -a 123456 10.0.0.17:6379> keys * 1) "PHPREDIS_SESSION:ad3nujfqfvcltkg2ml4snsf72h" 10.0.0.17:6379> get PHPREDIS_SESSION:ad3nujfqfvcltkg2ml4snsf72h "message|s:19:\"Hello, I'm in redis\";arr|a:6: {i:0;i:1;i:1;i:2;i:2;i:3;i:3;i:4;i:4;i:5;i:5;i:6;}"